<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><A title="[http://cafe.daum.net/_c21_/bbs_read?grpid=135gk&amp;mgrpid=&amp;fldid=JBja&amp;page=1&amp;prev_page=0&amp;firstbbsdepth=&amp;lastbbsdepth=zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;contentval=0000Szzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;datanum=28]로 이동합니다." href="http://cafe.daum.net/_c21_/bbs_read?grpid=135gk&amp;mgrpid=&amp;fldid=JBja&amp;page=1&amp;prev_page=0&amp;firstbbsdepth=&amp;lastbbsdepth=zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;contentval=0000Szzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;datanum=28" target=_blank><A class=tx-link href="http://cafe.daum.net/compmania/JBja/28" target=_blank>PT4 </A></A></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><A title="[http://cafe.daum.net/_c21_/bbs_read?grpid=135gk&amp;mgrpid=&amp;fldid=JBja&amp;page=1&amp;prev_page=0&amp;firstbbsdepth=&amp;lastbbsdepth=zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;contentval=0000Szzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;datanum=28]로 이동합니다." href="http://cafe.daum.net/_c21_/bbs_read?grpid=135gk&amp;mgrpid=&amp;fldid=JBja&amp;page=1&amp;prev_page=0&amp;firstbbsdepth=&amp;lastbbsdepth=zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;contentval=0000Szzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;datanum=28" target=_blank><A class=tx-link href="http://cafe.daum.net/compmania/JBja/28" target=_blank>에 이어</A></A><SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><A title="[http://cafe.daum.net/_c21_/bbs_read?grpid=135gk&amp;mgrpid=&amp;fldid=JBja&amp;page=1&amp;prev_page=0&amp;firstbbsdepth=&amp;lastbbsdepth=zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;contentval=0000Szzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;datanum=28]로 이동합니다." href="http://cafe.daum.net/_c21_/bbs_read?grpid=135gk&amp;mgrpid=&amp;fldid=JBja&amp;page=1&amp;prev_page=0&amp;firstbbsdepth=&amp;lastbbsdepth=zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;contentval=0000Szzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz&amp;datanum=28" target=_blank>&nbsp;</A></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">6.<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt">주포<SPAN>(</SPAN>포탑<SPAN>)</SPAN>의 변화 </SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt"><STRONG>&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;</STRONG><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN> </P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><STRONG>&nbsp;</STRONG></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><STRONG>&nbsp;</STRONG></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><STRONG><IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1751821049BD4E1202" width=1024 actualwidth="1024" id="A_1751821049BD4E12025046"/></STRONG></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><STRONG>&nbsp;<SPAN style="FONT-SIZE: 10pt"><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[셔만전차는 차체만큼이나 포탑의 형태 역시 복잡하기로 유명합니다. 헷치나 펠리스코프의 형태에 따라 각기 전기/중기/후기로 나뉩니다.&nbsp; 취미가 20호에서 발췌]</FONT></SPAN></STRONG></SPAN></FONT></P></SPAN></FONT></SPAN><SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></FONT>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>대부분의 셔먼은 주포와<SPAN> 1</SPAN>정의<SPAN> 12.7mm</SPAN>기관총<SPAN>, 2 </SPAN>정의<SPAN> 7.62mm</SPAN>기관총을 장비하고 있었습니다<SPAN>. (</SPAN>그러나 영연방군에서 사용된 차량은<SPAN> 12.7mm </SPAN>를 장비하지 않는 것이 일반적이다<SPAN>.)</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/110DED0A49BE83DC3C" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="568" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="568" id="A_110DED0A49BE83DC3CBED6"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;<STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[전방에 3정의 7.62 밀리 기관총이 달려 있는 M4A2 초기형의 모습 쌍권총 좋아하는 민족이라 그런지 중무장을 즐겨했나싶다 물론 1정만 빼고 전원 페지..]</FONT></STRONG></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">M4A1</SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">와<SPAN> A2 </SPAN>초기형은<SPAN> M3</SPAN>전차와 같이 차체 전방에<SPAN> 2</SPAN>정의<SPAN> 7.62mm </SPAN>기관총이 달려 있었다<SPAN>.</SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>주포는<SPAN> 75mm </SPAN>혹은<SPAN> 3</SPAN>인치<SPAN>(76.2mm)</SPAN>포가 표준이었지만<SPAN>, </SPAN>화력 지원용으로<SPAN> 105mm</SPAN>유탄포를 장비한 모델도 만들어졌다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;<img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1712810C49BE7CB4D7" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="611" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="611" id="A_1712810C49BE7CB4D775EC"/></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[M4A3 중에는 토치카나 바리케이트를 제거하기 위한 105밀리 단포신을 가진 타입도 존재했다 사진은 초기형 105밀리의 모습으로 3단으로 분리된 차체 앞 부분의 트렌스미션 커버로 쉽게 구분이 가능하다]&nbsp;</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>영국군에서는<SPAN> 76.2mm</SPAN>포 탑재형을<SPAN> A, 105mm</SPAN>포 탑재형을<SPAN> B, 17</SPAN>파운드포 탑재형을<SPAN> C</SPAN>로 분류하였다<SPAN>. (</SPAN>예를 들어<SPAN> '</SPAN>셔먼<SPAN>IC'</SPAN>는<SPAN> M4 </SPAN>베이스의 파이어 플라이<SPAN>, </SPAN>셔먼<SPAN>IIIA</SPAN>는<SPAN> M4A2 </SPAN>베이스의<SPAN> 76.2mm</SPAN>포 탑재형이 된다<SPAN>.)</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>초장기 제작된 셔만이 장착한<SPAN> 75</SPAN>밀리<SPAN> 40</SPAN>구경 주포는 독일군의<SPAN> 6</SPAN>호 전차 티이거의 정면장갑을 뚫을수 없었으며 반대로 독일군의 판터 같은 전차가 장착한 주포는<SPAN> 1000</SPAN>미터 이상에서도 셔만전차를 격파할 수 있었습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>또한 티이거가 장비한<SPAN> 88</SPAN>밀리 포로는<SPAN> 2</SPAN>천미터에서까지에서도 격파가 가능할 정도 였습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>이점은 큰 문제가 되어 셔만전차병은 티이거 같은 전차를 만나면 싸우지 말고 후퇴하는 것이 용인될 정도 였습니다<SPAN>.</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>그래서 재빠르게<SPAN> 76</SPAN>밀리<SPAN> 54</SPAN>구경의 주포를 장착한 포탑이 개발되기도 합니다<SPAN>.</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><STRONG><IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/2051821049BD4E1403" width=1024 actualwidth="1024" id="A_2051821049BD4E14038BEE"/></STRONG></P></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#5c7fb0><STRONG>&nbsp;[ 셔먼전차도 후반에 가셔난 무장을 강화하게 된다 그림의 76.2 밀리 54구경 주포가 그것으로 43년부터는 이런 중무장을 한 셔먼도 등장하게 된다 좌측에는 105밀리 곡사포 탑재모델로 이것은&nbsp;적 전차 파괴용도가 아닌 토치카나 바리케이트 등을 제거하기 위한 &nbsp;용도였다 물론 적전차가 맞으면 일격이 작살났겠지만 탄도가 곡선이라 맞추기가.. 105밀리 곡사포 모델은 트그히 시가전에서 높은 효과를 보여주였다고 한다. 그림은 취미가 20호중에서 발췌]</STRONG></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><STRONG></STRONG></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">75mm</SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">포에 비하여<SPAN> 76.2mm</SPAN>포는 장갑 관통력이 뛰어났다<SPAN>. </SPAN>그러나 포탄 탑재수가 적었고<SPAN>, </SPAN>발사시에 연기가 많이 발생하였으며<SPAN>, </SPAN>유탄 사용시 작약량이<SPAN> 75mm</SPAN>포보다 적은 것 등 장단점이 있었다<SPAN>. </SPAN>때문에 두 종류의 포를 탑재한<SPAN> M4</SPAN>는 비슷한 페이스로 생산되었다<SPAN>. </SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1718911649BDEC5547" width=800 actualwidth="800" id="A_1718911649BDEC5547E58D"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;&nbsp;<STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0> [ 신형 76.2 밀리 주포와 대형화 된 T23 포탑 그리고 HVSS 신형 현가장치로 교체된 M4A3 최후기형 후반기 셔먼전</FONT></STRONG></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; 차의 특징을 </FONT></STRONG></FONT></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>잘 보여주는 사진이라 하겠다]</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>대공포의 발전형인<SPAN> 76.2mm</SPAN>포는 텅스텐을 사용한 고속 철갑탄<SPAN>(HVAP)</SPAN>을 사용할 경우<SPAN>, </SPAN>스펙상 독일의<SPAN> 88mm</SPAN>포와 비슷한 수준의 관통력을 발휘했지만<SPAN>, </SPAN>텅스텐탄은<SPAN> M4</SPAN>에 충분히 공급되지 않았다<SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/205B100D49BE0D03C3" width=1024 actualwidth="1024" id="A_205B100D49BE0D03C377A6"/></P></FONT></SPAN>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#5c7fb0><STRONG>[미군이 개발한 76.2 밀리 주포는&nbsp;스펙상으로는 독일의 88밀리 포에 맞먹는 파워를 가졌지만 실제는 탄의 문제로 그렇치 못했다 대신 영국군이 비밀리 개발한 파이어플라이의 17파운드&nbsp;주포는 똑같은 76.2 밀리&nbsp;포였지만 신형&nbsp;APDS 철갑탄을이용할경우 800미터 정도에서 티이거를 격파할 정도의 파워를 낼수 있었다]&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;</STRONG></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>셔먼 전차는 차체 다음으로 변화가 많은 것이 바로 포탑인데 기본형인<SPAN> 75</SPAN>밀리<SPAN> 40</SPAN>구경 전차포를 장착한 타입외에 전기<SPAN>/</SPAN>중기<SPAN>/</SPAN>후기형으로 분류되는 몇가지 특징이 있습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>자세한것은 포함된 일러스트를 참고 하세요<SPAN>.. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">7.<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt">현가장치의 변화<SPAN> </SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>셔만전차의 다른 분류로는 현가장치의 변화를 들 수 있습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1251821049BD4E1504" width=1024 actualwidth="1024" id="A_1251821049BD4E1504FE5A"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;<STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[마지막으로 셔먼전차에서 살펴봐야 할 부분이 바로 현가장치이다. 초기형 VVSS 방식과 후기형 VVSS 의 형태 그리고 신형 HVSS 현가장치의 형태에 주의 특히 HVSS 는 M4A3 에만 장착되었다는고 하는데 요즘 사진을 보이 꼭 그런것만은 아닌듯 하다..]</FONT></STRONG></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>초기형의 셔만전차들은 대부분<SPAN> M3 LEE </SPAN>전차와의 공용되는 부품을 많이 사용하였는데 그중 현가장치등도 마찬가지였습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>하지만 전차의 무장이 변화하고 장착되는 장갑들이 추가되면서 현가장치에 무리를 주게되자 현가장치의 개량이 이어지게 됩니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1874080949BE7E84CD" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="300" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="300" id="A_1874080949BE7E84CDA015"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[그리고 짚고 넘어갈 부분중 하나가 바로 스프로켓 휠과 아이들러 휠의 형태로 메이커들이 종종 실수 하는 부분중 하나이다]</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>초기형의 셔만에는 <B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN>VVSS </SPAN>방식<SPAN> (Vertical Volute Suspension System)</SPAN></B><SPAN> </SPAN>이라 불리는 후기형 수직와권<SPAN>(</SPAN>일본식 표기이다 국내싸이트에서는 이를 <SPAN>‘</SPAN>수직소용돌이방식 현가장치<SPAN>’ </SPAN>라고도 변역한다<SPAN>) </SPAN>현가장치를 주로 사용하였으나 이후 후기형에는 강철제 스프링이 추가된 <B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal">수직와권 현가장치</B>를 성능과 완성도가 가장 높았던<SPAN> M4A3</SPAN>의 경우 <B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN>HVSS (Horizontal Volute Suspesion System) </SPAN>수평와권 현가장치를</B> 장착하기도 합니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1974080949BE7E84CE" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="612" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="612" id="A_1974080949BE7E84CE2BDB"/></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[후기형 VVSS 현가장치와 추가증가장갑 등을 장착한 M4A2 형 최후기형]</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>특히<SPAN> HVSS (Horizontal Volute Suspesion System) </SPAN>수평와권 현가장치를 장착한 타입을<SPAN> M4A3E8 </SPAN>이라고 명했는데 많은 전차병들이 편한 승차감으로 인해 이지에잇 이라는 애칭으로 더 많이 불렀으며 우리 한국군의 전차전력 역시 이 차량으로 시작되었습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>이후 이 차량들은 이스라엘로 매각되어<SPAN> M50/M51 </SPAN>수퍼셔먼 등을 개조하는데 널리 쓰이기도 합니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/20516E1749BDEE0962" width=785 actualwidth="785" id="A_20516E1749BDEE0962D320"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;<STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>['이지에잇(EASY EIGHT]' 이라는 명칭으로 더 잘 알려진 M4A3E8 은 셔먼전차의 최후 생산형으로 특히 승차감이 뛰어나 승무원들에게 인기가 좋았다 신형 HVSS 현가장치 에 주의!!]&nbsp;</FONT></STRONG></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>&nbsp;<SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></STRONG></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">8.<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt">W </SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt">자가 붙은 타입<SPAN> </SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>셔만은 피탄시 화재가 잘 발생하기로 유명한 전차이기도 했는데 이는 가솔린 엔진을 사용한 전차이기 때문에 특히 그런 단점이 더했습니다<SPAN>.</SPAN>그래서 이에 대한 개량으로 습식 화재방지 장비를 개발 하기도 하였습니다<SPAN>.</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/2074080949BE7E84CF" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="700" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="700" id="A_2074080949BE7E84CF3136"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#5c7fb0><STRONG>[M4A1 76(W) 차체가 둥근것으로 보아 M4A1&nbsp; 형인데&nbsp;주포는 76.2 밀리 신형주포&nbsp;특이하게 HVSS 현가장치를 장착하고 있는데 M4A3 만 장착된것으로 알려진 이 현가장치가 장착되어 있는것은 전후 설치한것으로 보인다. 암튼 W 자가 붙었다고 해서 외형상으로 특이한 것은 아니다]</STRONG></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">M4</SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">의 <B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal">명칭 끝에<SPAN> W</SPAN>가 부가되어 있는 것은 피탄시 탄약에 화재가 발생하지 않도록<SPAN>, </SPAN>주위에 물과 글리세린을 혼합한 부액을 둘러싸는 방식을 채용하였습니다 끝에 <SPAN>W</SPAN>자 붙는 것은 이러한 방식의<SPAN> 'Wet </SPAN>탄약고<SPAN>'</SPAN>가 장비되어 있다는 것을 나타냅니다</B><SPAN>..</SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>이런 장비가 장착된 타입은 별도의 지정없이 <B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal">끝에<SPAN> W </SPAN>자를 추가하는 것으로 분류하였습니다<SPAN> </SPAN></B></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">9.<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp; </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt">기타 파생형<SPAN> </SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>셔먼전차는 워낙 방대한 수량이 생산되다보니 종전후에도 각국에서 오랫동안 현용전차로 사용되어왔다<SPAN>. </SPAN>그런 가운데 각나라별로 셔면전차의 차대를 이용한 파생형도 엄청나서 이 역시 정리하려면 마음먹고 해도 수년은 걸릴듯한 양이다<SPAN>. </SPAN>일단 이번에는 미군에서 사용된 파생형만 간단히 짚고 넘어가도록 합니다<SPAN>. (</SPAN>각 링크를 누르면 이동됩니다<SPAN>)</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1812810C49BE7CB4D8" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="700" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="700" id="A_1812810C49BE7CB4D86F27"/></P></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>&nbsp;[105밀리 곡사포를 탑재한 M4A3 최후기형으로 신형 HVSS 스커트 연결부분의 연결구 그리고 신형 포탑의 특징이 잘 살아있다 이 모델은 아카데미에서 제품화 한 모델이기도 하다]</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">&nbsp;</SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><A title="M10 Wolverine" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/M10_Wolverine"><U><FONT color=#0000ff>3in Gun Motor Carriage M10</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> - </FONT><A title="Tank Destroyer" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tank_Destroyer"><U><FONT color=#0000ff>Tank Destroyer</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><A title="M36 Jackson" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/M36_Jackson"><U><FONT color=#800080>90 mm Gun Motor Carriage M36</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> - Tank Destroyer </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1512720C49BE7FD16A" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="800" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="800" id="A_1512720C49BE7FD16AFD78"/></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"></SPAN></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[셔만의 파생형은 한두가지가 아니다! 사진의 M36 잭슨도 그중하나로 차체는 셔만의 것을 쓰고 있다]</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"></SPAN></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"></SPAN></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><A title="M7 Priest" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/M7_Priest"><U><FONT color=#0000ff>105 mm Howitzer Motor Carriage M7</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> - </FONT><A title="Self-propelled artillery" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-propelled_artillery"><U><FONT color=#0000ff>self-propelled artillery</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000>, aka <I>Priest</I> </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><A title="M12 Gun Motor Carriage" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/M12_Gun_Motor_Carriage"><U><FONT color=#0000ff>155 mm Gun Motor Carriage M12</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> - GMC M12 with Cargo Carrier M30 (both used Sherman components) </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><A title="M40 GMC" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/M40_GMC"><U><FONT color=#0000ff>155/203/250 mm Motor Carriages</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> - 155 mm GMC M40, 8 in. (203&nbsp;mm) HMC M43, 250 mm (10 inch) MMC T94, and Cargo Carrier T30 </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><A title="Flame tank" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flame_tank#M4"><U><FONT color=#0000ff>Flame Tank Sherman</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> - M4A3R3 <I>Zippo</I>, M4 <I>Crocodile</I>, and other flame-throwing Shermans </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1612720C49BE7FD16B" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="400" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="400" id="A_1612720C49BE7FD16BAB81"/></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[화기방사형 셔먼도 있고 주로 태평양 전선에서 쓰였는데 해병대 사양이 M2A2 이니 아카데미 제품을 써서 만들어봐도 좋을듯..]</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><A title="T34 Calliope" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T34_Calliope"><U><FONT color=#800080>Rocket Artillery Sherman</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> - T34 <I>Calliope</I>, T40 <I>Whizbang</I>, and other Sherman rocket launchers </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1112810C49BE7CB3D2" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="431" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="431" id="A_1112810C49BE7CB3D2DCD3"/></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[셔먼전차중 가장 유명한 파생형 중 하나인 T34 <EM>Calliope</EM>,(갈리오페) 소련의 카추사 로켓포를 본떠 다련장 로켓포를 장착함 모델로 일명 울부짖는 미미 (로켓 비행시 소름끼치는 소리를 냈다고 한다) 라는 애칭으로 유명했다 과거 이탈래리에서 기가막힌 제품을 낸적이 있지만 현재는 절판중이다]</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000>Amphibious tanks - </FONT><A title="Duplex Drive" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duplex_Drive"><U><FONT color=#0000ff>Duplex Drive</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> (DD) swimming Sherman. A British variant used by US forces. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><A title="Combat engineering vehicle" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combat_engineering_vehicle"><U><FONT color=#0000ff>Engineer tanks</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> - D-8, M1, and M1A1 dozers, M4 <I>Doozit</I>, Mobile Assault Bridge, and <I>Aunt Jemima</I> and other mine-clearers </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><A title="Armoured recovery vehicle" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Armoured_recovery_vehicle"><U><FONT color=#800080>Recovery tanks</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> - M32 and M74 TRVs </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1612810C49BE7CB4D6" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="490" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="490" id="A_1612810C49BE7CB4D66EF9"/></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[그리고 셔먼전차중 유명한 것이 바로 M32B 장갑회수차 M88 이 등장하기전인 1970년대 까지 쓰인 장갑회수차로 역시 이탈래리에서 한정판으로 기가막힌 제품이 출시된적이 있었다]</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 58pt; mso-list: l1 level2 lfo3; tab-stops: list 72.0pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Courier New'; mso-fareast-font-family: 'Courier New'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore"><FONT color=#000000>o<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><A title="Artillery tractor" href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artillery_tractor"><U><FONT color=#0000ff>Artillery tractors</FONT></U></A><FONT color=#000000> - M34 and M35 prime movers </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-ansi-language: EN" lang=EN><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">10.<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt">기타 분류시 주의사항<SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>셔만전차는 앞서 이야기했듯 워낙 다양한 공장에서 많이 생산하다보니 생산년도나 공장에 따라 조금씩 차이가 있습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>특히 이중에는 현지에서 사정에 맞게 개량된 것 까지 합하면 더많은 분류가 가능하지만 일단 보기좋게 이정도만 하는 것이 낫겠다 싶어 이정도만 조사했습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>사실 이 분류라는게 딱 이거라는게 아닌 훗날 전사가들이 알기쉽게 분류해둔 것이라 저는 일단 예전 취미가의 이대영 선생님께서 분류해둔 것을 기반으로<SPAN> 5</SPAN>개의 종류로 크게 분류하였습니다만 외국에는 다른 분류법으로 분류하기도 합니다<SPAN>.</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>셔만전차 분류에 있어 중요한 점은<SPAN> </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">(1)<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'"> </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">어찌되었던 셔만전차를 분류하기 위해서는 엔진의 종류에 따라 틀리므로 후방의 엔진그릴을 보면 된다<SPAN>. (</SPAN>포함된 일러스트 참고<SPAN>) </SPAN>하지만 실제로는 엔진상면을 잘 나타내는 사진이 드물고 그위에도 각종 장비품이 가득함으로 이를 바탕으로 구분하기란 전문가도 어렵습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN>&nbsp; <IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/14782E0B49BE8268EF" width=800 actualwidth="800" id="A_14782E0B49BE8268EFE844"/></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P><FONT color=#5c7fb0><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><STRONG>[&nbsp; 셔만에 탑재된 Continental R-975 성형엔진 사진처럼 9개의 실린더가 별처럼 감싸고 있는 비행기용 엔진으로 셔먼 M4 와 M4A1 에 탑재된 엔진이다]</STRONG></SPAN></P></SPAN></SPAN></FONT>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN>&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; <IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1404C90D49BD4A8E11" width=450 actualwidth="450" id="A_1404C90D49BD4A8E11B058"/> <IMG style="WIDTH: 438px; FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1504C90D49BD4A8E12" width=450 height=372 actualwidth="450" id="A_1504C90D49BD4A8E120FF4"/></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN>&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; &nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; <IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/12177B1649BDEB985E" width=450 actualwidth="450" id="A_12177B1649BDEB985EA554"/><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN> <IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/12401E1849BDF1934B" width=450 actualwidth="450" id="A_12401E1849BDF1934BF419"/></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN>&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN>&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; <SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/14401E1849BDF1944C" width=450 actualwidth="450" id="A_14401E1849BDF1944C530A"/><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt"><FONT color=#000000> <IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/13177B1649BDEB985F" width=450 actualwidth="450" id="A_13177B1649BDEB985F9575"/></FONT></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN>&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt"><FONT color=#000000></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; &nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; <IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1622DA1049BE0A6ED9" width=450 actualwidth="450" id="A_1622DA1049BE0A6ED9275B"/></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt"><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[셔먼의 각형식을 잘 나타낸 도면 1978년에 D.P DYER씨에 의해&nbsp;작성된 이 도면은 유명한 셔먼전차 도면으로 모든 메이커들이 참고로 제품을 개발하는데 지대한 공헌을 한 도면이다 각 형식별 특징을 잘 그려내고 있지만 요새 최신 자료에 의하면 틀린 부분도 약간은 있는 모양 각 형식별 특징을 잘 보도록 하자~]&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></B></P></FONT></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;<SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN> <IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/14525A1049BD4B1B03" width=816 actualwidth="816" id="A_14525A1049BD4B1B033D7D"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[셔먼전차의 특징을 가장 잘 알려주는 부분은 엔진후방의 그릴이지만 보통 이부분의 사진은 잘 나오는 것이 없고 각종 짐들로 덮여있기 때문에 알아보기가 힘들다 그럴때 구분이 쉬운것이 바로 후방의 리어패널이다 긱형식별로 특징이 다르므로 쉽게 구분이 가능하다 사진은 A3 타입의 모습이다]</FONT></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"></SPAN></B><FONT color=#5c7fb0>&nbsp;</FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">(2)<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'"> </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">예외적으로<SPAN> M4</SPAN>와<SPAN> M4A1 </SPAN>은 같은 엔진을 사용하지만<SPAN> M4A1 </SPAN>은 주조제 상체를 이용하이용 둥글둥글한 것은 모두<SPAN> M4A1 </SPAN>이라고 봐도 무관 합니다<SPAN>.</SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN>&nbsp; <IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1769CF0F49BD4CCF05" width=794 actualwidth="794" id="A_1769CF0F49BD4CCF056676"/></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[포탑이나 포의 형태 그리고 현가장치를 제외하고라도 차체가 둥근건 무조건 M4A1 타입이다. 일명 터틀백 이라는 주조제 차체의 형태이다 이번에 드래곤에서 제품화 했다]</FONT></SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">(3)<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'"> </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;</SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">전기형 중기형 후기형은 분류하기 편한방편일뿐 꼭 그렇다는게 아닙니다<SPAN>.</SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">(4)<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'"> </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">셔먼 시리즈의 각 형식들은 생산시기마다 부품의 형태가 각기 다르지만 규격만은 철저하게 통일되어 있어 전장에서는 서로 호환성 있게 사용되었습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>다만 예외가 있는데<SPAN> M4A4 </SPAN>는 생산시기에 상관없이 줄곧<SPAN> M3 LEE </SPAN>전차에 사용된 구식의<SPAN> 3</SPAN>분할 트렌스미션 커버만이 사용되었습니다<SPAN>.</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN></B>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1212720C49BE7FD36F" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="550" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="550" id="A_1212720C49BE7FD36FBD90"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN></B>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[셔먼전차를 구분 하는 중요요소중 하나가 바로 차체 앞 부분의 트랜스미션 형태이다. 보통은 사진의 3단 구조로 되어 있지만 (M3 LEE 전차의 모습과 같다) 후기형으로 오면 주조제로 된 일체화된 트렌스미션 커버로 바뀌게 된다 참 이넘은 뒤늦게 구한 M4A5 중 캉카루 라 불리는 일종의 APC 다 오스트리아 군이 주로 사용했다]</FONT></SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN></B>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes"><IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/2022DA1049BE0A74DC" width=800 actualwidth="800" id="A_2022DA1049BE0A74DC16F8"/></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></B>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes"><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[이것이 후기형 차체에 등장하는 일체화된 트랜스미션 커버이다. 3단으로 분리된 트랜스 커버에 비해 방어력이 뛰어났다고 한다]</FONT></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN></B>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;</SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">또<SPAN> M4A3 </SPAN>의 경우 처음부터 끝까지 일체형 트랜스미션 커버만이 사용되었고<SPAN> M4</SPAN>에는<SPAN> M3</SPAN>와 동형인 현가장치가 사용된적이 없이 곧장 후기형 현가장치만 사용되었습니다<SPAN>.</SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 5.6gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">(5)<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'"> </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">하지만 꼭 이런 원칙이 지켜진 것이 아니라 후기형에 극초기형 부품이 장착되기도 하였는데 이는 전장에서 파괴된 셔만전차를 재생했거나 부족한 부품을 떼어다 쓴 경우로 셔만의 경우 앞서 이야기했듯 부품 디자인은 달라도 규격은 통일되어 있어 이런 것이 가능했습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;<SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/2012720C49BE7FD26E" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="1024" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="1024" id="A_2012720C49BE7FD26E1219"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></B>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[셔먼전차의 장점은 형식은 달라고 각 부분의 부품은 규격화 되어 있다는 점으로 사진처럼 페차된 차고에서 맞는 부위 부품을 가져다가 끼우면 어느시기에 생산된 차량도 장착이 가능했다는 점이다. 미국식의 효율성을 엿볼수 있는 부분으로 이로 인해 수많은 파생형과 특징들이 등장하게 된다]</FONT></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">(6)<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'"> </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">셔만에 장착된 특수장비는<SPAN> (</SPAN>지뢰제거장비나 도져<SPAN>, T34 </SPAN>다련장미사일발사기등<SPAN>) </SPAN>따로 형식이 있는 것이 아니라 그때마다 현지에서 구할수 있는 셔먼 전차를 개조해 장착하였습니다<SPAN>.<SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 56pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l2 level1 lfo2" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><IMG style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" class=tx-daum-image border=0 hspace=1 vspace=1 src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1169CF0F49BD4CD30A" width=1024 actualwidth="1024" id="A_1169CF0F49BD4CD30A71A9"/></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></FONT>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[간혹 보이는 특수장착 도구들은 차체의 형식에 구애받지 않았다. 즉 초기형인 M4나&nbsp; 최후기형인 M4A3E8 이던 장착되던 장비는 형식의 구애를 받지 않았으며 이점은 미군장비의 특징중 ㅏ나이기도 하다]</FONT></SPAN></SPAN></P></SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 40pt" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp; </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>이상 길고 다양한 셔만전차 파생형을 정리해봤습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>글에서도 밝혔듯히 분류라는게 <SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>꼭 절대적인 것이 아닌 편리에 의해 분류해둔것이라 딱히 이거라는건 없습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>다만 셔만 분류에 있어 국내의 최고 전문가이신 전 취미가의 편집장님이셨던 이대영 선생님이 정리하신 내용을 많이 참고하였지만 이런 분류라는게 시간이 지날수록 새로운 사실이 밝혀지면서 달라지는 터라<SPAN> 100% </SPAN>정확하다고는 신뢰할 수는 없습니다<SPAN>. (</SPAN>그래서 위키백과 사전 영문판 내용을 많이 참고하였습니다<SPAN>.) </SPAN>추후 새로운 사실이 밝혀지면 언제든 추가하겠습니다<SPAN>.</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: -18pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd; mso-list: l0 level1 lfo1" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 새굴림"><SPAN style="mso-list: Ignore">11.<SPAN style="FONT: 7pt 'Times New Roman'">&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt">마치며<SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>드디어 셔먼전차의 계보중 일부를 정리하게되었습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>사실 어릴적에는 몰랐는데 이런 기계적인 느낌이 물씬 풍겨나는 전차가 나이가 들면서 왜이리 좋은지 모르겠습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1712720C49BE7FD16C" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="1024" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="1024" id="A_1712720C49BE7FD16CFD40"/></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#5c7fb0><STRONG>[노르망디 상륙작전후 해변에 상륙중인 셔먼 차체 후방의 그릴을 봐야 하겠지만 차체의 각진 형태 와 트랜스미션 커버 그리고 포의 형태로 보건데 M4A3 로 보인다. 하지만 이는 전문가라도 딱 100% 맞추기 힘든것으로 보통 작전 시기나 특히 엔진커버등을 보여져야 한다]</STRONG></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><FONT color=#5c7fb0><STRONG>&nbsp;</STRONG></FONT></P></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>셔먼전차에 대해서는 어릴적 추억으로는 티비를 통해 즐겨보던 전투<SPAN>(combat) </SPAN>라는 드라마에서 간혹 보였고 <SPAN>(</SPAN>어릴적에는 그제 셔만인줄도 몰랐다<SPAN>.. </SPAN>그저 나와서 포만 쏴대는게 멋져보일뿐<SPAN>..) </SPAN>본격적으로 셔먼에 대해 관심을 가졌었던 것은 고등학생때부터 애독하던 취미가 라는 책을 통해서가 아닐까 생각 합니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN>&nbsp;&nbsp; <img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1912720C49BE7FD26D" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="1024" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="1024" id="A_1912720C49BE7FD26DC337"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[노르망디 상륙작전 이후 독일군에 협력한 여성을 체포해가는 프랑스 시민군의 모습과 셔먼... &nbsp;3단으로 분리된 트랜스미션 커버 구형 현가장치 그리고 75밀리 포로 보건데 M4 A3 중기형 (좌우로 열리는 커버와 탑승자가 미군이라는점에 주의) 으로 보인다]</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>국내최초 모형잡지 였던 취미가에서<SPAN> 18~27</SPAN>회까지 근<SPAN> 1</SPAN>년 넘게 특집으로<SPAN> MORE SHERMAN </SPAN>이라는 특집기사를 다룬적이 있었는데 당시 고등학생이였던 저에게 큰 충격이였습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>언젠가는 꼭 모아봐야지하고 생각 했었는데<SPAN>..</SPAN>풋풋한 고등학생이 어느덧<SPAN> 30</SPAN>대 중반의 아저씨가 되어버렸습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN>&nbsp; <img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1412720C49BE7FD472" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="1024" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="1024" id="A_1412720C49BE7FD4722746"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>그동안 셔먼전차들을 틈틈히 모아왔지만 어느게 맞고 어느게 틀린지<SPAN>..</SPAN>형식별로 뭐가 다른지 알수가 없었습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>간간히 취미가 특집기사를 찾고 뒤졌지만 작성된지<SPAN> 10</SPAN>년이 넘은 오래된 기사이다 보니 최근 자료와는 틀린 부분도 많더군요<SPAN>…</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1112720C49BE7FD370" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="638" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="638" id="A_1112720C49BE7FD370475A"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><FONT color=#5c7fb0><STRONG>[역시 이번에 늦게 구한 M4A5 의 사진 이것저것 짬봉이네..]</STRONG></FONT></SPAN></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>그래서 언젠가는 꼭 정리해보리라 하고 생각하고 있던차에 몇해전에 밴드 오브 브라더스라는 미니씨리즈물은 저로 하여금 셔먼전차의 매력에 푹 빠져들게 하기에 충분했습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>그리고 얼마전에는 드래곤에 새롭게 출시된<SPAN> M4A1 </SPAN>씨리즈를 모으게 되었습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>드래곤 특유의 찢고 나누고 분류한 여러종류의 셔먼전차를 보고 이제 더 이상 미루면 안되겠구나 하는 생각이 들더군요<SPAN>.. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>사실 그전에 아카데미에서 몇해전에 심혈을 기울여 만든<SPAN> M4A2 </SPAN>나<SPAN> M4A3 105 MM</SPAN>도져 등이 국내모델러들의 무관심과 일부 지각없는 모델러들의 국산제품 까대기로 판매에 무척 어려워 한다는걸 들었습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>모형역사가 짧은 우리나라 모형에서는 아직 대전물중 특히 연합군에 대한 매니아층이 적은게 사실입니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>잘해야 현용물이나 독일군 매니아들만 가득한게 현실인데 사실 밀리터리 장르에서 오래될수록 자연스럽게 미군이나 영국군 소련군 같은 연합군측의 깊은 묘미를 가지는 분들이 많습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1212720C49BE7FD371" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="607" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="607" id="A_1212720C49BE7FD371A238"/></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><SPAN><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[파이어플라이는 긴 55구경 장포신으로 쉽게 구분이 가능하다. 보통 M4A4 로 만들었지만 개중에는 M4A2 형으로 만든 것도 보인다]&nbsp;</FONT></STRONG></SPAN></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>연합군측 무기들은 비록 독일군 무기들에 비해 멋드러지거나 많은 활약을 한 기체는 드물지만 어디에서나 어디든 항상 그자리에서 묵묵히 자신의 임무를 마친 무기들이 많습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>셔먼전차의 경우도 그런 경우이지요<SPAN>… </SPAN>마치 우리네의 소 처럼 셔먼은 미군 및 연합군들이 있는 곳이면 어디던지 그 자리에 있었고 또 피를 흘리며 싸우다 사라졌습니다<SPAN>.</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>얼마전에 워낭소리 라는 독립영화를 봤는데 저는 그안에 보여진 소의 이미지와 셔먼전차의 이미지가 오버랩 되는 것을 느꼈습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;</SPAN><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;&nbsp;</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>특히 이번 조사를 통해 더 잘 알게되었지만 정말 외국에는 공부하며 모형을 만드는 것을 또 다른 취미로 여기는 분들이 많습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>이제는 우리도 좀 다르게 모형을 즐겨봐야 하지 않을까 하는 생각이 듭니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>이번 셔먼전차 정리를 톨해 새삼스럽게 다시 알게된 것은 해외에는 이런 무기를 소개하는 좋은 싸이트가 엄청나게 많습니다<SPAN>… </SPAN>우리와는 비교할수 없을 정도로 체계적으로 잘 정리해둔 좋은 정보들을 가득한 싸이트 내용들을 부족한 영어실력으로 인해 다 담아오지 못한게 한스럽네여<SPAN>.. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>그리고 이렇게 체계적으로 무기들을 정리하고 연구하는 것은 모형을 즐기는 또 다른 좋은 방법이 아닐까 하는 생각을 해봅니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>가끔 메이커의 제품에 대해 혹평을 하는 분들중에는 정말 잘 아시는 분들도 있겠지만 섣부르게 아는 분들이 태반이라는 점에서 저의 이런 작은 시도가 작은 도움이 되기를 바랍니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>셔먼전차에 대한 내용은 사실 평생을 공부해도 다 못할 정도로 방대하고 다양한 것이 사실 입니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>제가 정리한 것은 그 일부에 불과하며 앞으로 시간나는대로 차근차근 정리해보겠습니다<SPAN>. <SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;</SPAN><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;</SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>긴글 읽어주시고 성원해주신 분들께 감사의 말씀을 드리며 앞으로 정리된 내용을 바탕으로 본격적으로 좋은 킷들을 선정 리뷰해 나가도록 하겠습니다<SPAN>. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><FONT color=#000000><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><I style="mso-bidi-font-style: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt"><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN>2009</SPAN></I></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><I style="mso-bidi-font-style: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; FONT-SIZE: 12pt">년<SPAN> 3</SPAN>월<SPAN> 17</SPAN>일 미라지나이트 배상 <SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></I></B></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>참고자료<SPAN> </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>원문대로 게시함 <SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M4 Sherman variants</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◆<SPAN> US M4 Sub-Types</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4- Continental radial engine; welded hull; 75-mm and 105-mm versions onl</SPAN> <SPAN>y. Users: US, Britain, Poland, France (one vehicle). Some very late M4s had composite cast/welded hulls (cast hull front identical to M4A1 (76) W.). </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4(105) - Upgraded with 105 mm M4 howitzer. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4(105) HVSS - M4(105) w/ HVSS. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A1 - Continental radial engine; one</SPAN> <SPAN>-piece cast hull; 75-mm and 76-mm versions built. Users: US, Britain, South Africa, France (small numbers), China </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A1E4/M4A1(76)W - Upgraded with 76 mm M1 gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A1E8/M4A1(76)W HVSS - Upgraded with widetrack Horizontal Volute Spring Suspension (HVSS), fitted with the 76 mm M1 gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A1E9 - Unknown configuration, possibly an upgrade of existing M4A1s with 76 mm guns. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A2 - Diesel-powered; welded hull; 75-mm and 76-mm guns. Users: USSR (M4C), USMC, France, Britain, Poland. No US Army combat use. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A2E8/M4A2(76)W HVSS - Upgraded with widetrack Horizontal Volute Spring Suspension (HVSS), fitted with the 76mm M1 gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A3 - Ford GAA V-8 engine; welded hull; 75-mm, 76-mm, and 105-mm guns. Users: US, France (small numbers). The M4A3 was the preferred US Army vehicle. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A3(75) - M4A3 w/ 75mm M3 gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A3(105) - M4A3 w/ 105mm M4 howitzer. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A3E2 Assault Tank - postwar nickname "Jumbo" - extra armour (including 4" on front), vertical sided turret, but about 3-4 mph slower. Built with 75 mm gun but frequently re-armed by the using units with 76-mm guns. Grousers fitted to the tracks. Users: US, France (one vehicle) </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A3E4/M4A3(76)W - M4A3 w/ 76mm M1 gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A3E8/M4A3(76)W HVSS (Easy Eight) - Upgraded with widetrack Horizontal Volute Spring Suspension (HVSS), fitted with the 76mm M1 gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A3E9/M4A3(105) HVSS - Upgraded with widetrack Horizontal Volute Spring Suspension (HVSS), fitted with the 105mm M4 howitzer. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A4 - Chrysler A57 engine; welded, lengthened hull; 75-mm gun onl</SPAN> <SPAN>y as-built. Many re-armed with British 17-pounder guns ("Firefly"). Users: Britain, France, China </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A5 - No US vehicle was built with this designation; the number was meant to signify Canadian production. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A6 - Diesel engine; composite cast/welded hull lengthened similarly to the M4A4; 75-mm gun onl</SPAN> <SPAN>y. Onl</SPAN> <SPAN>y a few dozen of this variant were built and none were used in combat. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◆<SPAN> US Non-"M4" Sherman-Based Vehicles</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Variants without the M4 designation but built on the M4 medium chassis (While some began on the M3 chassis, some subvariants were switched to the M4 chassis during production. These are the models listed here):</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>▶<SPAN> Gun Motor Carriage</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> 105mm Howitzer Motor Carriage M7B1 - self-propelled 105 mm Howitzer Motor Carriage (HMC) based on the M4A3 Sherman chassis. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> 155mm Gun Motor Carriage M12 - self-propelled 155 mm Gun Motor Carriage (GMC). </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Cargo Carrier M30 - Cargo Carrier (an M12 with crew and ammunition space in lieu of the gun). </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> 155mm Gun Motor Carriage M40 - self-propelled 155 mm GMC (Either M1A1 or M2 gun) based on the M4A3 (HVSS) chassis. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> 8in Howitzer Motor Carriage M43 - self-propelled 8 inch HMC (standardized post-WWII). </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> 3in Gun Motor Carriage M10 - tank destroyer based on the M4A2 Sherman chassis. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> 3in Gun Motor Carriage M10A1 - Same as the M10, but based on the M4A3 Sherman chassis. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> 90mm Gun Motor Carriage M36 - tank destroyer based on M10A1 hull (M4A3 chassis); standard model. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> 90mm Gun Motor Carriage M36B1 - tank destroyer based on M4A3 Sherman hull and chassis; expedient model. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> 90mm Gun Motor Carriage M36B2 - tank destroyer based on M10 hull (M4A2 chassis, diesel); expedient model. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>▶<SPAN> Tank Recovery Vehicle </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M32 - based on M4 chassis with turret replaced by fixed superstructure, 60.000 lb winch and an 18 feet long pivoting A-frame jib installed. An 81mm Mortar was also added into the hull, primarily for screening purposes. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Tank Recovery Vehicle M32B1 - M32s converted from M4A1s. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Tank Recovery Vehicle M32A1B1 - M32B1's with HVSS, later removing the 81mm Mortar and incorporating crane improvements. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Tank Recovery Vehicle M32B2 - M32's converted from M4A2's. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Tank Recovery Vehicle M32B3 - M32's converted from M4A3's. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Tank Recovery Vehicle M32A1B3 - M32B3's brought to the same standard as the M32A1B1. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Tank Recovery Vehicle M32B4 - M32's converted from M4A4's. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M74 Tank Recovery Vehicle - Upgrade of the M32 to provide the same capability with regards to heavier post-war tanks, converted from M4A3 HVSS tanks. In appearance the M74 is very similar to the M32, fitted with an A-Frame crane, a main towing winch, an auxiliary winch, and a manual utility winch. The M74 also has a front mounted spade that can be used as a support or as a dozer blade. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M74B1 - Same as the M74, but converted from M32B3s. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◆<SPAN> US Special Attachment Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Rocket-firing, flame-thrower, mine-clearing, amphibious, engineer; mostly experimental (indicated by T instead of M)</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>▶<SPAN> mine-clearing, amphibious, engineer</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman DD (Duplex drive) - Amphibious M4. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4 Mobile Assault Bridge. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4 Dozer - fitted with dozer blade. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> T15/E1/E2 - Series of mine resistant Shermans based on the T14 kit. Cancelled at war's end. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploders / Mine Excavators - fitted with various mine exploding devices including plungers, rollers, mortars. Most of those remained experimental vehicles. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000></FONT></SPAN>&nbsp;</P><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1212810C49BE7CB3D3" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="640" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="640" id="A_1212810C49BE7CB3D324A7"/></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1412810C49BE7CB4D4" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="640" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="640" id="A_1412810C49BE7CB4D40234"/></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[셔만전차중 특이한 파생형중 하나가 바로 지뢰제거형 차량이다 퍼니(FUNNY) 전차라 불리던 이런 전차는 영국군에 의해 노르망디 작전전에 개발되었다 이런 도리깨 방식도 있었고..아래의 롤러방식도 있었다. 노르망디 투입에 투입되어 나름대로 큰 효과를 본 모양이다&nbsp;]</FONT></STRONG></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/1512810C49BE7CB4D5" class="txc-image" style="FLOAT: none; CLEAR: none" actualwidth="640" border="0" hspace="1" vspace="1" width="640" id="A_1512810C49BE7CB4D5A275"/></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph><STRONG><FONT color=#5c7fb0>[이런 대형 롤러를 단 지뢰제거 타입도 존재했다. 이것이 나중에 개량되어 현용 지뢰제거 롤러의 근원이 되었다 이것말고 쟁기타입의 지뢰제거차도 있었다고 한다]</FONT></STRONG></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: center; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; mso-para-margin-left: 0gd" class=MsoListParagraph>&nbsp;</P></SPAN></FONT></SPAN>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T1E1 Roller (Earthworm) - Discs made from armor plate. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T1E2 Roller - Two forward units with 7 discs onl</SPAN> <SPAN>y. Experimental. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T1E3/M1 Roller (Aunt Jemima) - Two forward units with 5 10' discs. Most widely used T1 variant, adopted as the M1. (picture) </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T1E4 Roller - 16 discs </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T1E5 Roller - T1E3/M1 w/ smaller wheels. Experimental. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T1E6 Roller - T1E3/M1 w/ serrated edged discs. Experimental </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T2 Flail - British Sherman Crab I mine flail. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T3 Flail - Based on British Scorpion flail. Development stopped in 1943. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T3E1 Flail - T3 w/ longer arms and sand filled rotor. Cancelled. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T3E2 Flail - E1 variant, rotor replaced with steel drum of larger diameter. Development terminated at war's end. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T4 - British Crab II mine flail. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T7 - Frame with small rollers with two discs each. Abandoned. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T8 (Johnny Walker) - Steel plungers on a pivot frame designed to pound on the ground. Vehicle steering was adversely affected. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T9 - 6' Roller. Difficult to maneauver. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T9E1 - Lightened version, but proved unsatisfactory because it failed to explode all mines. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T10 - Remote control unit designed to be controlled by the following tank. Cancelled. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T11 - 6 forward firing mortars to set off mines. Experimental. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T12 - 23 forward firing mortars. Apparently effective, but cancelled. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Exploder T14 - Direct modification to a Sherman tank, upgraded belly armor and reinforced tracks. Cancelled. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Excavator T4 - Plough device. Developed during 1942, but abandoned. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Excavator T5/E1/E2 - T4 variant w/ v-shaped plough. E1/E2 was a further improvement. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Excavator T5E3 - T5E1/E2 rigged to the hydraulic lift mechanism from the M1 dozer kit to control depth. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Excavator T6 - Based on the v-shape/T5, unable to control depth. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mine Excavator T2/E1/E2 - Based on the T4/T5's, but rigged to the hydraulic lift mechanism from the M1 dozer kit to control depth.</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>▶<SPAN> Rocket Launchers: </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Rocket Launcher T34 (Calliope) - armed with 60 4-6" rocket tubes mounted above the turret. Saw limited combat in 1944-1945. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Rocket Launcher T34E1 - T34 with 14 tubes in the 2 bottom units. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Rocket Launcher T34E2 - T34 modified to accept 7.2" rockets. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Rocket Launcher T39 - Enclosed box mount with doors, with 20 7.2" rockets. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Rocket Launcher T40/M17 WhizBang - armed with 20 7.2" rockets. Saw limited combat in 1944-45. A short variant of the T40 was also developed, but saw little usage. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Rocket Launcher T72 - T34 short tube variant. Never used. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Rocket Launcher T73 - Similar to the T40, but with onl</SPAN> <SPAN>y 10 tubes. Never used. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Rocket Launcher T76 - M4A1 w/ 7.2" rocket launcher in place of main gun. Never used. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Rocket Launcher T105 - M4A1 w/ rocket case instead of main gun. Never used. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Multiple Rocket Launcher T99 - 2 box mounts with 22 4.5" rockets, mounted on the turret. Never used. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>▶<SPAN> Flame Throwers: </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> M4A3R3 Flame thrower - Also known as "Zippo tanks" or more commonly Flame tanks. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◆<SPAN> UK and Commonwealth Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>▶<SPAN> UK Nomenclature</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>In British usage, Sherman I=M4, Sherman II=M4A1, Sherman III=M4A2, Sherman IV=M4A3. Additional letters denoted other features; A for the 76mm M1 gun, B for the 105 mm M4 L/22.5 howitzer, C for the OQF 17 Pounder gun, and Y for the wider tracked HVSS type suspension.</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman I - M4. The first Shermans to be received by the UK were equipped with two driver-operated fixed machine guns in the hull. This was a standard feature of very early Shermans and was one</SPAN> <SPAN> of the first things to be dropped from the design. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman Hybrid I - Sherman I w/ composite hull (cast front and welded rear end) </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IB - M4 with a 105 mm howitzer. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈ <SPAN>Sherman IBY - with the HVSS suspension. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IC (Firefly) - M4 with a 17 pounder (76.2 mm) gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman Hybrid IC - Sherman IC w/ composite hull (cast front and welded rear end) </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman II - M4A1 with a 75 mm gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IIA - M4A1(76)W </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈ <SPAN>Sherman IIAY - M4A1(76)W HVSS </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IIC (Firefly) - M4A1 witth a 17 pounder (76.2 mm) gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman III - M4A2 with a 75 mm gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IIIA - M4A2 with a 76 mm gun (unlikely to have been used by UK troops) </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IIIAY - M4A2(76)W HVSS (not used operationally by UK troops) </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IV - M4A3(75mm). M4A3 w/ 75mm M3 gun. (no Sherman IV's used operationally) </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IVA - M4A3(76)W </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IVB - M4A3(105). M4A3 with a 105 mm M4 howitzer. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IVBY - M4A3(105) HVSS. with HVSS. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman IVC (Firefly) - Planned M4A3 with a 17 pounder (76.2 mm) gun. Never built. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman V - M4A4 with a 75 mm gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman VC (Firefly) - M4A4 with a 17 pounder (76.2 mm) gun. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Shermans retrofitted with the British 17 pounder (76.2 mm) gun were known as Fireflies and were used by British and British-supplied Allied forces (Canada, Poland). Some were supplied to US units at the end of the war, but not in time for combat usage. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman VI - Not used, most likely for the same reasons as the M4A5 designation, to prevent confusion with Canadian Ram/Grizzly production. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman VII - M4A6 delivered into British use with Ordnance RD-1820 diesel engine. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>▶<SPAN> UK Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman DD (Duplex drive) - Amphibious M4. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman Kangaroo - Sherman III converted into Kangaroo armoured personnel carrier </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman III ARV Mk I - Amoured Recovery Vehicle conversion of Sherman III, similarly Sherman V ARV I and ARV II, but the Sherman II ARV III was a M32B1 TRV (see below) </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman BARV (Beach Armoured Recovery Vehicle) - converted and operated by the Royal Electrical and Mechanical Engineers to tow immobilised vehicles out of the water during the Normandy landings. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman Crab I and II - M4A4's with mine flail equipment. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Tank AA, 20mm Quad, Skink - prototype anti aircraft vehicle with four 20 mm Polsten cannons mounted in a turret on Canadian-made M4A1 hull. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Sherman V (Rocket) - a Sherman V with two 3-inch (60lb) RP-3 rockets on rails fitted to the turret. Used by the 1st Coldstream Guards at the Rhine in 1945. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◆<SPAN> Soviet Lend-Lease</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Diesel-powered M4A2s were sent to the Soviet Union under the Lend-Lease program. The Soviets received the wide range of M4A2-type Shermans, both with the 75mm and 76mm cannon. Some later HVSS suspension tanks were delivered and employed before war's end.</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>The M4 was called Em Cha by Soviet troops, because the Americans' open-topped figure 4 resembled the Cyrillic letter cha Ч.</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M4M&#8212;a few M4A2s in Soviet service were converted by adding an F-34 76.2mm gun, the same gun mounted on the T-34 medium tank. There was no shortage of U.S. 75mm ammunition, however, so there was little need to continue converting Shermans (Zaloga 1984:217). </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◆<SPAN> Post War Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Argentinian Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Repotenciado - Conversions of British Sherman VC and IC Hybrid to include a new armament suite, the 105 mm FTR L44/57 gun (an Argentine copy of the gun used on the AMX-13), a co-axial MAG-58 machine gun, and turret pintle mounted M2HB machine gun. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Chilean Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M50/60 - Converted Israeli M50/M51 Shermans, refitted with the IMI-OTO 60mm Hyper Velocity Medium Support (HVMS) gun. Claimed to be the very last fighting Sherman, remaining in Chilean service until 1989, when it was replaced by the Leopard 1V and AMX-30B2. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Egyptian Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M4A4 with FL-10 Turret - M4A4 fitted with the diesel engine of M4A2 and the FL-10 turret of the French AMX-13 light tank. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Israeli Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman with Krupp 75 mm gun - Six early salvaged Shermans had a Krupp 75 mm field gun to replace the original gun destroyed during post-WWII scrapping. Later these tanks were rearmed with 105 mm howitzers M4. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman M-1 - Israeli designation of any Sherman model armed with the 76 mm gun M1. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Super Sherman M-1 - Israeli designation of M4A1(76) fitted with HVSS suspension. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman M-3 (Sherman degem Alef prior to 1956) - Israeli designation of any Sherman model armed with the 75 mm gun M3. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman M-4 (Sherman degem Bet prior to 1956) - Israeli designation of any Sherman model armed with the 105 mm howitzer M4. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman M-50 (widely known abroad as Super Sherman) (1956) - Upgraded Sherman with the French CN 75-50 75 mm gun in the "old" turret fitted with a counterweight. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M-50 Continental - subvariant with Continental R-975 gasoline engine and VVSS suspension. 50 units converted. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M-50 Cummins - subvariant with Cummins diesel engine and HVSS suspension. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman M-51 (widely known abroad as Isherman or Super Sherman) - Upgraded M4A1 with Cummings diesel, HVSS and the French CN 105 F1 gun. The gun was shortened from 56 calibers to 44 and equipped with a massive muzzle brake; ammunition with smaller cartridge was used. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman Morag - Israeli designation of Sherman Crab. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Trail Blazer (Gordon) - A recovery/engineering vehicle based on HVSS equipped M4A1s, it featured a large single boom crane (as opposed to the A-Frame of the M32) and large spades at the front and rear of the vehicle to assist in lifting. It could also tow up to 72 tons. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman Medical Evacuation Tank (Ambutank) - A radical conversion of the M4 with the turret removed and the powerplant (changed to a diesel engine) moved to the front of the tank. A medical team and four casualties could be carried in an armoured compartment at the rear. Early vehicles were based on M4A1 hulls with VVSS suspension and are often referred to as "VVSS version". Later vehicles used hulls with HVSS suspension and were fitted with a big boxy superstructure. This version is often referred to as "HVSS version". Many were used during the Israeli-Egyptian War of Attrition (1968-70) and the Yom Kippur War. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M-50 - The M-50 was an open structured self-propelled artillery piece, mounting a single French Model 50 155 mm howitzer. Was developed in early 1960s. Saw combat in the War of Attrition and the Yom Kippur War. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Ro'em or L-33 - Based on M4 chassis with HVSS. Soltam of Israel designed a huge enclosed superstructure holding a 155 mm howitzer, also developed by Soltam. A Cummins diesel engine was fitted to deal with the increased weight. Was used in the Yom Kippur War and the 1982 Lebanon War. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>L-39 - Like L-33, but with longer barrel. Apparently was not adopted. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Makmat 160 mm - 160 mm mortar mounted on a Sherman chassis. It was developed in late 1960s and used in the Yom Kippur War and the Lebanon War. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>MAR-240 - In place of the turret, a side-looking launcher for 36 240 mm rockets was fitted. These were Israeli made versions of the Soviet BM-24 Katyusha rocket. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Episkopi or MAR-290 - As with the MAR-240, except mounting a rear-looking launcher for four 290 mm ground-to-ground rockets. Was used in the 1982 Lebanon War. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">Kilshon (Trident) or Kachlilit - The Kilshon was developed to reduce the losses suffered by SAM suppression aircraft by launching anti-radiation missiles from the ground. The Kilshon was based on turretless hull of the M51 Isherman on which a AGM-45 Shrike anti-radiation missile launcher was mounted. To deliver the desired range, a specially modified AGM-45 with booster was used. Later a prototype was developed for use with the AGM-78 Standard anti-radiation missile, but with the retirement of Shermans from IDF service the Keres (Hook) system was placed ont</SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"> <SPAN>o a heavy truck chassis for the finalized design instead. </SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Eyal Observation Post Vehicle - A Sherman that had the turret replaced with a 27 m (90 foot) tall hydraulically erected observation platform. This was used near the Suez Canal as a mobile observation post, before the Yom Kippur War</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◆<SPAN> US Foreign Aid Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> E4 Sherman - Perhaps the last US-made Sherman variants, in the early 1950s US Ordnance depots or private contractors mounted the 76 mm gun in the original, small turret of M4A3 and M4A1. The US provided these M4A3E4(76) or M4A1E4(76) to allies in Europe and Asia. </SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>HVSS - The US also retro-fitted the late-WWII wider-tracked HVSS suspension to many Shermans and this is sometimes noted after the main vehicle designation. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Canadian Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman Badger - Canada's replacement of its Ram Badger Flame tank, the Sherman Badger was a turretless M4A2 HVSS Sherman with Wasp IIC flamethrower in place of hull machine gun, developed sometime from 1945 to 1949. The 150 gallons at 250 psi was effective to 125 yards, with elevation of +30 to -10 degrees and traverse of 30 degrees left and 23 degrees right. This inspired the US T68.[1] </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">Sherman Kangaroo - From late WWII to the 1960s, Canada converted/used some Grizzlies (M4A1 Shermans made in Canada with different tracks and radios in 1943), at least one</SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"> <SPAN> very similar Skink (prototype Anti-aircraft-gun on the Grizzly hull), and M4A2(76)W HVSS Shermans to Kangaroo armored personnel carriers (APCs). </SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Mexican Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M32 Chenca - In 1998, Napco International of the USA upgraded M32B1 TRV Sherman-chassis armoured recovery vehicles with Detroit Diesel 8V-92-T diesel engines. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Indian Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">Sherman VA/M4A4(76) - although never a US production type (the 1950s E4 conversion was limited to M4A1 and M4A3), at least one</SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"> <SPAN> source claims that India had one</SPAN> <SPAN> regiment partly equipped with Sherman V ( British/Indian designation of M4A4) with 76 mm guns (the US 76 mm is not specified but British practice added an A suffix to denote the 76 mm). </SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Upgunned Sherman - two regiments of Shermans re-armed with the French 75 mm gun (derivative of the German Panther tank's gun) and referred to as upgunned Shermans. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Argentine Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Repotenciado - Conversions of British Sherman VC and IC Hybrid to include a new armament suite, the 105 mm FTR L44/57 gun (an Argentine copy of the gun used on the AMX-13), a co-axial MAG-58 machine gun, and turret pintle mounted M2HB machine gun</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Chilean Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M50/60 - Converted Israeli M50/M51 Shermans, refitted with the IMI-OTO 60mm Hyper Velocity Medium Support (HVMS) gun. Claimed to be the very last fighting Sherman, remaining in Chilean service until 1989, when it was replaced by the Leopard 1V and AMX-30B2. (Chilean Sherman photos) </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Egyptian Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M4A4 with FL-10 Turret - M4A4 fitted with the diesel engine of M4A2 and the FL-10 turret of the French AMX-13 light tank. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Israeli Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◎<SPAN> Gun tanks</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman (Krupp) - Six early salvaged Shermans had a Krupp 75 mm field gun to replace the original gun destroyed during post-WWII scrapping. Later these tanks were rearmed with 105 mm howitzers M4. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman M-1 - Israeli designation of any Sherman model armed with the 76 mm gun M1. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Super Sherman M-1 - Israeli designation of M4A1(76) fitted with HVSS suspension. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman M-3 (Sherman degem Alef prior to 1956) - Israeli designation of any Sherman model armed with the 75 mm gun M3. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman M-4 (Sherman degem Bet prior to 1956) - Israeli designation of any Sherman model armed with the 105 mm howitzer M4. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman M-50 - Upgraded Sherman with the French CN 75-50 75 mm gun, as used in the French light tank AMX 13, in the "old" turret fitted with a counterweight. Entered service in 1956. Was used in the Suez Crisis (1956), the Six Days War (1967) and the Yom Kippur War (1973). Sometimes colloquially mis-named as Super Sherman. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M-50 Continental - subvariant with Continental R-975 gasoline engine and VVSS suspension. 50 units converted. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M-50 Cummins - subvariant with Cummins diesel engine and HVSS suspension. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman M-51 - Upgraded M4A1 (HVSS) with improved engine and T23 turret modified to fit a shortened variant of the French CN 105 F1 gun with large muzzle brake. Was used in the Six Days War and the Yom Kippur War. Sometimes colloquially referred to as Isherman. About 100 of the remaining tanks of this model were seold to Chile in late 70's, were they received a new engine and transmission in early 90's. All of them were replaced by ex-Dutch Leopard 1V in late 90's </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◎<SPAN> Artillery tanks</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>M-50 155 mm - The M-50 was an open structured self-propelled artillery piece, mounting a single French Model 50 155 mm howitzer at the back of the hull, which was based on the "long" hull of M4A4 fitted with Continental engine (late production vehicles possibly used "short" hulls from other variants). The gun was developed in early 1960s by Israeli Ordnance Corps in cooperation with France. Probably about 120 units were produced. In early 1970s M-50s were fitted with HVSS and Cummins diesel engines. Was used in the War of Attrition and the Yom Kippur War. Some reserve units were armed with the M-50 at least until late 1970s. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Ro'em (colloquially known as L-33) - A self-propelled artillery piece mounting Soltam M-68 155 mm L/33 howitzer in large enclosed superstructure. Uses Sherman chassis with Cummins VT-8-460Bi diesel engine and HVSS. Probably about 200 units were produced. The gun saw combat in the Yom-Kippur War and the 1982 Lebanon War. Currently out of active service. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>L-39 - Like L-33, but with longer (39 calibers) barrel. Apparently was not adopted. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Makmat 160 mm - Soltam M-66 160 mm mortar mounted on a Sherman chassis, in an open-topped compartment with folding front plate. It was adopted in 1968 and used in the War of Attrition, the Yom Kippur War and the 1982 Lebanon War. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>MAR-240 - In place of the turret, a side-looking launcher for 36 240 mm rockets was fitted. These were Israeli made copies of the Soviet rockets used by the BM-24 multiple launch rocket system. Apparently never reached mass production. MAR stands for Medium Artillery Rocket. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Episkopi - Similar to MAR-240, but mounting a back-looking launcher for four 290 mm ground-to-ground rockets with high-explosive/fragmentation (Ivry-1) or cluster (Haviv) warhead. Was adopted in 1973, saw combat for the first time in the 1982 Lebanon War. Is colloquially known as MAR-290, and the name Ivry is also sometimes applied to the launching vehicle. An improved launcher on the Centurion tank chassis was later developed, but remained experimental. In 1990s was replaced in active service by the M270 MLRS. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">Kilshon (Trident) or Kachlilit - The Kilshon was developed to reduce the losses suffered by SAM suppression aircraft by launching anti-radiation missiles from the ground. The Kilshon was based on turretless hull of the Sherman M-51 on which a AGM-45 Shrike anti-radiation missile launcher was mounted. To deliver the desired range, a specially modified AGM-45 with booster was used. Later a prototype was developed for use with the AGM-78 Standard anti-radiation missile, but with the retirement of Shermans from IDF service the Keres (Hook) system was placed ont</SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"> <SPAN>o a heavy truck chassis for the finalized design instead. </SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◎<SPAN> Support tanks</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman Morag - Israeli designation of Sherman Crab. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Trail Blazer (Gordon) - A recovery/engineering vehicle based on HVSS equipped M4A1s, it featured a large single boom crane (as opposed to the A-Frame of the M32) and large spades at the front and rear of the vehicle to assist in lifting. It could also tow up to 72 tons. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Sherman Medical Evacuation Tank (Ambutank) - A radical conversion of the M4 with the turret removed and the powerplant (changed to a diesel engine) moved to the front of the tank. A medical team and four casualties could be carried in an armoured compartment at the rear. Early vehicles were based on M4A1 hulls with VVSS suspension and are often referred to as "VVSS version". Later vehicles used hulls with HVSS suspension and were fitted with a big boxy superstructure. This version is often referred to as "HVSS version". Many were used during the Israeli-Egyptian War of Attrition (1968-70) and the Yom Kippur War. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>Eyal Observation Post Vehicle - A Sherman that had the turret replaced with a 27 m (90 foot) tall hydraulically erected observation platform. This was used near the Suez Canal as a mobile observation post, before the Yom Kippur War. </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>◈<SPAN> Civilian Variants</SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>After World War 2, demilitarized Shermans were widely and cheaply available. Many were heavily modified for use in the construction, forestry and mining industries. Often, the turret and upper hull were completely removed and replaced with whatever equipment that was required for the vehicle's new role.</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>A Canadian company, Morpac Industries, Inc.[1], still produces heavy-duty, off-road load carriers based on Sherman components. These vehicles are used in the construction of electricity transmission lines in remote areas.</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;<A class=tx-link href="http://cafe.daum.net/compmania/J3wm/5" target=_blank>PT6에 계속 </A></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 9pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">참고 싸이트 및 서적</SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt"></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 9pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">&nbsp;</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: #333333">&nbsp;</SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">유용원의 군사세계<SPAN> (</SPAN></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: #333333"><A href="http://bemil.chosun.com/"><SPAN style="COLOR: purple"><U>http://bemil.chosun.com/</U></SPAN></A></SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">)</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">&nbsp;</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; COLOR: black">비겐님의 블로그<SPAN> (<A href="http://kr.blog.yahoo.com/shinecommerce/3817.html?p=1&amp;t=3"><SPAN style="COLOR: blue"><U>http://kr.blog.yahoo.com/shinecommerce/3817.html?p=1&amp;t=3</U></SPAN></A>)</SPAN></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; COLOR: black">&nbsp;</SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; COLOR: black">위키 대백과 사전<SPAN> (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/M4_Sherman )</SPAN></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'; COLOR: black">&nbsp;</SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 10pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 10pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>http:://necrosant.oranc.co.kr/zb5/?article_srl=2070 </FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 10pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">(</SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">각종 무기에 대해 소상히 잘 정리되어 있는 블로그<SPAN>)</SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 10pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 11pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 11pt"><A href="http://afvdb.50megs.com/usa/m4sherman.html"><U><FONT color=#800080>http://afvdb.50megs.com/usa/m4sherman.html</FONT></U></A></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 11pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 11pt">&nbsp;</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 11pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 11pt"><A href="http://web.inter.nl.net/users/spoelstra/g104/"><U><FONT color=#800080>http://web.inter.nl.net/users/spoelstra/g104/</FONT></U></A></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 11pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 11pt">&nbsp;</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 11pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 11pt"><A href="http://imperialclub.com/Yr/1945/46Tanks/Page048.htm"><FONT color=#800080><U>http://imperialclub.com/Yr/1945/46Tanks/Page048.htm</U></FONT></A></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 11pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 11pt"><A href="http://mailer.fsu.edu/~akirk/tanks/UnitedStates/mediumtanks/M4/M4.html"><FONT color=#800080><U>http://mailer.fsu.edu/~akirk/tanks/UnitedStates/mediumtanks/M4/M4.html</U></FONT></A></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 11pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 11pt"><A href="http://mailer.fsu.edu/~akirk/tanks/UnitedStates/lighttanks/LightTanks.html"><U><FONT color=#800080>http://mailer.fsu.edu/~akirk/tanks/UnitedStates/lighttanks/LightTanks.html</FONT></U></A></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 11pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 11pt">&nbsp;</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 10pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 'Arial','sans-serif'"><A href="http://www.strijdbewijs.nl/tanks/sherman/eng.htm"><U><FONT color=#800080>www.strijdbewijs.nl/tanks/sherman/eng.htm</FONT></U></A></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 11pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 11pt">&nbsp;</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 11pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 11pt">참고서적<SPAN> </SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 12pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt">&nbsp;</SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 20pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 2.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">세계의 전차<SPAN> (</SPAN>주식회사 군사정보<SPAN> 2000.9.1)</SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 20pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 2.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">98 </SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">전차연감<SPAN> (</SPAN>주식회사 군사정보<SPAN> 1998.5.1)</SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 20pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 2.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">취미가<SPAN> (18</SPAN>호<SPAN>~ 27</SPAN>호 특집<SPAN> MORE SHERMAN </SPAN>편<SPAN>)</SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 20pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 2.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">Future Weapon (</SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">군사연구 황재연 정경찬 저자<SPAN> 2008.5.25) </SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 20pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 2.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">&nbsp;</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 10pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">ㅇ 한상철<SPAN>, </SPAN>한기상<SPAN>, CD </SPAN>롬<SPAN> : </SPAN>세계 각국 전차 소개<SPAN>, </SPAN>현대정공 기술연구소<SPAN>, 1999</SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 10pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 1.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black">ㅇ 유승식<SPAN>, 21</SPAN>세기의 주력병기<SPAN>, (</SPAN>주<SPAN>)</SPAN>군사정보<SPAN>, 1998, pp206~207</SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-INDENT: 30.05pt; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; mso-char-indent-count: 3.0"><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black"><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;</SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><FONT color=#000000><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">NGC.</SPAN><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'">다큐먼터리 진화하는 전투병기<SPAN>-TANK </SPAN>편<SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></FONT></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>디스커버리 채널 다큐먼터리 세계의<SPAN> TOP 10 </SPAN>최고의 전차편 <SPAN></SPAN></FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;</FONT></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: left; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; TEXT-AUTOSPACE: ideograph-numeric; WORD-BREAK: keep-all; mso-pagination: widow-orphan" align=left><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt">* Wrighten By Mirageknight (2014.7.6<SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;</SPAN>ver 1.0A) *</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: left; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; TEXT-AUTOSPACE: ideograph-numeric; WORD-BREAK: keep-all; mso-pagination: widow-orphan" align=left><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: #333333; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt">&nbsp;</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: left; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; TEXT-AUTOSPACE: ideograph-numeric; WORD-BREAK: keep-all; mso-pagination: widow-orphan" align=left><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt">(</SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt">본 게시물의 권리는 미라지콤프<SPAN>(www.</SPAN>미라지콤프<SPAN>.com) </SPAN>에 있습니다<SPAN>.)</SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: left; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; TEXT-AUTOSPACE: ideograph-numeric; WORD-BREAK: keep-all; mso-pagination: widow-orphan" align=left><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt">&nbsp;</SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: left; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; TEXT-AUTOSPACE: ideograph-numeric; WORD-BREAK: keep-all; mso-pagination: widow-orphan" align=left><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt">본 게시물의 상업적 이용과 무단게재를 엄격히 금합니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>게재를 원할시는<SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: left; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; TEXT-AUTOSPACE: ideograph-numeric; WORD-BREAK: keep-all; mso-pagination: widow-orphan" align=left><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt">king75@hanafos.com </SPAN></B><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt">으로 메일 주시길 바랍니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>단 개인적 사용하시는건 마음껏 퍼가셔<SPAN></SPAN></SPAN></B></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: left; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt; TEXT-AUTOSPACE: ideograph-numeric; WORD-BREAK: keep-all; mso-pagination: widow-orphan" align=left><B style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt">도 됩니다<SPAN>. </SPAN>다만 출처는 꼭 밝혀주시길… 글 내용에 문제가 있거나 틀린부분은 지적해주시면 감사하겠습니다</SPAN></B><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: #333333; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt"></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: left; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; TEXT-AUTOSPACE: ideograph-numeric; WORD-BREAK: keep-all; mso-para-margin-left: 3.8gd; mso-pagination: widow-orphan" align=left><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림체; COLOR: black; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt"><SPAN style="mso-spacerun: yes">&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp;&nbsp; </SPAN></SPAN></P>
<P style="TEXT-ALIGN: left; MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt 38pt; TEXT-AUTOSPACE: ideograph-numeric; WORD-BREAK: keep-all; mso-pagination: widow-orphan" align=left><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: 굴림; COLOR: #333333; FONT-SIZE: 12pt; mso-bidi-font-family: 굴림; mso-font-kerning: 0pt">&nbsp;</SPAN></P>
<P style="MARGIN: 0cm 0cm 0pt"><SPAN style="FONT-FAMILY: '새굴림','serif'"><FONT color=#000000>&nbsp;<span id="PIE_MjYyNzA2MA.."></span>
<div class="unsupported component-pie"><p>파이 서비스가 종료되어<br>더이상 콘텐츠를 노출 할 수 없습니다.</p><a href="https://cafe.daum.net/supporters/MbmU/123" target="_blank" rel="noopener">자세히보기</a></div></FONT></SPAN></P>
<!-- -->
카페 게시글
Ⅱ 정보 & 자료실
[개발사]
M4 Sherman TANK PT5 (셔먼전차의 분류 #4) END -
다음검색


첫댓글 자료 내용도 훌륭하지만 미라지님 성의에 경의를 표합니다.
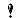
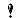
감사합니다 !!
셔먼 논문이네요.. 정말 정말 늦은시간까지 작성하신 노고와 노력에 저 또한 경의를 표합니다.
정말 한편의 논문을 쓰셨습니다.^^ 곧 미라지대학 총장님께서 학위를 수여하실 듯 합니다. 셔먼 특집~! 잘 보았습니다.
고생하셧네요. 차분하게 읽어봐야겠습니다.ㅎㅎ