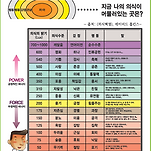
<p><span style="font-size: 11pt;">beyond reason</span><br></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;">치유는 기쁨, 감사, 축복 540 치유의 에너지 장에서 일어난다.</span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;">어떤 사람에게는 좋은 음식이 어떤 사람에게는 독이 된다.&nbsp;</span><br></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;"></span><br></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/996551335E0BCA8412" class="txc-image" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" actualwidth="473" width="473" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2020-01-01 오전 7.23.28.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_996551335E0BCA84127434"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;">기능의학에서 호모시스테인 수치를 7이하로 권장함.</span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;">호모시스테인 수치가 높으면 산화스트레스, 혈관 염증, 동맥경화, 심장병의 위험도가 높음.&nbsp;</span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;"><br></span></p><p><b style="font-family: YGO12-Identity-H; font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">호모시스테인(Homocysteine)은 설파기를 포함한 아미노산으로 필수 아미노산인 Methionine (메티오닌)의 대사과정에서 생성</span></b><br></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;">- 즉 탄수화물 금지식이를 하는 과정에서 육식을 많이 하면 호모시스테인이 높아질 가능성이 있음.</span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;">비타민 B6,9,12를 잘 복용하고 혈액검사로 점검해야!!</span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><br></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/9986F44C5DE1CC592B" class="txc-image" actualwidth="647" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="647" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 10.55.52.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_9986F44C5DE1CC592B0433"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><b><span style="color: rgb(9, 0, 255);">1) 호모시스테인은 혈액검사로 확인</span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><br></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/998C6C4C5DE1B4511A" class="txc-image" actualwidth="1014" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="1014" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.13.41.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_998C6C4C5DE1B4511A859D"/></p><p></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/9972F44A5DE1B4EF1B" class="txc-image" actualwidth="436" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="436" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.16.12.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_9972F44A5DE1B4EF1B9104"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><b><span style="color: rgb(0, 85, 255);">2) 고호모시스테인의 결과는<span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);"> 동맥경화, 심장병, 산화스트레스</span></span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/9969B8415DE1B3C119" class="txc-image" actualwidth="701" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="701" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.07.37.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_9969B8415DE1B3C119C2F0"/></p><p></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/996A28415DE1B3C11A" class="txc-image" actualwidth="556" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="556" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.08.17.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_996A28415DE1B3C11AAEB5"/></p><p></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/995FBF415DE1B3C11B" class="txc-image" actualwidth="710" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="710" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.08.42.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_995FBF415DE1B3C11B8D39"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><b><br></b></span></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/99B7BD455DE1B9101A" class="txc-image" actualwidth="1014" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="1014" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.33.35.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_99B7BD455DE1B9101A28F0"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><b><span style="color: rgb(9, 0, 255);"><br></span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><b><span style="color: rgb(9, 0, 255);"><br></span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><b><span style="color: rgb(9, 0, 255);">3) 호모시스테인의 대사</span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p>
</p><div class="page" title="Page 1">
<div class="section">
<div class="layoutArea">
<div class="column">
<p><span style="font-size: 11pt; font-family: YGO12-Identity-H;"><b><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">호모시스테인(Homocysteine)은 설파기를 포함한 아미노산으로 필수 아미노산인 Methionine
(메티오닌)의 대사과정에서 생성</span></b>된다. 호모시스테인은 재메틸화(remethylation)과정으로
Methionine synthase에 의해 메티오닌으로 재합성되며, 이 과정에서 비타민B</span><span style="font-size: 11pt; font-family: YGO12-Identity-H;">12 </span><span style="font-size: 11pt; font-family: YGO12-Identity-H;">(cobalamin)
가 보조인자로 작용한다.&nbsp;</span></p><span style="font-size: 11pt;">
</span></div><span style="font-size: 11pt;">
</span></div><span style="font-size: 11pt;">
</span></div><span style="font-size: 11pt;">
</span></div><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><br></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/992E0C425DE1B57D1A" class="txc-image" actualwidth="708" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="708" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.18.32.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_992E0C425DE1B57D1A713C"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><b><span style="color: rgb(9, 0, 255);">4) 고호모시스테인 혈증의 6가지 원인</span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p>
</p><div class="page" title="Page 1">
<div class="section">
<div class="layoutArea">
<div class="column">
<p><span style="font-size: 11pt; font-family: YGO12-Identity-H;"><b><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);"># 메티오닌이 많은 동물성 단백을 과다 섭취하는 것도 호모시스테인의 증가를 가져올 수 있음</span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; font-family: YGO12-Identity-H;"><b><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);"># 비타민 B6, 9, 12가 부족할때 고호모시스테인혈증이 발생할 수 있음.&nbsp;</span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt; font-family: YGO12-Identity-H;"><b><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);"># 호모시스테인 대사와 관련된 유전적 결함(CBS, MTHFR, methione synthase결핍)</span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"># 만성신부전, 크레아티닌의 증가, 갑상선기능저하, 악성빈혈, 유방암, 난소암, 췌장암, 백혈병 등</span><br></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;">#&nbsp;</span><span style="font-family: YGO12-Identity-H; font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;">methotrexate, sulfasalazine, phenytoin, theophylline, 경구피임약 등의 약물</span></p><p><span style="font-family: YGO12-Identity-H; font-size: 11pt; line-height: 1.6;"># <b><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">흡연</span></b></span></p><p><br></p><div class="cit" style="font-size: 0.8465em; line-height: 1.45em; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif;"><span role="menubar"><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21143017#" title="Clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine." abstractlink="yes" alsec="jour" alterm="Clin Chem Lab Med." role="menuitem" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); border-bottom-width: 0px; text-decoration: underline;">Clin Chem Lab Med.</a></span>&nbsp;2011 Mar;49(3):479-83. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.062. Epub 2010 Dec 14.</div><h1 style="font-size: 1.4em; margin: 0.5em 0px; line-height: 1.25em; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif;">Effect of cigarette smoking on plasma homocysteine concentrations.</h1><div class="auths" style="font-size: 0.923em; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif;"><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Haj%20Mouhamed%20D%5BAuthor%5D&amp;cauthor=true&amp;cauthor_uid=21143017" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); border-bottom-width: 0px; text-decoration: underline;">Haj Mouhamed D</a><span style="font-size: 0.8461em; line-height: 1.6363em; position: relative; vertical-align: baseline; top: -0.5em;">1</span>,&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Ezzaher%20A%5BAuthor%5D&amp;cauthor=true&amp;cauthor_uid=21143017" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); border-bottom-width: 0px; text-decoration: underline;">Ezzaher A</a>,&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Neffati%20F%5BAuthor%5D&amp;cauthor=true&amp;cauthor_uid=21143017" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); border-bottom-width: 0px; text-decoration: underline;">Neffati F</a>,&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Douki%20W%5BAuthor%5D&amp;cauthor=true&amp;cauthor_uid=21143017" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); border-bottom-width: 0px; text-decoration: underline;">Douki W</a>,&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Najjar%20MF%5BAuthor%5D&amp;cauthor=true&amp;cauthor_uid=21143017" style="color: rgb(102, 0, 102); border-bottom-width: 0px; text-decoration: underline;">Najjar MF</a>.</div><div class="afflist" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 13px; line-height: 17px; zoom: 1;"><h3 style="font-size: 1.0769em; line-height: 1.2857; margin: 0.5em 0em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); zoom: 1;"><a title="Open/close author information list" class="jig-ncbitoggler-open ui-widget ui-ncbitoggler-open" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21143017#" id="ui-ncbitoggler-2" role="button" aria-expanded="true" style="padding-left: 16px; position: relative; display: block; color: rgb(102, 0, 102); border-bottom-width: 0px; text-decoration: underline; outline: none; font-family: arial, sans-serif !important;"><span class="ui-ncbitoggler-master-text">Author information</span><span class="ui-icon ui-icon-triangle-1-s" style="display: inline; text-indent: -99999px; overflow: hidden; background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4188643/img/3974597); width: 16px; height: 16px; position: absolute; left: 0px; background-attachment: scroll; background-color: transparent; border: none; border-bottom-left-radius: 3px; border-bottom-right-radius: 3px; margin: 0px; padding: 0px; right: 0px; top: 3px; background-position: 0px 0px; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;"></span></a></h3><div class="ui-helper-reset" aria-live="assertive" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border: 0px; outline: 0px; line-height: 1.3; list-style: none; font-size: 100% !important;"><dl class="ui-ncbi-toggler-slave-open ui-ncbitoggler ui-ncbitoggler-slave-open" aria-hidden="false" style="margin: 0px;"><dt style="padding: 0px 0px 0.2em; white-space: nowrap; float: left; width: 30px; margin: 0px !important;">1</dt><dd style="margin: 0px 0px 0px 30px; padding: 0px 0px 0.2em;">Laboratory of Biochemistry-Toxicology, University Hospital of Monastir, Monastir, Tunisia. hajdhouha@yahoo.fr</dd></dl></div></div><div class="abstr" style="line-height: 1.538em; margin: 1.2em auto auto; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 13px;"><h3 style="font-size: 1.0769em; line-height: 1.2857; margin: 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); display: inline;">Abstract</h3><div class=""><h4 style="font-size: 1em; margin: 0px 0.25em 0px 0px; text-transform: uppercase; float: left;">BACKGROUND:&nbsp;</h4><p style="margin-bottom: 0.5em; font-size: 1.04em;">Cigarette smoking has been recognized as a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, while the role of homocysteine is still not clear. This study investigated the effects of smoking on plasma homocysteine concentration and determined the correlation between this parameter and biological markers of tobacco use, such as plasma thiocyanate and urine cotinine.</p><h4 style="font-size: 1em; margin: 0px 0.25em 0px 0px; text-transform: uppercase; float: left;">METHODS:&nbsp;</h4><p style="margin-bottom: 0.5em; font-size: 1.04em;">Folate, vitamin B12 and homocysteine were measured in 300 subjects: 138 non-smokers and 162 smokers using immunoassay methods. Cotinine was measured using an enzymatic colorimetric method and thiocyanate by a selective electrode.</p><h4 style="font-size: 1em; margin: 0px 0.25em 0px 0px; text-transform: uppercase; float: left;">RESULTS:&nbsp;</h4><p style="margin-bottom: 0.5em; font-size: 1.04em;">I<b><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">n smokers, we found a significant increase in homocysteine and a decrease in folate and vitamin B12 levels compared to non-smokers. Homocysteine was strongly correlated with the duration of use and the number of cigarettes consumed. Folate and vitamin B12 were significantly reduced in subjects smoking for more than 20 years compared to those who smoked less than 5 years</span></b>. Among smokers, we noted a positive correlation between homocysteine and both plasma thiocyanates and cotininuria, and a negative-correlation between cotininuria and plasma folate.</p><h4 style="font-size: 1em; margin: 0px 0.25em 0px 0px; text-transform: uppercase; float: left;">CONCLUSIONS:&nbsp;</h4><p style="margin-bottom: 0.5em; font-size: 1.04em;"><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">Cigarette smoking increases homocysteine, which is strongly correlated with cotininuria and plasma thiocyanates. </span>Moreover, smokers had tendency to develop hypofolatemia and hypovitamin B12, particularly when the duration of consumption exceeded 20 years.</p><p style="margin-bottom: 0.5em; font-size: 1.04em;"><br></p></div></div><p><font face="YGO12-Identity-H"><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;">참고) <b><span style="color: rgb(0, 85, 255);">남자가 여자보다 혈중 호모시스테인 농도 25% 높음</span></b></span></font></p><p><font face="YGO12-Identity-H"><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;">&nbsp; &nbsp; &nbsp; &nbsp;여성호르몬 치료는 호모시스테인 농도를 낮춤.&nbsp;</span></font></p><span style="font-size: 11pt;">
</span><span style="font-size: 11pt;">
</span><div class="page" title="Page 2"><span style="font-size: 11pt;">
</span><div class="section"><span style="font-size: 11pt;">
</span><div class="layoutArea"><span style="font-size: 11pt;">
</span><div class="column"><span style="font-size: 11pt;">
</span><p><span style="font-size: 10.000000pt; font-family: 'YGO12-Identity-H'"><span style="font-size: 11pt;">&nbsp;</span><br></span></p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div><p><span style="font-size: 10.000000pt; font-family: 'YGO12-Identity-H'"><br></span></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/9907C3395DE1B65B1E" class="txc-image" actualwidth="707" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="707" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.21.09.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_9907C3395DE1B65B1E181B"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 10.000000pt; font-family: 'YGO12-Identity-H'">&nbsp;</span></p><p><br></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/99D3C0375DE1B7281D" class="txc-image" actualwidth="556" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="556" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.25.24.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_99D3C0375DE1B7281DF422"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 10.000000pt; font-family: 'YGO12-Identity-H'"><br></span></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/992B91425DE1B99E1D" class="txc-image" actualwidth="538" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="538" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.35.53.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_992B91425DE1B99E1D7125"/></p><p></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/9995C3465DE1B9F51D" class="txc-image" actualwidth="558" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="558" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.37.32.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_9995C3465DE1B9F51D0B19"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 10.000000pt; font-family: 'YGO12-Identity-H'"><span style="font-size: 11pt; font-family: YGO12-Identity-H;"><br></span></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 10.000000pt; font-family: 'YGO12-Identity-H'"><span style="font-size: 11pt; font-family: YGO12-Identity-H;"><br></span></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 10.000000pt; font-family: 'YGO12-Identity-H'"><span style="font-size: 11pt; font-family: YGO12-Identity-H;">5) 호모시스테인 검사정보</span><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 10.000000pt; font-family: 'YGO12-Identity-H'"><span style="font-size: 11pt; font-family: YGO12-Identity-H;"><br></span></span></p><p><br></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/999F74365DE1B8611E" class="txc-image" actualwidth="718" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="718" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.30.15.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_999F74365DE1B8611E870D"/></p><p>클릭클릭</p><p><br></p><p style="text-align: center;"><a href="http://www.samsunghospital.com/home/healthInfo/content/contenView.do?CONT_SRC_ID=31619&amp;CONT_SRC=HOMEPAGE&amp;CONT_ID=3917&amp;CONT_CLS_CD=001021003002" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer" class="tx-link"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/99F0AB3C5DE1B89F1E" class="txc-image" actualwidth="1024" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="1024" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 9.31.56.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_99F0AB3C5DE1B89F1ED14E"/></a></p><p><br></p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div><p><br></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;">참고) <b><span style="color: rgb(0, 85, 255);">알콜과 커피는 호모시스테인 수치를 올림</span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;">&nbsp; &nbsp; &nbsp; &nbsp;<b><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">운동은 호모시스테인 수치를 내려주고</span></b></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;">클릭클릭 - 논문 읽어야</span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p><p><br></p><p style="text-align: center;"><a href="https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1191/1358863x04vm542oa" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer" class="tx-link"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/99B89F4D5DE1D30030" class="txc-image" actualwidth="517" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="517" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 11.23.12.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_99B89F4D5DE1D30030DCB8"/></a></p><p></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/99B9404D5DE1D3002F" class="txc-image" actualwidth="893" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" width="893" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2019-11-30 오전 11.24.14.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_99B9404D5DE1D3002F852D"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;">참고1)&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">In the chemical sciences,</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><b style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">methylation</b><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">denotes the addition of a</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methyl" class="mw-redirect" title="Methyl" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">methyl group</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">on a</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Substrate_(chemistry)" title="Substrate (chemistry)" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">substrate</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alkylation" title="Alkylation" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">alkylation</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">, with a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen#Compounds" title="Hydrogen" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">hydrogen</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">atom. These terms are commonly used in</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemistry" title="Chemistry" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">chemistry</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">,</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biochemistry" title="Biochemistry" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">biochemistry</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">,</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Soil_science" title="Soil science" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">soil science</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">, and the</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biology" title="Biology" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">biological sciences</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">.</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">In</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biological_systems" class="mw-redirect" title="Biological systems" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">biological systems</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">, methylation is</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalysis" title="Catalysis" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">catalyzed</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">by</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme" title="Enzyme" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">enzymes</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">; such methylation can be involved in modification of</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heavy_metals" title="Heavy metals" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">heavy metals</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">, regulation of</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gene_expression&#8206;" title="Gene expression&#8206;" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">gene expression&#8206;</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">, regulation of</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein#Functions" title="Protein" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">protein function</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">, and</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_processing" class="mw-redirect" title="RNA processing" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">RNA processing</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">. In vitro methylation of tissue samples is also one method for reducing certain</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histology#Histological_Artifacts" title="Histology" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">histological staining artifacts</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">. The counterpart of methylation is called</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demethylation" title="Demethylation" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">demethylation</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">.</span><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;">&nbsp;</span></p><p><b style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;"><br></b></p><p><b style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">참고2) Transmethylation</b><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">is a biologically important organic chemical reaction in which a</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methyl_group" title="Methyl group" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">methyl group</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">is transferred from one compound to another.&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">An example of transmethylation is the recovery of</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methionine" title="Methionine" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">methionine</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">from</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homocysteine" title="Homocysteine" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">homocysteine</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">. In order to sustain sufficient reaction rates during metabolic stress, this reaction requires adequate levels of</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin_B12" title="Vitamin B12" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">vitamin B<sub style="line-height: 1; font-size: 11px;">12</sub></a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">and</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Folate" title="Folate" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">folate</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">.</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methyl_tetrahydrofolate" class="mw-redirect" title="Methyl tetrahydrofolate" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">Methyl tetrahydrofolate</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">delivers methyl groups to form the active methyl form of vitamin B</span><sub style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; line-height: 1; font-size: 11px;">12</sub><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">that is required for methylation of homocysteine. Deficiencies of vitamin B</span><sub style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; line-height: 1; font-size: 11px;">12</sub><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">or</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Folate" title="Folate" style="font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px; color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">folate</a><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">&nbsp;</span><span style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">cause increased levels of circulating homocysteine. Elevated homocysteine is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and is linked to the metabolic syndrome (insulin insensitivity).</span><sup id="cite_ref-pmid14633777_1-0" class="reference" style="color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; line-height: 1; unicode-bidi: -webkit-isolate; white-space: nowrap; font-size: 11px;"><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmethylation#cite_note-pmid14633777-1" style="color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">[1]</a></sup></p><p style="margin-top: 0.5em; margin-bottom: 0.5em; color: rgb(34, 34, 34); font-family: sans-serif; font-size: 14px; line-height: 22px;">Transmethylation is decreased sometimes in parents of children with&nbsp;<a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autism" title="Autism" style="color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">autism</a>.<sup id="cite_ref-pmid18512136_2-0" class="reference" style="line-height: 1; unicode-bidi: -webkit-isolate; white-space: nowrap; font-size: 11px;"><a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmethylation#cite_note-pmid18512136-2" style="color: rgb(11, 0, 128); background-image: none;">[2]</a></sup></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p><p><br></p><p style="text-align: center;"><br></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p>
<!-- -->