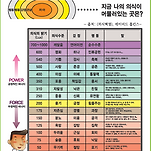
<p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"> beyond reason</span><br></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;">고농도 비타민 E 요법이 알츠하이머 치매에 연구되고 있음</span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;">권장량 400IU</span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;">고농도 비타민 E는 2000 IU</span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"></span><br></p><p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://t1.daumcdn.net/cfile/cafe/990E54445E12FE8805" class="txc-image" hspace="1" vspace="1" border="0" actualwidth="713" width="713" exif="{}" data-filename="스크린샷 2020-01-06 오후 6.26.21.png" style="clear:none;float:none;" id="A_990E54445E12FE88053F33"/></p><p><span style="font-size: 15px; line-height: 23px;"><br></span></p><p><span style="font-size: 11pt;"><br></span></p><div class="fm-sec half_rhythm no_top_margin" style="margin: 0px 0px 0.6923em; font-size: 0.8425em; line-height: 1.6363em; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0);"><div class="fm-citation half_rhythm no_top_margin clearfix" style="margin: 0px 0px 0.6923em; zoom: 1;"><div class="inline_block eight_col va_top" style="max-width: 100%; vertical-align: top; display: inline-block; zoom: 1; width: 452.3125px;"><div><span class="cit"><span role="menubar"><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" role="menuitem" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Clin Interv Aging</a></span>. 2019; 14: 1303&#8211;1317.&nbsp;</span></div><div><span class="fm-vol-iss-date">Published online 2019 Jul 18.&nbsp;</span><span class="doi" style="white-space: nowrap;">doi:&nbsp;<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.2147%2FCIA.S186760" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CFront%20Matter&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">10.2147/CIA.S186760</a></span></div></div><div class="inline_block four_col va_top show-overflow align_right" style="max-width: 100%; vertical-align: top; text-align: right; display: inline-block; zoom: 1; width: 222.703125px;"><div class="fm-citation-ids"><div class="fm-citation-pmcid"><span class="fm-citation-ids-label">PMCID:&nbsp;</span>PMC6645610</div><div class="fm-citation-pmid">PMID:&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31409980" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">31409980</a></div></div></div></div><h1 class="content-title" style="font-size: 1.5384em; margin: 1em 0px 0.5em; line-height: 1.35em; font-weight: normal;">Vitamin E and Alzheimer’s disease: what do we know so far?</h1><div class="half_rhythm" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;"><div class="contrib-group fm-author"><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Browne%20D%5BAuthor%5D&amp;cauthor=true&amp;cauthor_uid=31409980" class="affpopup" co-rid="_co_idm140477999779616" co-class="co-affbox" style="white-space: nowrap; color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Declan Browne</a>,<span style="font-size: 0.8461em; line-height: 1.6363em; position: relative; vertical-align: baseline; top: -0.5em;">1</span>&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=McGuinness%20B%5BAuthor%5D&amp;cauthor=true&amp;cauthor_uid=31409980" class="affpopup" co-rid="_co_idm140477927747056" co-class="co-affbox" style="white-space: nowrap; color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Bernadette McGuinness</a>,<span style="font-size: 0.8461em; line-height: 1.6363em; position: relative; vertical-align: baseline; top: -0.5em;">1</span>&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Woodside%20JV%5BAuthor%5D&amp;cauthor=true&amp;cauthor_uid=31409980" class="affpopup" co-rid="_co_idm140477929238272" co-class="co-affbox" style="white-space: nowrap; color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Jayne V Woodside</a>,<span style="font-size: 0.8461em; line-height: 1.6363em; position: relative; vertical-align: baseline; top: -0.5em;">1</span>&nbsp;and&nbsp;&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=McKay%20GJ%5BAuthor%5D&amp;cauthor=true&amp;cauthor_uid=31409980" class="affpopup" co-rid="_co_idm140477929236064" co-class="co-affbox" style="white-space: nowrap; color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Gareth J McKay</a><span style="font-size: 0.8461em; line-height: 1.6363em; position: relative; vertical-align: baseline; top: -0.5em;"></span><span style="font-size: 0.8461em; line-height: 1.6363em; position: relative; vertical-align: baseline; top: -0.5em;">1</span></div></div><div class="fm-panel half_rhythm" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;"><div class="togglers"><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" class="pmctoggle" rid="idm140477931044976_ai" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Author information</a>&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" class="pmctoggle" rid="idm140477931044976_an" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Article notes</a>&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" class="pmctoggle" rid="idm140477931044976_cpl" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Copyright and License information</a>&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/about/disclaimer/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Disclaimer</a></div></div><div id="pmclinksbox" class="links-box whole_rhythm" style="border: 1px solid rgb(234, 195, 175); background-color: rgb(255, 244, 206); padding: 0.3923em 0.6923em; margin: 1.3846em 0px; border-top-left-radius: 5px; border-top-right-radius: 5px; border-bottom-right-radius: 5px; border-bottom-left-radius: 5px;"><div class="fm-panel">This article has been&nbsp;<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/citedby/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">cited by</a>&nbsp;other articles in PMC.</div></div></div><div class="sec" style="clear: both; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"></div><div id="idm140477965355232" lang="en" class="tsec sec" style="clear: both; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><span role="menubar"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="menuitem" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></span></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="idm140477965355232title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Abstract</h2><div><p id="__p1" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;"><b><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">Vitamin E has been proposed as a potential clinical intervention for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) given the plausibility of its various biological functions in influencing the neurodegenerative processes associated with the condition.</span></b> <b><span style="color: rgb(9, 0, 255);">The tocopherol and tocotrienol isoforms of vitamin E have multiple properties including potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory characteristics, in addition to influences on immune function, cellular signalling and lowering cholestero</span></b>l.&nbsp;</p><p id="__p1" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;"><br></p><p id="__p1" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;"><b><span style="color: rgb(255, 0, 0);">Several of these roles offer a theoretical rationale for providing benefit for the treatment of AD-associated pathology.</span></b> Diminished circulating concentrations of vitamin E have been demonstrated in individuals with AD. Reduced plasma levels have furthermore been associated with an increased risk of AD development while intake, particularly from dietary sources, may limit or reduce the rate of disease progression. This benefit may be linked to synergistic actions between vitamin E isoforms and other micronutrients. Nevertheless, randomised trials have found limited and inconsistent evidence of vitamin E supplementation as an effective clinical intervention.&nbsp;</p><p id="__p1" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;"><br></p><p id="__p1" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Thus, <b><span style="color: rgb(9, 0, 255);">despite a strong rationale in support of a beneficial role for vitamin E for the treatment of AD, the evidence remains inconclusive.</span></b> Several factors may partly explain this discrepancy and represent the difficulties of translating complex laboratory evidence and dietary interactions into clinical interventions. Methodological design limitations of existing randomised trials and restrictions to supplementation with a single vitamin E isoform may also limit the influence of effect.&nbsp;</p><p id="__p1" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;"><br></p><p id="__p1" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Moreover, several factors influence individual responsiveness to vitamin E intake and recent findings suggest variation in the underlying genetic architecture attenuates vitamin E biological availability and activity which likely contributes to the variation in clinical responsiveness and the failure of randomised trials to date. Importantly, the clinical safety of vitamin E remains controversial and warrants further investigation.</p></div><div class="sec" style="clear: both;"><strong class="kwd-title">Keywords:&nbsp;</strong><span class="kwd-text">vitamin E, Alzheimer’s disease, tocopherols, tocotrienols, antioxidants</span></div></div><div id="S0001" class="tsec sec" style="clear: both; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="S0001title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Introduction</h2><p id="__p2" class="p p-first" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that accounts for up to 80% of dementia cases.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0001" rid="CIT0001" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241745" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">1</a>&nbsp;It is clinically characterised by the insidious onset of episodic memory impairment that evolves over time and is associated with subsequent decline in other cognitive domains that diminish functional ability.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0002" rid="CIT0002" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706963" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">2</a>&nbsp;Its histopathological hallmarks include neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), amyloid plaques and loss of neuronal synapses in the brain.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0003" rid="CIT0003" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706905" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">3</a>&nbsp;AD represents a major global disease burden with an estimated 50 million people currently living with dementia, a figure expected to increase threefold by 2050 with associated global economic costs expected to double to US$2 trillion by 2030.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0004" rid="CIT0004" class=" bibr popnode" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">4</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0005" rid="CIT0005" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706917" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">5</a>&nbsp;As such, prevention and treatment interventions for AD are paramount, given an estimated 9.2 million deaths could be prevented by 2050 if AD onset was delayed by one year.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0006" rid="CIT0006" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707038" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">6</a></p><p id="__p3" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">It is widely accepted that AD pathology begins decades before the appearance of clinical manifestations; changes may be present up to 30&nbsp;years before the onset of symptoms.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0007" rid="CIT0007" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707041" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">7</a>&nbsp;Advances in neuro-imaging modalities and the ongoing development of biomarkers from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) offer some aid to predicting the development of AD in those with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) when combined with validated clinical tests.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0008" rid="CIT0008" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707019" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">8</a></p><p id="__p4" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">However, existing therapeutic options are largely limited to delayed disease progression and ease of symptom burden, albeit without modification of disease-course.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0009" rid="CIT0009" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706967" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">9</a>&nbsp;This has resulted in greater focus on the development of alternative interventions to delay or prevent onset that have included dietary and antioxidant measures.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0010" rid="CIT0010" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241724" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">10</a>&nbsp;Vitamin E has been studied extensively, primarily due to its potent antioxidant properties and the biological plausibility of its potential role in combatting the pathological processes of AD. However, its use as an effective clinical intervention remains controversial.</p><p id="__p5" class="p p-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">This review will assess the current evidence for the role of vitamin E as a treatment option in the context of AD. A literature search of Medline, a major article database, was conducted using the keywords “Alzheimer Disease” AND “Vitamin E” OR “tocopherols” OR “tocotrienols”. The keywords were searched in all possible combinations. Original journal articles that were written in English and published prior to 1st March 2019 were retrieved. All studies incorporating cell, animal and human evidence were included in addition to review articles to achieve a comprehensive search of the topic and to retrieve the maximum number of articles possible. A total of 341 articles were retrieved.</p></div><div id="S0002" class="tsec sec" style="clear: both; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="S0002title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Pathogenesis of AD</h2><p id="__p6" class="p p-first" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Several theories have proposed the onset and progression of AD as a corollary of the uncertainty of the pathogenic mechanisms that lead to disease and the likely overlapping contributions they make to the phenotype observed. Since the characteristic “plaques” and “tangles” of AD were first reported by Alois Alzheimer in 1907, the role of amyloid and tau protein deposits have remained central to AD pathogenesis.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0011" rid="CIT0011" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707045" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">11</a>&nbsp;The amyloid cascade hypothesis postulates that excessive accumulation of senile plaques, composed of amyloid-beta (Aβ) protein, directly induces the clinical manifestations of AD through neurodegeneration mediated by inflammation, immunological mechanisms and the effects of free radical species.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0012" rid="CIT0012" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706992" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">12</a>&nbsp;Aβ is a beta-sheet protein derived from the amyloid beta precursor protein (AβPP) molecule through the activity of β and γ-secretase.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0013" rid="CIT0013" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706968" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">13</a>&nbsp;Importantly, expression&#8206; of the ApoE4 allele reduces elimination of Aβ and is associated with increased AD risk.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0014" rid="CIT0014" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241748" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">14</a></p><p id="__p7" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Similarly, the accumulation of intra-cellular NFTs have been implicated in AD pathology.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0015" rid="CIT0015" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706948" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">15</a>&nbsp;NFTs consist of hyper-phosphorylated tau-protein, an important component of the neuronal cytoskeleton. Significantly, an increased quantity of NFTs is inversely associated with cognitive impairment and is more closely correlated with dementia severity than Aβ plaques.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0016" rid="CIT0016" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706995" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">16</a>&nbsp;Furthermore, hypercholesterolaemia has been associated with AD pathology through its association with the amyloid pathway, although its precise role remains uncertain.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0017" rid="CIT0017" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706974" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">17</a>&nbsp;Laboratory studies have shown higher cholesterol levels are associated with increased proteolysis of AβPP and Aβ production through secretase enzyme activity.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0018" rid="CIT0018" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707011" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">18</a>&nbsp;Dysfunctional cholesterol metabolism has also been associated with its accumulation in the brains of AD patients.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0019" rid="CIT0019" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707012" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">19</a>&nbsp;However, the clinical application of this remains controversial as evidence from randomised trials indicates that cholesterol-reducing statins have no effect on validated measures of cognition.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0020" rid="CIT0020" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241741" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">20</a>&nbsp;Despite the obvious implications of the amyloid cascade theory, several concerns have questioned the assumption of direct causality, including the failure of therapeutic interventions targeting the amyloid pathway to provide clinical benefit<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0021" rid="CIT0021" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706911" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">21</a>&nbsp;and an extensive body of evidence suggests the pathological processes of AD are complex and multifactorial.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0022" rid="CIT0022" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707034" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">22</a></p><p id="__p8" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">The mitochondrial cascade hypothesis of AD pathogenesis postulated that genetic variation influences the impact of age-related mitochondrial changes which upon reaching a threshold value initiate a pathological cascade, including the amyloid pathway.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0023" rid="CIT0023" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706941" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">23</a>&nbsp;In addition, critical mitochondrial dysfunction may precipitate other cellular and molecular changes associated with AD including synaptic degeneration, production of free radical species and neuro-inflammation.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0024" rid="CIT0024" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707047" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">24</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0025" rid="CIT0025" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706949" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">25</a>&nbsp;The processes of neuro-inflammation have been reported as an early event in AD, perhaps occurring before the appearance of Aβ deposits.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0026" rid="CIT0026" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_799469116" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">26</a>&nbsp;In vitro studies have demonstrated elevation of multiple interleukins (ILs), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CFS) in AD murine models early in the disease process.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0027" rid="CIT0027" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706932" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">27</a>&nbsp;Additionally, elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines have been detected in the brain and CSF of AD patients.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0027" rid="CIT0027" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707010" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">27</a></p><p id="__p9" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">While it is likely each of these mechanisms contribute to AD pathogenesis, oxidative stress (OS) represents a common underlying theme. The role of OS in disease is characterised by the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) through the metabolism of oxygen within the mitochondria that manifests as structural and functional alterations in various biomolecules.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0028" rid="CIT0028" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241731" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">28</a>&nbsp;Multiple indicators of OS are significantly elevated in AD with detectable oxidative effects on lipids, proteins, nucleic acids and sugars.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0029" rid="CIT0029" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706916" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">29</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0030" rid="CIT0030" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241749" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">30</a>Importantly, cerebral glucose metabolism is reduced early in the AD process and may be accompanied by metabolic dysregulation and increased production of ROS.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0031" rid="CIT0031" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706981" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">31</a></p><p id="__p10" class="p p-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Several factors render the brain particularly vulnerable to the effects of ROS including its high oxygen demand and consumption, the proportion of polyunsaturated fats in neural tissues and the relative scarcity of endogenous antioxidants to address this high metabolic demand.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0032" rid="CIT0032" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241734" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">32</a>&nbsp;Interestingly, AD-associated mitochondrial defects beyond the central nervous system represent characteristic features of a systemic disease.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0033" rid="CIT0033" class=" bibr popnode" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">33</a>&nbsp;This is supported by factors such as diabetes mellitus, obesity and physical inactivity as potential risk factors for AD development.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0034" rid="CIT0034" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707032" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">34</a>&nbsp;In addition, strong associations have been reported between vascular risk factors and AD development, with Aβ protein deposition found within vessels early in the disease course.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0035" rid="CIT0035" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707049" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">35</a>&nbsp;As such, there is a strong rationale in support of systemic antioxidant therapy as a preventative or therapeutic intervention for AD with particular support for vitamin E in accordance with its biological activities.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0036" rid="CIT0036" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706957" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">36</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0037" rid="CIT0037" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706965" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">37</a></p></div><div id="S0003" class="tsec sec" style="clear: both; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="S0003title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Basis of vitamin E as a clinical intervention in AD</h2><div id="S0003-S2001" class="sec sec-first" style="clear: both;"><h3 id="S0003-S2001title" style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Biological properties of vitamin E</h3><p id="__p11" class="p p-first" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Vitamin E is a collective term that describes a family of eight naturally-occurring homologues with potent antioxidant properties. The group is composed of four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, each of which has an α, β, γ and δ isoform. All eight congeners are differentially distributed within food sources such as vegetable oils, grains and various nuts and seeds<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0038" rid="CIT0038" class=" bibr popnode" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">38</a>&nbsp;and α-tocopherol is the primary isoform normally found within vitamin E supplements.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0039" rid="CIT0039" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241742" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">39</a>&nbsp;The recommended dietary allowance for α-tocopherol is currently 15&nbsp;mg/day in adults with a recommended upper intake level of 1000&nbsp;mg/day for supplemental vitamin E as the highest dose unlikely to result in haemorrhage - however, high-doses (&gt;1000&nbsp;mg/day) have been used in a number of studies of vitamin E supplementation to date.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0032" rid="CIT0032" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241735" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">32</a></p><p id="__p12" class="p p-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Plasma levels of vitamin E are dependent upon the absorption, distribution and excretion rates of each isoform. All eight homologues have lipophilic properties and are absorbed from the intestine following ingestion in micelles formed by pancreatobiliary secretions.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0032" rid="CIT0032" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241723" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">32</a>&nbsp;The plasma half-life of α-tocopherol is estimated at 20&nbsp;hrs, which is considerably longer than that of other isoforms, particularly the tocotrienol congeners.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0040" rid="CIT0040" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707064" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">40</a>&nbsp;This is significant in that α-tocopherol is therefore the predominant isoform found in tissues whereas the other congeners are metabolised and more quickly removed.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0041" rid="CIT0041" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706929" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">41</a>&nbsp;Additionally, important interactions have been previously reported between various isoforms including antagonistic interactions between plasma α and γ-tocopherol.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0042" rid="CIT0042" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706939" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">42</a></p></div><div id="S0003-S2002" class="sec" style="clear: both;"><h3 id="S0003-S2002title" style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Biological functions of vitamin E</h3><p id="__p13" class="p p-first" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Vitamin E has a broad range of biological functions that vary according to the relevant isoform. The tocopherol and tocotrienol sub-groups possess varying properties and functions linked with the level of chemical saturation in their molecular structures with tocopherols having phytyl side-chains, while tocotrienols possess three carbon-carbon double bonds.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0032" rid="CIT0032" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241729" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">32</a>&nbsp;However, as a collective group, the potent antioxidant capabilities of vitamin E are well known and each of the eight tocopherol and tocotrienol congeners are considered free-radical scavengers.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0043" rid="CIT0043" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706962" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">43</a>&nbsp;The antioxidant capacity results from the presence of a hydroxyl group on the aromatic ring of tochocromanols that quenches free radicals through hydrogen atom donation.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0044" rid="CIT0044" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707040" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">44</a></p><p id="__p14" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">The various vitamin E isoforms enact a key role in the protection of cell membranes, rich in highly unsaturated fatty acids, from oxidative damage.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0045" rid="CIT0045" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706914" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">45</a>&nbsp;Several studies have shown that different isoforms are differentially located within the cell membrane and that this may influence their biological activity in the lipid membrane.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0046" rid="CIT0046" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706909" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">46</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0047" rid="CIT0047" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707002" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">47</a>&nbsp;In vivo studies have reported that the antioxidant activity of α-tocopherol is superior to other tocopherol congeners, followed in potency by the β, γ and δ isoforms, respectively.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0048" rid="CIT0048" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706976" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">48</a>&nbsp;While the effectiveness of α-tocopherol has also been reported through in vitro evidence, it has been suggested that its relative laboratory efficacy may be dependent upon experimental conditions.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0049" rid="CIT0049" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707043" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">49</a>&nbsp;Tocotrienols may exhibit more potent antioxidant activities than tocopherols due to their shorter side-chains enabling easier incorporation into the cell membrane and the presence of their unsaturated side-chain.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0050" rid="CIT0050" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706945" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">50</a>&nbsp;However, it has been suggested that α-tocopherol retains a superior in vivo role in neuroprotection due to its relatively greater bioavailability and preferential retention by tissues.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0051" rid="CIT0051" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707052" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">51</a>&nbsp;Similar to tocopherols, the δ-tocotrienol isoform demonstrates reduced antioxidant potency compared to the other tocotrienol congeners.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0048" rid="CIT0048" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706997" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">48</a></p><p id="__p15" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Importantly, the scope of vitamin E activity extends beyond its antioxidant capabilities and includes other neuro-protective, anti-inflammatory and cholesterol-reducing properties, in addition to influencing gene expression&#8206; and potentially ensuing AD pathology.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0050" rid="CIT0050" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706998" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">50</a></p><p id="__p16" class="p p-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Several studies have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin E supplementation on various markers of inflammatory stress, cellular signalling and immune function in humans and its influence on AD-associated pathology.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0052" rid="CIT0052" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707020" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">52</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0053" rid="CIT0053" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706990" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">53</a>&nbsp;Additionally, studies in murine AD models have identified associations between vitamin E deficiency and increased expression&#8206; of genes associated with AD progression including those involved in the regulation of apoptosis, neuro-transmission and Aβ metabolism.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0054" rid="CIT0054" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706938" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">54</a>&nbsp;Similarly, vitamin E has been shown to confer a protective effect against hyper-phosphorylated tau protein.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0055" rid="CIT0055" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706934" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">55</a>&nbsp;The enzyme-inhibiting activity of various tocopherol and tocotrienol isoforms also incorporates several AD-associated enzymes, including cyclo-oxygenases (COX), which contribute to neuro-inflammation and OS.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0056" rid="CIT0056" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706919" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">56</a>&nbsp;The activity of both sub-groups have also been associated with reduced Aβ production through inhibiting secretase enzyme activity.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0039" rid="CIT0039" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241747" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">39</a></p></div><div id="S0003-S2003" class="sec sec-last" style="clear: both;"><h3 id="S0003-S2003title" style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Comparison of tocopherol and tocotrienol isomers</h3><p id="__p17" class="p p-first" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Tocopherols are a necessary constituent of physiological neuronal activity with high levels of the vitamin E transfer protein (α-tocopherol transfer protein, α-TPP) found in the cerebellum.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0057" rid="CIT0057" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706918" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">57</a>&nbsp;Its importance is emphasised by a loss-of-function mutation within the α-TPP gene that results in a rare condition known as ataxia with vitamin E deficiency (AVED)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0058" rid="CIT0058" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241743" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">58</a>&nbsp;and several studies have also reported potential benefits of α-tocopherol in other neurodegenerative disorders: for example, increasing duration (years) of vitamin E supplement use has been inversely correlated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) rates while a meta-analysis found a protective influence from moderate-high intake of vitamin E in participants with regards to their risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0059" rid="CIT0059" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706977" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">59</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0060" rid="CIT0060" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706944" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">60</a></p><p id="__p18" class="p p-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">In contrast, research on tocotrienols has been limited, although not all are believed to be essential for normal physiological function and there is no evidence to date for any genetic mutations that alter tocotrienol metabolism and result in clinically significant sequelae.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0061" rid="CIT0061" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241740" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">61</a>&nbsp;However, tocotrienols are an important vitamin E sub-group with biological functions that differ from tocopherols, with stronger antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects according to some measures.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0017" rid="CIT0017" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706985" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">17</a>&nbsp;Tocotrienols influence the meval&#8206;onate pathway by suppressing hydroxyl-methyl-glutaryl co-enzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase resulting in cholesterol-lowering and anti-inflammatory properties that influence AD pathology.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0062" rid="CIT0062" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707062" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">62</a>&nbsp;These findings have been reported for several tocotrienol isoforms including the δ congener which suppresses the action of HMG-CoA reductase at the transcriptional level.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0063" rid="CIT0063" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707017" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">63</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0064" rid="CIT0064" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707023" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">64</a>&nbsp;However, combined supplementation with α-tocopherol has been shown to attenuate these inhibitory effects with a dose-dependent relationship in hamster models.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0065" rid="CIT0065" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241732" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">65</a>&nbsp;This study furthermore found that α-tocopherol supplementation alone may act as a stimulant to HMG-CoA activity and therefore demonstrate hypercholesterolaemic activity.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0065" rid="CIT0065" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241726" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">65</a>&nbsp;Such interactions highlight the importance of a thorough understanding of the interactions between isoforms and the appropriate selection of congeners in interventional studies.</p></div></div><div id="S0004" class="tsec sec" style="clear: both; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="S0004title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">AD and vitamin E: human studies</h2><div id="S0004-S2001" class="sec sec-first" style="clear: both;"><h3 id="S0004-S2001title" style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Plasma, serum and CSF concentrations of vitamin E in AD</h3><p id="__p19" class="p p-first" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">A large number of case-control studies have previously eval&#8206;uated vitamin E levels in the plasma, serum and CSF of patients with AD (<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/table/T0001/" target="table" class="fig-table-link figpopup" rid-figpopup="T0001" rid-ob="ob-T0001" co-legend-rid="" style="display: inline-block !important; zoom: 1 !important; cursor: pointer; color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Table 1</a>). An early study reported reduced vitamin E levels in a small number of AD patients compared with cognitively intact controls.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0083" rid="CIT0083" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707058" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">83</a>&nbsp;Many studies have since replicated these findings and have been summarised in a 2014 meta-analysis.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0084" rid="CIT0084" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707000" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">84</a>&nbsp;This study reviewed the plasma status of several micro-nutrients in AD and reported diminished vitamin E levels in AD patients compared with cognitively intact controls and concluded this was not as a consequence of patient malnourishment.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0084" rid="CIT0084" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706993" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">84</a>Similar findings were reported in the sensitivity analysis of a 2017 case-control study that found no correlation between AD severity and plasma vitamin E levels, suggesting diminished plasma antioxidant status may result from early disease pathology rather than as a consequence of reduced vitamin E intake.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0077" rid="CIT0077" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241738" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">77</a></p><div class="table-wrap table anchored whole_rhythm" id="T0001" style="clear: both; margin: 1.3846em 0px; background-color: rgb(255, 252, 240); border: 1px solid rgb(234, 195, 175); border-top-left-radius: 5px; border-top-right-radius: 5px; border-bottom-right-radius: 5px; border-bottom-left-radius: 5px; padding: 1.3846em;"><h3 style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Table 1</h3><div class="caption"><p id="__p20" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Cross-sectional studies investigating vitamin E levels in AD patients</p></div><div data-largeobj="" data-largeobj-link-rid="largeobj_idm140477933324112" class="xtable" style="clear: both; max-height: 80vh; overflow: auto;"><table frame="hsides" rules="groups" class="rendered small default_table" style="clear: both; border-collapse: collapse; border-spacing: 0px; margin: 1.3846em 0px; font-size: 0.8461em; line-height: 1.6363em; border-top-width: 1px; border-top-style: solid; border-top-color: rgb(0, 0, 0); border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(0, 0, 0);"><thead style="border: none;"><tr><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Study (Publication year)</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Isoform(s)</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Population cases</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Results</th></tr></thead><tbody style="border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(136, 136, 136); border-top-width: 1px; border-top-style: solid; border-top-color: rgb(136, 136, 136);"><tr><td colspan="4" rowspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;"><strong><em>Significant associations:</em></strong></td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Zaman et al (1992)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0066" rid="CIT0066" class=" bibr popnode" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">66</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Unspecified</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">10 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower serum vitamin E levels compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Jimenez-Jimenez et al (1997)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0067" rid="CIT0067" class=" bibr popnode" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">67</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">44 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower vitamin E levels in both serum and CSF compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Sinclair et al (1998)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0068" rid="CIT0068" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707022" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">68</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">25 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower plasma vitamin E levels compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Foy et al (1999)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0069" rid="CIT0069" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241728" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">69</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">79 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower plasma vitamin E levels compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Bourdel-Marchasson et al (2001)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0070" rid="CIT0070" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706904" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">70</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">20 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower plasma vitamin E levels compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Polidori et al (2002)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0071" rid="CIT0071" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706902" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">71</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">35 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower plasma vitamin E levels and increased lipid peroxidation compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Mecocci et al (2002)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0072" rid="CIT0072" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707029" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">72</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">40 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower plasma vitamin E levels and increased oxidative damage markers compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Rinaldi et al (2003)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0073" rid="CIT0073" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707042" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">73</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">63 AD, 25 MCI</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower plasma vitamin E levels compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Baldeiras et al (2008)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0074" rid="CIT0074" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707061" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">74</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">42 AD, 85 MCI</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower plasma vitamin E levels and increased oxidative damage markers in both AD and MCI compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Mangialasche et al (2012)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0075" rid="CIT0075" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241730" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">75</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-, β-, γ-, δ-tocopherols &amp; α-, β-, γ-, δ-tocotrienols</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">168 AD, 166 MCI</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower plasma vitamin E levels across all isoforms in AD and MCI cases compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Giavarotti et al (2013)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0076" rid="CIT0076" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706935" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">76</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">23 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower plasma vitamin E levels and increased oxidative stress markers compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Mullan et al (2017)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0077" rid="CIT0077" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241751" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">77</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α- and γ-tocopherols</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">251 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lower plasma levels of both vitamin E isoforms compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td colspan="4" rowspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;"><strong><em>No significant associations:</em></strong></td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Schippling et al (2000)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0078" rid="CIT0078" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706950" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">78</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">29 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">No significant differences between vitamin E levels in plasma and CSF compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Ryglewicz et al (2002)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0079" rid="CIT0079" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707008" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">79</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">26 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Patients with vascular dementia had significantly lower plasma vitamin E levels than AD patients.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Charlton et al (2004)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0080" rid="CIT0080" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707006" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">80</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">15 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">No significant difference in plasma vitamin E levels compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Mas et al (2006)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0081" rid="CIT0081" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707021" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">81</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">100 AD</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">No significant difference in plasma vitamin E levels compared with controls.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">von Arnim et al (2012)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0082" rid="CIT0082" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706986" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">82</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">74 MCI</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">No significant associations between plasma vitamin E levels and dementia.</td></tr></tbody></table></div><div id="largeobj_idm140477933324112" class="largeobj-link align_right" style="margin-top: 0.692em; text-align: right;"><a target="object" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/table/T0001/?report=objectonly" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Open in a separate window</a></div><div class="tblwrap-foot" style="font-size: 0.8461em; margin: 1.3846em 0px;"><div id="idm140477928010784"><p id="__p21" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;"><strong>Note:&nbsp;</strong>Detection method for all studies was high-performance liquid chromatography.</p></div><div id="idm140477928009808"><p id="__p22" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;"><strong>Abbreviations:</strong>&nbsp;AD, Alzheimer’s disease; MCI, mild cognitive impairment.</p></div></div></div><p id="__p23" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">The most recent meta-analysis conducted by Mullan and colleagues (2018) eval&#8206;uated 51 studies comparing the plasma nutrient status in AD participants compared to cognitively intact controls.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0085" rid="CIT0085" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706954" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">85</a>&nbsp;This study reported that vitamin E was the most extensively studied dietary plasma antioxidant and concluded that vitamin E levels are 11% lower in AD patients compared to cognitively normal subjects<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0085" rid="CIT0085" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707014" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">85</a>&nbsp;corroborating the findings from a previous smaller meta-analysis of 17 studies.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0086" rid="CIT0086" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706988" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">86</a></p><p id="__p24" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">In addition to diminished plasma vitamin E levels in AD, a meta-analysis of 116 studies reported significantly reduced levels in the central nervous system of participants with AD and suggested nutrient status of the brain parallels that of the systemic circulation.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0087" rid="CIT0087" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241722" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">87</a>&nbsp;One cross-sectional study was notable for its measurement of tocotrienol isoforms: 521 subjects were recruited including 168 AD, 166 MCI cases and 187 cognitively intact controls.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0075" rid="CIT0075" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241753" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">75</a>&nbsp;The study reported significantly diminished plasma vitamin E levels for each isoform in those with AD compared to controls and low tocopherol and tocotrienol levels were associated with increased risk of both MCI and AD.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0075" rid="CIT0075" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241727" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">75</a></p><p id="__p25" class="p p-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Despite a substantial body of evidence in support of reduced vitamin E levels in AD, a relatively small number of case-control studies have reported no significant differences in plasma levels compared with cognitively normal controls (<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/table/T0001/" target="table" class="fig-table-link figpopup" rid-figpopup="T0001" rid-ob="ob-T0001" co-legend-rid="" style="display: inline-block !important; zoom: 1 !important; cursor: pointer; color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Table 1</a>). Although these studies were of limited sample size, they were supported by findings from a larger Mendelian randomised study which included data from two genome-wide association studies of vitamin E (n=7,781) and AD cases and controls (17,007 AD cases and 37,154 controls) that found no association between circulating vitamin E levels and AD.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0088" rid="CIT0088" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241750" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">88</a></p></div><div id="S0004-S2002" class="sec" style="clear: both;"><h3 id="S0004-S2002title" style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Prospective studies of vitamin E concentrations and subsequent AD risk</h3><p id="__p26" class="p p-first" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Several prospective cohort studies have also investigated plasma vitamin E levels and the subsequent risk of developing AD (<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/table/T0002/" target="table" class="fig-table-link figpopup" rid-figpopup="T0002" rid-ob="ob-T0002" co-legend-rid="" style="display: inline-block !important; zoom: 1 !important; cursor: pointer; color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Table 2</a>). In 2010, a prospective study assessed plasma levels of all eight vitamin E isoforms in 232 subjects aged at least 80&nbsp;years from the Kungsholmen Project with a six-year follow-up.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0089" rid="CIT0089" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706907" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">89</a>Individuals with total plasma tocopherols, tocotrienols or vitamin E in the highest tertile had a reduced risk of incident AD compared with participants in the lowest tertile. The authors suggested that any neuro-protective effects may result from the combination of vitamin E isoforms rather than specifically to any individual congener.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0089" rid="CIT0089" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706994" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">89</a></p><div class="table-wrap table anchored whole_rhythm" id="T0002" style="clear: both; margin: 1.3846em 0px; background-color: rgb(255, 252, 240); border: 1px solid rgb(234, 195, 175); border-top-left-radius: 5px; border-top-right-radius: 5px; border-bottom-right-radius: 5px; border-bottom-left-radius: 5px; padding: 1.3846em;"><h3 style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Table 2</h3><div class="caption"><p id="__p27" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Studies investigating cross-sectional levels of vitamin E and subsequent risk of AD development</p></div><div data-largeobj="" data-largeobj-link-rid="largeobj_idm140477930721120" class="xtable" style="clear: both; max-height: 80vh; overflow: auto;"><table frame="hsides" rules="groups" class="rendered small default_table" style="clear: both; border-collapse: collapse; border-spacing: 0px; margin: 1.3846em 0px; font-size: 0.8461em; line-height: 1.6363em; border-top-width: 1px; border-top-style: solid; border-top-color: rgb(0, 0, 0); border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(0, 0, 0);"><thead style="border: none;"><tr><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Study (Publication year)</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Isoform(s)</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Study population</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Follow-up</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Results</th></tr></thead><tbody style="border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(136, 136, 136); border-top-width: 1px; border-top-style: solid; border-top-color: rgb(136, 136, 136);"><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Mangialasche et al (2010)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0089" rid="CIT0089" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707036" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">89</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-, β-, γ-, δ-tocopherols &amp; α-, β-, γ-, δ-tocotrienols</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">232 cognitively normal elderly participants</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">6&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Higher total tocopherol, total tocotrienol and total vitamin E plasma levels were associated with a reduced risk of AD development.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Mangialasche et al (2013)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0090" rid="CIT0090" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707053" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">90</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-, β-, γ-, δ-tocopherols &amp; α-, β-, γ-, δ-</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">81 AD, 86 MCI, 86 Control</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">1&nbsp;year</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">AD and MCI participants had lower plasma vitamin E levels. Combination of plasma vitamin E and MRI was superior to MRI alone in predicting conversion of MCI to AD.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Mangialasche et al (2013)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0091" rid="CIT0091" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706915" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">91</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-, β-, γ-, δ-tocopherols &amp; α-, β-, γ-, δ-</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">140 cognitively normal elderly participants</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">8.2&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Elevated serum tocopherols and tocotrienols were associated with reduced risk of cognitive impairment (MCI and AD).</td></tr></tbody></table></div><div class="tblwrap-foot" style="font-size: 0.8461em; margin: 1.3846em 0px;"><div id="idm140477933582928"><p id="__p28" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;"><strong>Abbreviations:</strong>&nbsp;AD, Alzheimer’s disease; MCI, mild cognitive impairment; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.</p></div></div></div><p id="__p29" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Another prospective study eval&#8206;uated vitamin E status and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with regard to MCI conversion to AD.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0090" rid="CIT0090" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706979" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">90</a>&nbsp;Data from 253 participants including 81 AD, 86 MCI cases and 86 cognitively intact controls revealed lower absolute values for all vitamin E isomers in both the AD and MCI subjects compared to controls. The authors suggested the combination of vitamin E measures and MRI scanning was superior to imaging alone in predicting MCI conversion to AD, with 95% sensitivity after one-year follow-up.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0090" rid="CIT0090" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706999" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">90</a></p><p id="__p30" class="p p-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Similar findings were reported from the Cardiovascular Risk Factor, Aging and Dementia (CAIDE) study,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0091" rid="CIT0091" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707007" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">91</a>&nbsp;which analysed data from 140 cognitively intact participants with a follow-up time of 8&nbsp;years. Elevated values of both tocopherol and tocotrienol isoforms were associated with a reduced risk of “cognitive impairment”, defined as the development of either MCI or AD.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0091" rid="CIT0091" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706922" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">91</a></p></div><div id="S0004-S2003" class="sec" style="clear: both;"><h3 id="S0004-S2003title" style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Eval&#8206;uation of vitamin E intake and AD risk</h3><p id="__p31" class="p p-first" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Associations between vitamin E intake through supplementary or dietary sources and the risk of developing AD have also been extensively investigated (<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/table/T0003/" target="table" class="fig-table-link figpopup" rid-figpopup="T0003" rid-ob="ob-T0003" co-legend-rid="" style="display: inline-block !important; zoom: 1 !important; cursor: pointer; color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Table 3</a>). A prospective study investigated vitamin E supplementation and incident AD in a population of 633 individuals with a mean 4.3-year follow-up and reported that none of the 27 subjects taking vitamin E supplements developed AD in contrast to the predicted incidence of 3.9.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0092" rid="CIT0092" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706933" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">92</a>&nbsp;Similarly, the prospective Cache County Study reported that individuals taking vitamin E supplements in addition to multivitamins containing vitamin C had reduced AD risk.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0093" rid="CIT0093" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706984" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">93</a>However, the study found no significant benefit from use of vitamin E supplements alone.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0093" rid="CIT0093" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707009" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">93</a>&nbsp;A more recent study published in 2017 reported that vitamin E supplementation was associated with decreased risk of cognitive decline in a cohort of 560 AD patients from the Canadian Study of Health and Aging although, no significant association was detected between vitamin E intake and AD risk specifically.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0094" rid="CIT0094" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706960" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">94</a></p><div class="table-wrap table anchored whole_rhythm" id="T0003" style="clear: both; margin: 1.3846em 0px; background-color: rgb(255, 252, 240); border: 1px solid rgb(234, 195, 175); border-top-left-radius: 5px; border-top-right-radius: 5px; border-bottom-right-radius: 5px; border-bottom-left-radius: 5px; padding: 1.3846em;"><h3 style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Table 3</h3><div class="caption"><p id="__p32" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Epidemiological studies investigating associations between vitamin E intake and risk of AD</p></div><div data-largeobj="" data-largeobj-link-rid="largeobj_idm140477929802480" class="xtable" style="clear: both; max-height: 80vh; overflow: auto;"><table frame="hsides" rules="groups" class="rendered small default_table" style="clear: both; border-collapse: collapse; border-spacing: 0px; margin: 1.3846em 0px; font-size: 0.8461em; line-height: 1.6363em; border-top-width: 1px; border-top-style: solid; border-top-color: rgb(0, 0, 0); border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(0, 0, 0);"><thead style="border: none;"><tr><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Study (Publication year)</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Vitamin E source</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Study population</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Mean follow-up</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Results</th></tr></thead><tbody style="border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(136, 136, 136); border-top-width: 1px; border-top-style: solid; border-top-color: rgb(136, 136, 136);"><tr><td colspan="5" rowspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;"><strong><em>Significant association:</em></strong></td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Morris et al (1998)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0092" rid="CIT0092" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706924" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">92</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Supplements</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">633 cognitively-intact elderly</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">4.3&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">None of the vitamin E supplement users developed AD (predicted incidence of 3.9).</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Zandi et al (2004)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0093" rid="CIT0093" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706913" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">93</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Supplements</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">4,740 elderly</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">3&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Use of combined vitamin E and vitamin C supplementation was associated with decreased AD incidence.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Basambombo et al (2017)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0094" rid="CIT0094" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706908" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">94</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Supplements</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">5,269</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">5.2&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Use of vitamin E and/or vitamin C supplements was associated with reduced AD risk.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Morris et al (2002)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0095" rid="CIT0095" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707055" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">95</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Dietary</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">815 elderly</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">3.9&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">High vitamin E intake from foods was associated with decreased risk of incident AD in ApoE4 negative persons. Vitamin E supplementation was not significantly associated with AD risk.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Engelhart et al (2002)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0096" rid="CIT0096" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707024" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">96</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Dietary</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">5,395</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">6&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">High dietary vitamin E intake was associated with reduced risk of AD. This effect was greatest in smokers.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Morris et al (2005)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0097" rid="CIT0097" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706956" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">97</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Dietary</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">1,041</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">3.9&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">High dietary vitamin E intake was associated with reduced AD incidence. α- and γ-tocopherol had independently associated with delayed cognitive decline.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Devore et al (2010)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0098" rid="CIT0098" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707039" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">98</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Dietary</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">5,395</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">9.6&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">High dietary intake of vitamin E at baseline was associated with a modest reduction in AD risk over follow-up.</td></tr><tr><td colspan="5" rowspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;"><strong><em>No significant associations:</em></strong></td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Masaki et al (2000)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0099" rid="CIT0099" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707031" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">99</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Supplements</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">3,385 elderly male</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">10&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">No reduction in AD risk was detectable in those taking vitamin E supplements. Supplement use was associated with better cognitive performance at 10-year follow-up.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Luchsinger et al (2003)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0100" rid="CIT0100" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707035" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">100</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Supplements and dietary</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">980 elderly</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">4&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Neither supplemental or dietary vitamin E intake were associated with decreased AD risk.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Gray et al (2008)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0101" rid="CIT0101" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706943" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">101</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Supplements</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">2,969 elderly</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">5.5&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Supplemental vitamin E and/or vitamin was not associated with a reduction in AD risk.</td></tr></tbody></table></div><div id="largeobj_idm140477929802480" class="largeobj-link align_right" style="margin-top: 0.692em; text-align: right;"><a target="object" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/table/T0003/?report=objectonly" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Open in a separate window</a></div><div class="tblwrap-foot" style="font-size: 0.8461em; margin: 1.3846em 0px;"><div id="idm140477927191136"><p id="__p33" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;"><strong>Abbreviations:</strong>&nbsp;AD, Alzheimer’s disease.</p></div></div></div><p id="__p34" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Several prospective studies of vitamin E dietary intake also reported beneficial effects associated with reduced AD risk. One study eval&#8206;uated 815 cognitively normal elderly individuals with a mean follow-up time of 3.9-years and found that increased vitamin E intake from dietary sources was associated with a lower risk of developing AD, although the benefit was limited to those not carrying the ApoE4 risk allele.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0095" rid="CIT0095" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706946" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">95</a>&nbsp;Interestingly, this study suggested that vitamin E supplementation from non-dietary sources was not significantly associated with diminished AD risk.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0095" rid="CIT0095" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706973" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">95</a>&nbsp;Similar findings in a study of 5,395 participants reported that high dietary intake of both vitamin E and vitamin C was associated with a reduced risk of developing AD.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0096" rid="CIT0096" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707005" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">96</a>&nbsp;This effect was greatest among smokers and was independent of the ApoE4 risk allele.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0096" rid="CIT0096" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706996" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">96</a>&nbsp;Furthermore, Morris and colleagues found that subjects with higher dietary intake of vitamin E had a lower incidence of AD and that plasma α- and γ-tocopherol levels were independently associated with AD risk.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0097" rid="CIT0097" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706928" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">97</a>&nbsp;Finally, the prospective population based Rotterdam Study included 365 participants with AD and identified a modest reduction in risk over the longer term in participants from the highest tertile of dietary vitamin E intake compared with those in the lowest tertile, independent of any supplement use and other potential confounders.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0098" rid="CIT0098" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706927" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">98</a></p><p id="__p35" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">However, several studies failed to detect associations between either dietary intake or vitamin E supplementation and AD. The Honolulu-Asia Aging Study analysed data from 3,385 men who reported taking vitamin E and vitamin C supplements at baseline in addition to measuring AD preval&#8206;ence ten-years later.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0099" rid="CIT0099" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706921" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">99</a>&nbsp;Although the study identified a protective effect of vitamin E with vascular dementia, no association with AD risk was noted.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0099" rid="CIT0099" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707028" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">99</a>&nbsp;The analysis of 980 individuals within the Washington Heights-Inwood Columbia Aging Project concluded that neither supplementary nor dietary intake of vitamin E, alone or in combination, significantly attenuated AD risk.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0100" rid="CIT0100" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707050" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">100</a>&nbsp;A prospective study of 2,969 individuals followed-up over a mean 5.5&nbsp;years found no association between AD risk and the use of vitamin E supplements, with or without vitamin C.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0101" rid="CIT0101" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706989" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">101</a></p><p id="__p36" class="p p-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">While these prospective studies provide limited evidence for the benefits of vitamin E supplementation, they nevertheless suggest that a high intake from dietary sources may confer some benefit in reducing the risk of developing AD compared to those with lower intake.</p></div><div id="S0004-S2004" class="sec sec-last" style="clear: both;"><h3 id="S0004-S2004title" style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Randomised clinical trials of vitamin E supplementation</h3><p id="__p37" class="p p-first" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Several randomised trials have investigated the efficacy of vitamin E as a potential therapeutic intervention for AD (<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/table/T0004/" target="table" class="fig-table-link figpopup" rid-figpopup="T0004" rid-ob="ob-T0004" co-legend-rid="" style="display: inline-block !important; zoom: 1 !important; cursor: pointer; color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Table 4</a>). The first of these was published over 20&nbsp;years ago and was a double-blind, randomised multi-centre clinical trial which compared the effectiveness of selegiline (a selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor) and α-tocopherol (2000&nbsp;IU/day), individually or in combination, with a placebo in 341 subjects with moderate AD for 2&nbsp;years.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0102" rid="CIT0102" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706912" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">102</a>&nbsp;Several outcome measures were considered including time-to-death, institutionalisation, functional ability and dementia severity. The study concluded that vitamin E and selegiline slow the progression of moderate AD both independently and as a combination therapy compared with placebo but with no additive benefit of the combined regimen.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0102" rid="CIT0102" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706987" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">102</a></p><div class="table-wrap table anchored whole_rhythm" id="T0004" style="clear: both; margin: 1.3846em 0px; background-color: rgb(255, 252, 240); border: 1px solid rgb(234, 195, 175); border-top-left-radius: 5px; border-top-right-radius: 5px; border-bottom-right-radius: 5px; border-bottom-left-radius: 5px; padding: 1.3846em;"><h3 style="font-size: 1em; line-height: 1.25em; margin: 1.2856em 0px 0.6428em; color: rgb(114, 65, 40); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Table 4</h3><div class="caption"><p id="__p38" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Randomised trials investigating vitamin E supplementation as a treatment for AD</p></div><div data-largeobj="" data-largeobj-link-rid="largeobj_idm140477928857840" class="xtable" style="clear: both; max-height: 80vh; overflow: auto;"><table frame="hsides" rules="groups" class="rendered small default_table" style="clear: both; border-collapse: collapse; border-spacing: 0px; margin: 1.3846em 0px; font-size: 0.8461em; line-height: 1.6363em; border-top-width: 1px; border-top-style: solid; border-top-color: rgb(0, 0, 0); border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(0, 0, 0);"><thead style="border: none;"><tr><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Study (Publication year)</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Study population</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Isoform</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Dose</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Duration</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Primary outcome measures</th><th rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="text-align: center; background-color: inherit; padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Results</th></tr></thead><tbody style="border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(136, 136, 136); border-top-width: 1px; border-top-style: solid; border-top-color: rgb(136, 136, 136);"><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Sano et al (1997)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0102" rid="CIT0102" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707059" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">102</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">341 AD cases</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">2000&nbsp;IU/day</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">2&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">ADCS; MMSE; Blessed-Dementia Scale</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Slowed AD progression with α-tocopherol and/or selegiline compared with placebo group.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Petersen et al (2005)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0103" rid="CIT0103" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706966" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">103</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">769 MCI cases</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Not specified</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">2000&nbsp;IU/day</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">3&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">15 cognitive tests including MMSE</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">No significant difference between progression to AD in group treated with vitamin E compared with placebo group.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Lloret et al (2009)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0104" rid="CIT0104" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706983" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">104</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">33 AD cases</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">800&nbsp;IU/day</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">6&nbsp;months</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">MMSE; Blessed-Dementia Scale</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Cognition maintained in one sub- group treated with α-tocopherol while cognition decreased sharply in a second.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Dysken et al (2014)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0105" rid="CIT0105" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706901" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">105</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">613 AD cases</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">α-tocopherol</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">2000&nbsp;IU/day</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">2&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">MMSE; ADCS-ADL Inventory</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Slowed functional decline in AD in patients receiving α-tocopherol compared with placebo.</td></tr><tr><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Kryscio et al (2017)<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0106" rid="CIT0106" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706959" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">106</a></td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">7,540 cognitively normal men</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">Not specified</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">400&nbsp;IU/day</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">6&nbsp;years</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">MIS; CERAD test-battery</td><td rowspan="1" colspan="1" style="padding: 0.2em 0.4em; border: none; vertical-align: top;">No significant effects on AD prevention detected. No evidence of increased mortality with vitamin E treatment.</td></tr></tbody></table></div><div id="largeobj_idm140477928857840" class="largeobj-link align_right" style="margin-top: 0.692em; text-align: right;"><a target="object" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/table/T0004/?report=objectonly" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Open in a separate window</a></div><div class="tblwrap-foot" style="font-size: 0.8461em; margin: 1.3846em 0px;"><div id="idm140477926702544"><p id="__p39" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;"><strong>Abbreviations:</strong>&nbsp;AD, Alzheimer’s disease; MCI, mild cognitive impairment; ADCS, Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale; MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination; ADCS-ADL, Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study/Activities of Daily Living; MIS, memory impairment screen; CERAD, Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s disease.</p></div></div></div><p id="__p40" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">A larger double-blind study was undertaken several years later and compared the effects of 2000&nbsp;IU/day of vitamin E, donepezil or placebo daily for 3&nbsp;years in 769 subjects with the amnestic subtype of MCI.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0103" rid="CIT0103" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707030" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">103</a>Although the authors did not specify the vitamin E isoform used in supplementation, no significant difference in the rate of conversion to AD was found at any point during follow-up in the group receiving vitamin E and only minimal effects on secondary measures of cognition were detected compared with those receiving placebo.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0103" rid="CIT0103" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707057" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">103</a></p><p id="__p41" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">In a small trial, 57 AD participants were randomised (33 completed the study) to receive either vitamin E (800&nbsp;IU/day) or placebo for six-months and markers of OS and cognitive function were assessed.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0104" rid="CIT0104" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706991" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">104</a>Among those randomised to receive vitamin E, two sub-groups were identified: (1) those who had lower measures of OS and retained their cognitive function and (2) those with no significant changes in OS levels who demonstrated marked cognitive decline throughout the six months of the study.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0104" rid="CIT0104" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706903" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">104</a>&nbsp;This cognitive decline was greater in the latter sub-group compared with the group of participants who received placebo.</p><p id="__p42" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Another double-blind, randomised clinical trial (The TEAM-AD VA Cooperative Randomised Trial) investigated supplementation of α-tocopherol (2000&nbsp;IU/day) and/or memantine compared to placebo in 613 patients with mild-to-moderate AD.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0105" rid="CIT0105" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706931" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">105</a>&nbsp;The study reported that α-tocopherol supplementation alone resulted in slower functional decline compared with the placebo group.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0105" rid="CIT0105" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706955" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">105</a>&nbsp;Unexpectedly, the combination of α-tocopherol and memantine demonstrated less benefit than α-tocopherol supplementation alone, although a convincing rationale for this was lacking. Furthermore, eval&#8206;uation of the α-tocopherol safety data suggested no significant increase in mortality in contrast to an earlier meta-analysis.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0105" rid="CIT0105" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707048" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">105</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0107" rid="CIT0107" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706910" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">107</a></p><p id="__p43" class="p p-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">More recently, the double-blind PREADViSE study (2017) eval&#8206;uated the effects of low-dose vitamin E (400&nbsp;IU/d, unspecified isoform) and/or selenium versus placebo in 7,540 cognitively intact elderly men.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0106" rid="CIT0106" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706964" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">106</a>The study found that neither vitamin E nor selenium, individually or in combination, offered any benefit in delaying the onset of AD.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0106" rid="CIT0106" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707046" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">106</a>&nbsp;Of note, Naeini and colleagues investigated the effects of combined vitamin E and vitamin C supplementation for 1&nbsp;year versus placebo in elderly individuals with MCI in a double-blind, randomised trial.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0108" rid="CIT0108" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707026" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">108</a>&nbsp;Although supplementation offered some improvement in selected measures of oxidative stress, there were no detectable benefits in cognition.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0108" rid="CIT0108" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707044" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">108</a>&nbsp;A further small trial investigating the effects of supplementation with vitamin E and other nutrients similarly found reductions in measures of OS with treatment but no derived clinical benefit.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0109" rid="CIT0109" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706937" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">109</a></p></div></div><div id="S0005" class="tsec sec" style="clear: both; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="S0005title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Failure of vitamin E as a clinical intervention so far</h2><p id="__p44" class="p p-first" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Since Harman first postulated the “free radical theory of ageing” in 1956, the potential implications for providing “chemical means of prolonging effective life” has received significant attention.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0110" rid="CIT0110" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707037" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">110</a>Nevertheless, evidence in support of vitamin E providing clinical benefit against AD remains inconsistent and inconclusive. Despite substantial evidence of increased OS in AD aetiology and reduced circulating vitamin E levels, the findings from clinical trials investigating vitamin E as an intervention have yet to match the expectation.</p><p id="__p45" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">This translational discrepancy is not uncommon among studies investigating the role of OS in disease and its implication in pathogenesis and potential therapeutic approaches.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0111" rid="CIT0111" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706958" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">111</a>&nbsp;Indeed, several studies have shown that antioxidant supplementation is ineffective or possibly even harmful.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0112" rid="CIT0112" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241752" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">112</a>&nbsp;In the context of vitamin E and AD, the failure of clinical trials may be due to general weaknesses in the studies investigating OS or limitations of studies specific to this area. A major and controversial limitation includes determination of the most appropriate OS markers.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0113" rid="CIT0113" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707054" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">113</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0114" rid="CIT0114" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707016" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">114</a>&nbsp;Consequently, it has been suggested that disease specific proteins or combinations of markers in large-scale panels should be considered for monitoring therapeutic response and predicting outcomes.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0115" rid="CIT0115" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706972" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">115</a>&nbsp;In the specific context of AD, the use of myeloperoxidase (MPO),&nbsp;<em>trans</em>-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) or several advanced glycation end products (AGEs) resulting from glycoxidation have been suggested as potentially useful OS markers.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0115" rid="CIT0115" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706953" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">115</a></p><p id="__p46" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">However, several factors may reflect the translational difficulties from laboratory to clinical evidence in the existing vitamin E studies in AD. While increased OS and reduced plasma vitamin E levels have been associated with AD, a weakness of many vitamin E supplementation trials has been their failure to measure antioxidant and nutritional levels at baseline. As such, an unknown proportion of participants may not have had sufficiently depleted vitamin E levels upon study entry and therefore the likelihood of observing any beneficial effects of vitamin E on primary outcome measures in these individuals may have been reduced.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0022" rid="CIT0022" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707056" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">22</a>&nbsp;The requirement of low baseline levels for supplementation to cause an efficacious increase in plasma levels has been highlighted in non-vitamin E studies and suggests that supplementation is beneficial only in the setting of deficient or insufficient nutrient status.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0116" rid="CIT0116" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706947" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">116</a></p><p id="__p47" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">In addition, differences in study design between randomised trials may explain, in part, the inconsistent findings to date. For example, a study by Lloret and colleagues consisted of a relatively small number of participants with a lower vitamin E dose and shorter duration while in the study by Sano et al there were large differences in baseline Mini-Mental State Examinations between the placebo and vitamin E groups.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0102" rid="CIT0102" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706936" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">102</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0104" rid="CIT0104" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706923" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">104</a>&nbsp;It also remains unclear whether the duration of intervention in these studies is sufficient for the detection of clinical effects. A 2017 Cochrane review concluded that only the study by Dysken and colleagues (which found that that vitamin E slows functional decline in AD) was of moderate quality and that future trials were likely to counter its findings of a lack of support for the beneficial effects of vitamin E in AD.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0117" rid="CIT0117" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241739" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">117</a></p><p id="__p48" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Importantly, a major limitation of trials to date may have been the choice of intervention. While two studies (Petersen et al and Kryscio et al) failed to specify which vitamin E isoform was used, the remaining studies have focused solely on α-tocopherol. There is support that supplementation with a single vitamin E isoform (aside from questions of dose and duration) is a less than optimal approach. Firstly, there is sufficient evidence for the biological activity of the other vitamin E isoforms to warrant their investigation in randomised trials.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0017" rid="CIT0017" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707027" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">17</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0061" rid="CIT0061" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241736" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">61</a>&nbsp;There have been no trials to date investigating tocotrienol supplements. Secondly, the administration of high-doses of α-tocopherol alone may inhibit the absorption of other tocopherol and tocotrienol isoforms, leading to a damaging biochemical imbalance rather than clinical benefit.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0022" rid="CIT0022" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707060" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">22</a></p><p id="__p49" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Furthermore, existing epidemiological studies suggest that dietary sources of vitamin E are more effective in reducing the risk of developing AD than supplementation alone. It is therefore likely that this benefit can be attributed to synergistic interactions which are obscured in trials that investigate supplementation with only a single isoform.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0118" rid="CIT0118" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707003" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">118</a>&nbsp;It is worth noting that dietary vitamin E consumption is more likely to reflect long-term intake than supplement use which may offer partial explanation as to why diet-based sources seem more effective than supplementation in reducing associated AD risk.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0119" rid="CIT0119" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241725" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">119</a></p><p id="__p50" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">There is also evidence to suggest that the combination of vitamin intake is influential. Vitamin C plays an important role in the reduction of vitamin E after it has been oxidised by free radicals and therefore in maintaining its antioxidant capabilities in tissues.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0120" rid="CIT0120" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707051" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">120</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0121" rid="CIT0121" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706940" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">121</a>&nbsp;It is possible that α-tocopherol radicals can themselves induce lipid peroxidation in the context of inadequate co-antioxidant (including vitamin C) levels, particularly in settings of increased oxidative stress or where α-tocopherol levels have been increased alone.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0122" rid="CIT0122" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707033" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">122</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0123" rid="CIT0123" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706926" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">123</a>&nbsp;The possibility of α-tocopherol exhibiting pro-oxidant activity under such circumstances is supported by a small randomised trial which found increased plasma oxidant activity in patients receiving vitamin E supplementation compared with placebo.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0124" rid="CIT0124" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706920" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">124</a>&nbsp;It may therefore be important to consider the effects of supplementation with other vitamins in combination with vitamin E to maximise antioxidant efficacy. This is supported by studies that have shown that vitamin E contributes only a relatively small proportion to overall serum antioxidant capacity.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0105" rid="CIT0105" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707004" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">105</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0125" rid="CIT0125" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241746" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">125</a></p><p id="__p51" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Consideration of the complex bioavailability of vitamin E is important as it is influenced by several factors. The intestinal absorption of vitamin E can vary significantly depending on the food source and its composition of tocopherol or tocotrienol isomers and other nutrients.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0126" rid="CIT0126" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706930" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">126</a>&nbsp;It has been shown that various dietary compounds, including sterols, can reduce intestinal absorption of vitamin E.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0127" rid="CIT0127" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706942" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">127</a>&nbsp;Furthermore, there is large variation between individuals in the availability of high-density lipoproteins (HDLs) which are necessary for vitamin E integration into the central nervous system.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0128" rid="CIT0128" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706970" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">128</a>&nbsp;There is evidence to suggest this may explain the apparently higher maximum plasma levels of vitamin E in women compared to men.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0129" rid="CIT0129" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706925" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">129</a></p><p id="__p52" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Several other variables, including age, smoking status and obesity, have also been associated with variation in vitamin E bioavailability, with reduced plasma levels reported in those over 80&nbsp;years of age although this may be partially attributable to comorbid illness and diminished food intake.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0130" rid="CIT0130" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707001" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">130</a>&nbsp;Low α-tocopherol levels have also been demonstrated in smokers, while obesity has been inversely correlated with plasma α-tocopherol levels<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0131" rid="CIT0131" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706980" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">131</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0132" rid="CIT0132" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706978" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">132</a>&nbsp;although potential confounding through variation in dietary patterns and nutrient intake may exist.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0131" rid="CIT0131" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706961" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">131</a>&nbsp;Such variations may have important consequences for determining which individuals are likely to benefit from vitamin E intervention. This concept is augmented by the recent identification of 28 genetic polymorphisms that have been shown to influence vitamin E absorption, metabolism and bioavailability.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0133" rid="CIT0133" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707063" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">133</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0134" rid="CIT0134" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706906" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">134</a>&nbsp;These genetic variants have been proposed as a rationale that explains the substantial individual variability of vitamin E bioavailability and responsiveness of randomised trial participants.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0133" rid="CIT0133" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706952" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">133</a>&nbsp;Improved understanding of the genetic architecture that underpins vitamin E bioavailability and bioactivity will enable personalised and more effective recommendations of vitamin E intake.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0135" rid="CIT0135" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241754" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">135</a>&nbsp;Such factors may also clarify responder status in vitamin E supplementation studies and warrants further consideration.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0104" rid="CIT0104" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707025" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">104</a></p><p id="__p53" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">While vitamin E is an essential micronutrient and has been internationally incorporated into many guidelines for dietary intake, its safety as a clinical intervention remains controversial.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0136" rid="CIT0136" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706951" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">136</a>&nbsp;Significantly, it has been reported to have a modifying effect on platelet function and may therefore theoretically increase the risk of clinically significant bleeding.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0137" rid="CIT0137" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706982" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">137</a>&nbsp;One meta-analysis found that supplementation with low-dose vitamin E increased the risk of haemorrhagic stroke amongst study participants.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0138" rid="CIT0138" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706971" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">138</a>&nbsp;These effects may be important in the setting of individuals taking other anticoagulant or antiplatelet agents including aspirin. Increased risk of prostate cancer has also been linked with vitamin E supplementation.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0139" rid="CIT0139" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707015" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">139</a>&nbsp;Similar concerns have been raised by several meta-analyses which concluded that vitamin E supplementation may lead to increased overall mortality.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0107" rid="CIT0107" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706969" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">107</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0112" rid="CIT0112" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241733" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">112</a>&nbsp;However, the conclusions of such meta-analyses have been questioned and different analytical approaches have produced contradictory results.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0140" rid="CIT0140" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788706975" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">140</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0141" rid="CIT0141" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_788707018" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">141</a>&nbsp;Therefore, the potential adverse effects of vitamin E remain an important clinical consideration and should be explored in future studies.</p><p id="__p54" class="p p-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">Several reviews that provide an overview to various aspects of the relationship between vitamin E and AD already exist.<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0039" rid="CIT0039" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241744" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">39</a>,<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#CIT0061" rid="CIT0061" class=" bibr popnode tag_hotlink tag_tooltip" id="__tag_789241737" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">61</a>&nbsp;However, this narrative review is broader in scope with a flexible structure which has allowed the authors to be more exploratory and current in their approach that considers the use of vitamin E as a potential therapeutic for the treatment of AD. This review reflects certain points based on the authors’ experience and uses a specified strategy that details how the literature was searched (keywords), time limits of searches, and bibliographic databases accessed. The methodological approach described provides a reference point in time from which future narrative reviews may focus on new literature, thereby limiting redundancy.</p></div><div id="S0006" class="tsec sec" style="clear: both; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="S0006title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Conclusions</h2><p id="__p55" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">In spite of a strong rationale for the role of vitamin E as an effective intervention for AD, the existing clinical evidence remains inconclusive. This review has presented findings from cross-sectional studies that reported significantly lower plasma and CSF levels of vitamin E in those with AD. Additionally, reduced plasma vitamin E status has been associated with increased future risk of developing AD. Epidemiological studies have offered mixed results with regards to vitamin E supplementation but have suggested that intake of high levels of vitamin E from dietary sources may be beneficial. However, clinical trials to date have investigated only the α-tocopherol isoform and have several limitations including failure to measure antioxidant and nutritional levels of participants at baseline. Therefore, there is insufficient evidence to accept or reject the premise that vitamin E is an effective clinical intervention for delaying or preventing the onset of AD and further research is necessary. Importantly, investigation of the underlying genetic architecture with regard to responder status to vitamin E supplementation is warranted, given it is a likely significant contributor to the failure of clinical trials to date.</p></div><div id="idm140477926788352" class="tsec sec" style="clear: both; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="idm140477926788352title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Acknowledgments</h2><div class="sec" style="clear: both;"><p id="__p56" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">No sources of funding were used to assist in the conduct of this study</p></div></div><div id="S0008" class="tsec bk-sec" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="S0008title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Author contributions</h2><p id="__p57" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and revising the paper, gave final approval of the version to be published and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.</p></div><div id="S0009" class="tsec bk-sec" style="color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="S0009title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">Disclosure</h2><p id="__p58" class="p p-first-last" style="margin-top: 0.6923em; margin-bottom: 0.6923em;">The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.</p></div><div id="idm140477926784336" class="tsec sec" style="clear: both; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-family: 'Times New Roman', stixgeneral, serif; font-size: 16px; line-height: 21px;"><div class="goto jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-container" style="float: right; text-align: right; font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-size: 0.86666em !important;"><a class="tgt_dark page-toc-label jig-ncbiinpagenav-goto-heading" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6645610/#" title="Go to other sections in this page" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="background-image: url(https://static.pubmed.gov/portal/portal3rc.fcgi/4160049/img/2846531); background-color: transparent; padding-right: 17px; margin-right: 3px; color: rgb(100, 42, 143); background-position: 100% 43.5%; background-repeat: no-repeat no-repeat;">Go to:</a></div><h2 class="head no_bottom_margin ui-helper-clearfix" id="idm140477926784336title" style="font-size: 1.125em; line-height: 1.1111em; margin: 1.125em 0px 0px; color: rgb(152, 87, 53); min-height: 0px; border-bottom-width: 1px; border-bottom-style: solid; border-bottom-color: rgb(151, 176, 200); font-family: arial, helvetica, clean, sans-serif; font-weight: normal;">References</h2><div class="ref-list-sec sec" id="reference-list" style="clear: both;"><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0001" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">1.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Ashraf GM, Chibber S, Zaidi SK, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Recent updates on the association between Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Med Chem</em></span>. 2016;<span class="ref-vol">12</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):226&#8211;237. doi:10.2174/1573406411666151030111820 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26527156" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.2174%2F1573406411666151030111820" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Med+Chem&amp;title=Recent+updates+on+the+association+between+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+and+vascular+dementia&amp;volume=12&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2016&amp;pages=226-237&amp;doi=10.2174/1573406411666151030111820&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0002" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">2.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Scheltens P, Blennow K, Breteler MBM, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Lancet</em></span>. 2016;<span class="ref-vol">388</span>(<span class="ref-iss">10043</span>):505&#8211;517. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01124-1 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26921134" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2FS0140-6736(15)01124-1" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Lancet&amp;title=Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=388&amp;issue=10043&amp;publication_year=2016&amp;pages=505-517&amp;pmid=26921134&amp;doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01124-1&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0003" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">3.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Perl DP.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Mt Sinai J Med</em></span>. 2010;<span class="ref-vol">77</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):32&#8211;42. doi:10.1002/msj.20157&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2918894/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20101720" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fmsj.20157" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Mt+Sinai+J+Med&amp;title=Neuropathology+of+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=77&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2010&amp;pages=32-42&amp;pmid=20101720&amp;doi=10.1002/msj.20157&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0004" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">4.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Prince M, Wimo A, Guerchet M, Ali GC, Wu YT, Prina N&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Alzheimer’s Disease International</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>World Alzheimer Report</em></span>; Alzheimers Disease International: London, UK; 2015.&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?title=World+Alzheimer+Report&amp;publication_year=2015&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0005" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">5.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Wimo A, Jonsson L, Bond J, Prince M, Winblad B.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The worldwide economic impact of dementia 2010</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Alzheimers Dement</em></span>. 2013;<span class="ref-vol">9</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):1. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2012.11.006 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23305821" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.jalz.2012.11.006" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Alzheimers+Dement&amp;title=The+worldwide+economic+impact+of+dementia+2010&amp;volume=9&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2013&amp;pages=1&amp;pmid=23305821&amp;doi=10.1016/j.jalz.2012.11.006&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0006" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">6.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi HM.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Alzheimers Dement</em></span>. 2007;<span class="ref-vol">3</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):186&#8211;191. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2007.04.381 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19595937" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.jalz.2007.04.381" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Alzheimers+Dement&amp;title=Forecasting+the+global+burden+of+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=3&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2007&amp;pages=186-191&amp;pmid=19595937&amp;doi=10.1016/j.jalz.2007.04.381&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0007" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">7.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Niemantsverdriet E, Valckx S, Bierke M and Engelborghs S.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Alzheimer’s disease and CSF biomarkers: clinical indications and rationale use</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Acta Neurol Belg</em></span>. 2017;<span class="ref-vol">117</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):591&#8211;602. doi:10.1007/s13760-017-0816-5&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5565643/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28752420" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2Fs13760-017-0816-5" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Acta+Neurol+Belg&amp;title=Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+and+CSF+biomarkers:+clinical+indications+and+rationale+use&amp;volume=117&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2017&amp;pages=591-602&amp;pmid=28752420&amp;doi=10.1007/s13760-017-0816-5&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0008" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">8.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Cui Y, Liu B, Luo S, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. Identification of conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease using multivariate predictors</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>PLoS One</em></span>. 2011;<span class="ref-vol">6</span>(<span class="ref-iss">7</span>):e21896. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021896&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3140993/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21814561" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0021896" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=PLoS+One&amp;title=Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+neuroimaging+initiative.+Identification+of+conversion+from+mild+cognitive+impairment+to+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+using+multivariate+predictors&amp;volume=6&amp;issue=7&amp;publication_year=2011&amp;pages=e21896&amp;pmid=21814561&amp;doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0021896&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0009" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">9.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Kumar A, Singh A.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">A review on Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology and its management: an update</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Pharmacol Rep</em></span>. 2015;<span class="ref-vol">67</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):195&#8211;203. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25712639" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Pharmacol+Rep&amp;title=A+review+on+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+pathophysiology+and+its+management:+an+update&amp;volume=67&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2015&amp;pages=195-203&amp;pmid=25712639&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0010" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">10.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Ghezzi L, Scarpini E, Galimberti D.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Disease-modifying drugs in Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Drug Des Devel Ther</em></span>. 2013;<span class="ref-vol">7</span>:1471.&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3862506/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24353405" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Drug+Des+Devel+Ther&amp;title=Disease-modifying+drugs+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=7&amp;publication_year=2013&amp;pages=1471&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0011" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">11.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Alzheimer A, Stelzmann RA, Schnitzlein HN, Murtagh FR.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">An English translation of Alzheimer’s 1907 paper, “Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde”</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Clin Anat</em></span>. 1995;<span class="ref-vol">8</span>(<span class="ref-iss">6</span>):429&#8211;431. doi:10.1002/ca.980080612 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8713166" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fca.980080612" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Clin+Anat&amp;title=An+English+translation+of+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+1907+paper,+%E2%80%9CUber+eine+eigenartige+Erkankung+der+Hirnrinde%E2%80%9D&amp;volume=8&amp;issue=6&amp;publication_year=1995&amp;pages=429-431&amp;pmid=8713166&amp;doi=10.1002/ca.980080612&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0012" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">12.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Cummings JL, Cole G.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Alzheimer disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>JAMA</em></span>. 2002;<span class="ref-vol">287</span>(<span class="ref-iss">18</span>):2335&#8211;2338. doi:10.1001/jama.287.18.2335 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11988038" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1001%2Fjama.287.18.2335" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=JAMA&amp;title=Alzheimer+disease&amp;volume=287&amp;issue=18&amp;publication_year=2002&amp;pages=2335-2338&amp;pmid=11988038&amp;doi=10.1001/jama.287.18.2335&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0013" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">13.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Masters CL, Simms G, Weinman NA, Multhaup G, McDonald BL, Beyreuther K.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down Syndrome</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Proc Natl Acad Sci USA</em></span>. 1985;<span class="ref-vol">82</span>(<span class="ref-iss">12</span>):4245&#8211;4249. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC397973/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3159021" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1073%2Fpnas.82.12.4245" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Proc+Natl+Acad+Sci+USA&amp;title=Amyloid+plaque+core+protein+in+Alzheimer+disease+and+Down+Syndrome&amp;volume=82&amp;issue=12&amp;publication_year=1985&amp;pages=4245-4249&amp;pmid=3159021&amp;doi=10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0014" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">14.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Castellano JM, Kim J, Stewart FR, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Human apoE isoforms differentially regulate brain amyloid- β peptide clearance</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Sci Transl Med</em></span>. 2011;<span class="ref-vol">3</span>:89ra57. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3002156&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3192364/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21715678" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1126%2Fscitranslmed.3002156" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Sci+Transl+Med&amp;title=Human+apoE+isoforms+differentially+regulate+brain+amyloid-+%CE%B2+peptide+clearance&amp;volume=3&amp;publication_year=2011&amp;pages=89ra57&amp;doi=10.1126/scitranslmed.3002156&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0015" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">15.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Lee VM, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Neurodegenerative tauopathies</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Ann Rev Neurosci</em></span>. 2001;<span class="ref-vol">24</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):1121&#8211;1159. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.1121 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11520930" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1146%2Fannurev.neuro.24.1.1121" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Ann+Rev+Neurosci&amp;title=Neurodegenerative+tauopathies&amp;volume=24&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2001&amp;pages=1121-1159&amp;pmid=11520930&amp;doi=10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.1121&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0016" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">16.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Giannakopoulos P, Herrmann FR, Bussi&#232;re T, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Tangle and neuron numbers, but not amyloid load, predict cognitive status in Alzheimer’s Disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Neurology</em></span>. 2003;<span class="ref-vol">60</span>(<span class="ref-iss">9</span>):1495&#8211;1500. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000063311.58879.01 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12743238" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1212%2F01.wnl.0000063311.58879.01" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Neurology&amp;title=Tangle+and+neuron+numbers,+but+not+amyloid+load,+predict+cognitive+status+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+Disease&amp;volume=60&amp;issue=9&amp;publication_year=2003&amp;pages=1495-1500&amp;pmid=12743238&amp;doi=10.1212/01.wnl.0000063311.58879.01&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0017" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">17.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Xia W, Mo H.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Potential of tocotrienols in the prevention and therapy of Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Nutr Biochem</em></span>. 2016;<span class="ref-vol">31</span>:1&#8211;9. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.10.011 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27133418" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.jnutbio.2015.10.011" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Nutr+Biochem&amp;title=Potential+of+tocotrienols+in+the+prevention+and+therapy+of+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=31&amp;publication_year=2016&amp;pages=1-9&amp;pmid=27133418&amp;doi=10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.10.011&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0018" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">18.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Yao ZX, Papadopoulos.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Function of β-amyloid in cholesterol transport: a lead to neurotoxicity</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Faseb J</em></span>. 2002;<span class="ref-vol">16</span>(<span class="ref-iss">12</span>):1677&#8211;1679. doi:10.1096/fj.02-0285fje [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12206998" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1096%2Ffj.02-0285fje" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Faseb+J&amp;title=Function+of+%CE%B2-amyloid+in+cholesterol+transport:+a+lead+to+neurotoxicity&amp;volume=16&amp;issue=12&amp;publication_year=2002&amp;pages=1677-1679&amp;pmid=12206998&amp;doi=10.1096/fj.02-0285fje&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0019" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">19.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Cutler RG, Kelly J, Storie K, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Involvement of oxidative stress-induced abnormalities in ceramide and cholesterol metabolism in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Proc Natl Acad Sci USA</em></span>. 2004;<span class="ref-vol">101</span>(<span class="ref-iss">7</span>):2070&#8211;2075. doi:10.1073/pnas.0305799101&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC357053/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14970312" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1073%2Fpnas.0305799101" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Proc+Natl+Acad+Sci+USA&amp;title=Involvement+of+oxidative+stress-induced+abnormalities+in+ceramide+and+cholesterol+metabolism+in+brain+aging+and+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=101&amp;issue=7&amp;publication_year=2004&amp;pages=2070-2075&amp;pmid=14970312&amp;doi=10.1073/pnas.0305799101&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0020" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">20.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">McGuinness B, Craig D, Bullock R, Passmore P.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Statins for the prevention of dementia</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Cochrane Databse Syst Rev</em></span>. 2016;(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):CD003160. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003160.pub3 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26727124" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2F14651858.CD003160.pub3" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Cochrane+Databse+Syst+Rev&amp;title=Statins+for+the+prevention+of+dementia&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2016&amp;pages=CD003160&amp;doi=10.1002/14651858.CD003160.pub3&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0021" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">21.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Karran E, Mercken M, De Strooper B.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: an appraisal for the development of therapeutics</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Nat Rev Drug Discov</em></span>. 2011;<span class="ref-vol">10</span>(<span class="ref-iss">9</span>):698. doi:10.1038/nrd3505 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21852788" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1038%2Fnrd3505" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Nat+Rev+Drug+Discov&amp;title=The+amyloid+cascade+hypothesis+for+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease:+an+appraisal+for+the+development+of+therapeutics&amp;volume=10&amp;issue=9&amp;publication_year=2011&amp;pages=698&amp;pmid=21852788&amp;doi=10.1038/nrd3505&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0022" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">22.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mecocci P, Boccardi V, Cecchetti R, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">A long journey into aging, brain aging, and Alzheimer’s disease following the oxidative stress tracks</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Alzheimers Dis</em></span>. 2018;<span class="ref-vol">62</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):1319&#8211;1335. doi:10.3233/JAD-170732&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5870006/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29562533" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.3233%2FJAD-170732" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Alzheimers+Dis&amp;title=A+long+journey+into+aging,+brain+aging,+and+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+following+the+oxidative+stress+tracks&amp;volume=62&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2018&amp;pages=1319-1335&amp;pmid=29562533&amp;doi=10.3233/JAD-170732&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0023" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">23.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Swerdlow RH, Khan SM.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">A “mitochondrial cascade hypothesis” for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Med Hypotheses</em></span>. 2004;<span class="ref-vol">63</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):8&#8211;20. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2003.12.045 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15193340" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.mehy.2003.12.045" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Med+Hypotheses&amp;title=A+%E2%80%9Cmitochondrial+cascade+hypothesis%E2%80%9D+for+sporadic+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=63&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2004&amp;pages=8-20&amp;pmid=15193340&amp;doi=10.1016/j.mehy.2003.12.045&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0024" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">24.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Swerdlow RH.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Alzheimer’s disease pathologic cascades: who comes first, what drives what</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Neurotox Res</em></span>. 2012;<span class="ref-vol">22</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):182&#8211;194. doi:10.1007/s12640-011-9272-9&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3635146/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21913048" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2Fs12640-011-9272-9" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Neurotox+Res&amp;title=Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+pathologic+cascades:+who+comes+first,+what+drives+what&amp;volume=22&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;pages=182-194&amp;pmid=21913048&amp;doi=10.1007/s12640-011-9272-9&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0025" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">25.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Swerdlow RH.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Brain aging, Alzheimer’s disease, and mitochondria</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Biochim Biophys Acta</em></span>. 2011;<span class="ref-vol">1812</span>(<span class="ref-iss">12</span>):1630&#8211;1639. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.08.012&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3210037/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21920438" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.bbadis.2011.08.012" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Biochim+Biophys+Acta&amp;title=Brain+aging,+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease,+and+mitochondria&amp;volume=1812&amp;issue=12&amp;publication_year=2011&amp;pages=1630-1639&amp;pmid=21920438&amp;doi=10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.08.012&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0026" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">26.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Kitazawa M, Oddo S, Yamasaki TR, Green KN, LaFerla FM.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation exacerbates tau pathology by a cyclin-dependent kinase 5-mediated pathway in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Neurosci</em></span>. 2005;<span class="ref-vol">25</span>(<span class="ref-iss">39</span>):8843&#8211;8853. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2868-05.2005&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6725603/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16192374" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1523%2FJNEUROSCI.2868-05.2005" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Neurosci&amp;title=Lipopolysaccharide-induced+inflammation+exacerbates+tau+pathology+by+a+cyclin-dependent+kinase+5-mediated+pathway+in+a+transgenic+model+of+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=25&amp;issue=39&amp;publication_year=2005&amp;pages=8843-8853&amp;pmid=16192374&amp;doi=10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2868-05.2005&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0027" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">27.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Heppner FL.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Ransohoff RM and Becher B. Immune attack: the role of inflammation in Alzheimer disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Nat Rev Neurosci</em></span>. 2015;<span class="ref-vol">16</span>(<span class="ref-iss">6</span>):358. doi:10.1038/nrn3880 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25991443" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1038%2Fnrn3880" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Nat+Rev+Neurosci&amp;title=Ransohoff+RM+and+Becher+B.+Immune+attack:+the+role+of+inflammation+in+Alzheimer+disease&amp;volume=16&amp;issue=6&amp;publication_year=2015&amp;pages=358&amp;pmid=25991443&amp;doi=10.1038/nrn3880&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0028" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">28.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Zuo L, Zhou T, Pannell BK, Ziegler AC, Best TM.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Biological and physiological role of reactive oxygen species&#8211;the good, the bad and the ugly</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Acta Physiol</em></span>. 2015;<span class="ref-vol">214</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):329&#8211;348. doi:10.1111/apha.2015.214.issue-3 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25912260" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1111%2Fapha.2015.214.issue-3" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Acta+Physiol&amp;title=Biological+and+physiological+role+of+reactive+oxygen+species%E2%80%93the+good,+the+bad+and+the+ugly&amp;volume=214&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2015&amp;pages=329-348&amp;doi=10.1111/apha.2015.214.issue-3&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0029" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">29.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Nunomura A, Perry G, Aliey G, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Neuropath Exp Neurol</em></span>. 2001;<span class="ref-vol">60</span>(<span class="ref-iss">8</span>):759&#8211;767. doi:10.1093/jnen/60.8.759 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11487050" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fjnen%2F60.8.759" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Neuropath+Exp+Neurol&amp;title=Oxidative+damage+is+the+earliest+event+in+Alzheimer+disease&amp;volume=60&amp;issue=8&amp;publication_year=2001&amp;pages=759-767&amp;pmid=11487050&amp;doi=10.1093/jnen/60.8.759&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0030" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">30.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Gustaw-Rothenberg K, Kowalczuk K, Stryjecka-Zimmer M.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Lipids’ peroxidation markers in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Geriatr Gerontol</em></span>. 2010;<span class="ref-vol">10</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):161&#8211;166. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20446930" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Geriatr+Gerontol&amp;title=Lipids%E2%80%99+peroxidation+markers+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+and+vascular+dementia&amp;volume=10&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2010&amp;pages=161-166&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0031" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">31.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mosconi L, Pupi A, De Leon MJ.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Brain glucose hypometabolism and oxidative stress in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Ann NY Acad Sci</em></span>. 2008;<span class="ref-vol">1147</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):180&#8211;195. doi:10.1196/annals.1427.007&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2661241/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19076441" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1196%2Fannals.1427.007" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Ann+NY+Acad+Sci&amp;title=Brain+glucose+hypometabolism+and+oxidative+stress+in+preclinical+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=1147&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2008&amp;pages=180-195&amp;pmid=19076441&amp;doi=10.1196/annals.1427.007&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0032" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">32.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Boccardi V, Baroni M, Mangialasche F, Mecocci P.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E family: role in the pathogenesis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Alzheimers Dement</em></span>. 2016;<span class="ref-vol">2</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):182&#8211;191.&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5651353/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29067305" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Alzheimers+Dement&amp;title=Vitamin+E+family:+role+in+the+pathogenesis+and+treatment+of+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=2&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2016&amp;pages=182-191&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0033" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">33.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Curti D, Rognoni F, Gasparini L, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Oxidative metabolism in fibroblasts derived from sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Neurosci Lett</em></span>. 2008;<span class="ref-vol">1147</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):180&#8211;195.&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Neurosci+Lett&amp;title=Oxidative+metabolism+in+fibroblasts+derived+from+sporadic+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+(AD)+patients&amp;volume=1147&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2008&amp;pages=180-195&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0034" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">34.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Nelson ME, Reieski WJ, Blair SN, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Physical activity and public health in older adults: recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Circulation</em></span>. 2007;<span class="ref-vol">116</span>(<span class="ref-iss">9</span>):1094. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.185650 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17671236" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1161%2FCIRCULATIONAHA.107.185650" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Circulation&amp;title=Physical+activity+and+public+health+in+older+adults:+recommendation+from+the+American+College+of+Sports+Medicine+and+the+American+Heart+Association&amp;volume=116&amp;issue=9&amp;publication_year=2007&amp;pages=1094&amp;pmid=17671236&amp;doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.185650&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0035" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">35.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Jack C.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The vascular hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: bench to bedside and beyond</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Neurodegener Dis</em></span>. 2010;<span class="ref-vol">7</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1&#8211;3</span>):116&#8211;121. doi:10.1159/000285520 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20173340" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1159%2F000285520" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Neurodegener+Dis&amp;title=The+vascular+hypothesis+of+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease:+bench+to+bedside+and+beyond&amp;volume=7&amp;issue=1%E2%80%933&amp;publication_year=2010&amp;pages=116-121&amp;pmid=20173340&amp;doi=10.1159/000285520&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0036" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">36.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Feng Y, Wang X.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Antioxidant therapies for Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Oxid Med Cell Longev</em></span>. 2012;<span class="ref-vol">2012</span>:472932. doi:10.1155/2012/472932&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3410354/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22888398" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1155%2F2012%2F472932" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Oxid+Med+Cell+Longev&amp;title=Antioxidant+therapies+for+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=2012&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;pages=472932&amp;pmid=22888398&amp;doi=10.1155/2012/472932&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0037" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">37.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Grundman M.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E and Alzheimer disease: the basis for additional clinical trials</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Am J Clin Nutr</em></span>. 2000;<span class="ref-vol">71</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):630S&#8211;636S. doi:10.1093/ajcn/71.2.630s [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10681271" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fajcn%2F71.2.630s" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Am+J+Clin+Nutr&amp;title=Vitamin+E+and+Alzheimer+disease:+the+basis+for+additional+clinical+trials&amp;volume=71&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2000&amp;pages=630S-636S&amp;pmid=10681271&amp;doi=10.1093/ajcn/71.2.630s&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0038" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">38.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Bieri JG.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Sources and consumption of antioxidants in the diet</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Am Oil Chem Soc</em></span>. 1984;<span class="ref-vol">61</span>(<span class="ref-iss">12</span>):1917&#8211;1918. doi:10.1007/BF02540831 [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2FBF02540831" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Am+Oil+Chem+Soc&amp;title=Sources+and+consumption+of+antioxidants+in+the+diet&amp;volume=61&amp;issue=12&amp;publication_year=1984&amp;pages=1917-1918&amp;doi=10.1007/BF02540831&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0039" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">39.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Grimm M, Mett J, Hartmann T.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The impact of vitamin E and other fat-soluble vitamins on Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Int J Mol Sci</em></span>. 2016;<span class="ref-vol">17</span>(<span class="ref-iss">11</span>):1785. doi:10.3390/ijms17111785&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5133786/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27792188" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.3390%2Fijms17111785" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Int+J+Mol+Sci&amp;title=The+impact+of+vitamin+E+and+other+fat-soluble+vitamins+on+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=17&amp;issue=11&amp;publication_year=2016&amp;pages=1785&amp;doi=10.3390/ijms17111785&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0040" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">40.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Yap SP, Yuen KH, Wong JW.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of α&#8722;, γ&#8722;and δ&#8722; tocotrienols under different food status</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Pharm Pharmacol</em></span>. 2001;<span class="ref-vol">53</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):67&#8211;71. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11206194" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Pharm+Pharmacol&amp;title=Pharmacokinetics+and+bioavailability+of+%CE%B1%E2%88%92,+%CE%B3%E2%88%92and+%CE%B4%E2%88%92+tocotrienols+under+different+food+status&amp;volume=53&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2001&amp;pages=67-71&amp;pmid=11206194&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0041" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">41.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Joshi YB, Pratic&#242; D.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E in aging, dementia and Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Biofactors</em></span>. 2012;<span class="ref-vol">38</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):90&#8211;97. doi:10.1002/biof.195 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22422715" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fbiof.195" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Biofactors&amp;title=Vitamin+E+in+aging,+dementia+and+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=38&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;pages=90-97&amp;pmid=22422715&amp;doi=10.1002/biof.195&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0042" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">42.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Weinstein SJ, Peters U, Ahn J, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Serum a-tocopherol and g-tocopherol concentrations and prostate cancer risk in the PLCO screening trial: a nested case-control study</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>PLoS One</em></span>. 2012;<span class="ref-vol">7</span>:e40204. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040204&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3390343/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22792240" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0040204" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=PLoS+One&amp;title=Serum+a-tocopherol+and+g-tocopherol+concentrations+and+prostate+cancer+risk+in+the+PLCO+screening+trial:+a+nested+case-control+study&amp;volume=7&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;pages=e40204&amp;pmid=22792240&amp;doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0040204&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0043" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">43.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Wang X, Quinn PJ.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E and its function in membranes</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Prog Lipid Res</em></span>. 1999;<span class="ref-vol">38</span>(<span class="ref-iss">4</span>):309&#8211;336. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10793887" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Prog+Lipid+Res&amp;title=Vitamin+E+and+its+function+in+membranes&amp;volume=38&amp;issue=4&amp;publication_year=1999&amp;pages=309-336&amp;pmid=10793887&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0044" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">44.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">M&#252;ller L, Theile K, B&#246;hm V.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">In vitro antioxidant activity of tocopherols and tocotrienols and comparison of vitamin E concentration and lipophilic antioxidant capacity in human plasma</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Mol Nutr Food Res</em></span>. 2010;<span class="ref-vol">54</span>(<span class="ref-iss">5</span>):731&#8211;742. doi:10.1002/mnfr.200900399 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20333724" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fmnfr.200900399" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Mol+Nutr+Food+Res&amp;title=In+vitro+antioxidant+activity+of+tocopherols+and+tocotrienols+and+comparison+of+vitamin+E+concentration+and+lipophilic+antioxidant+capacity+in+human+plasma&amp;volume=54&amp;issue=5&amp;publication_year=2010&amp;pages=731-742&amp;pmid=20333724&amp;doi=10.1002/mnfr.200900399&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0045" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">45.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Raederstorff D, Wyss A, Calder PC, Weber P, Eggersdorfer M.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E function and requirements in relation to PUFA</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Br J Nutr</em></span>. 2015;<span class="ref-vol">114</span>(<span class="ref-iss">8</span>):1113&#8211;1122. doi:10.1017/S000711451500272X&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4594047/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26291567" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1017%2FS000711451500272X" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Br+J+Nutr&amp;title=Vitamin+E+function+and+requirements+in+relation+to+PUFA&amp;volume=114&amp;issue=8&amp;publication_year=2015&amp;pages=1113-1122&amp;pmid=26291567&amp;doi=10.1017/S000711451500272X&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0046" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">46.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Serbinova EA, Packer L.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Antioxidant properties of α-tocopherol and α-tocotrienol</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Meth Enzym</em></span>. 1994;<span class="ref-vol">234</span>:354&#8211;366. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7808307" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Meth+Enzym&amp;title=Antioxidant+properties+of+%CE%B1-tocopherol+and+%CE%B1-tocotrienol&amp;volume=234&amp;publication_year=1994&amp;pages=354-366&amp;pmid=7808307&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0047" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">47.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Huang D, Ou B, Hampsch-Woodill M, Flanagan JA, Deemer EK.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Development and validation of oxygen radical absorbance capacity assay for lipophilic antioxidants using randomly methylated β-cyclodextrin as the solubility enhancer</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Agric Food Chem</em></span>. 2002;<span class="ref-vol">50</span>(<span class="ref-iss">7</span>):1815&#8211;1821. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11902917" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Agric+Food+Chem&amp;title=Development+and+validation+of+oxygen+radical+absorbance+capacity+assay+for+lipophilic+antioxidants+using+randomly+methylated+%CE%B2-cyclodextrin+as+the+solubility+enhancer&amp;volume=50&amp;issue=7&amp;publication_year=2002&amp;pages=1815-1821&amp;pmid=11902917&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0048" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">48.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Brigelius-Floh&#233; R.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E: the shrew waiting to be tamed</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Free Radic Biol Med</em></span>. 2009;<span class="ref-vol">46</span>(<span class="ref-iss">5</span>):543&#8211;554. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.12.007 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19133328" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.freeradbiomed.2008.12.007" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Free+Radic+Biol+Med&amp;title=Vitamin+E:+the+shrew+waiting+to+be+tamed&amp;volume=46&amp;issue=5&amp;publication_year=2009&amp;pages=543-554&amp;pmid=19133328&amp;doi=10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.12.007&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0049" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">49.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Yoshida Y, Niki E, Noguchi N.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Comparative study on the action of tocopherols and tocotrienols as antioxidant: chemical and physical effects</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Chem Phys Lipids</em></span>. 2003;<span class="ref-vol">123</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):63&#8211;75. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12637165" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Chem+Phys+Lipids&amp;title=Comparative+study+on+the+action+of+tocopherols+and+tocotrienols+as+antioxidant:+chemical+and+physical+effects&amp;volume=123&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2003&amp;pages=63-75&amp;pmid=12637165&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0050" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">50.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Jiang Q.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Natural forms of vitamin E: metabolism, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities and their role in disease prevention and therapy</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Free Radic Biol Med</em></span>. 2014;<span class="ref-vol">72</span>:76&#8211;90. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.03.035&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4120831/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24704972" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.freeradbiomed.2014.03.035" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Free+Radic+Biol+Med&amp;title=Natural+forms+of+vitamin+E:+metabolism,+antioxidant,+and+anti-inflammatory+activities+and+their+role+in+disease+prevention+and+therapy&amp;volume=72&amp;publication_year=2014&amp;pages=76-90&amp;pmid=24704972&amp;doi=10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.03.035&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0051" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">51.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Saito Y, Nishio K, Akazawa YO, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Cytoprotective effects of Vitamin E homologues against glutamate-induced cell death in immature primary cortical neuron cultures: tocopherols and tocotrienols exert similar effects by antioxidant function</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Free Radic Biol Med</em></span>. 2010;<span class="ref-vol">49</span>:1542&#8211;1549. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.08.016 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20736061" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.freeradbiomed.2010.08.016" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Free+Radic+Biol+Med&amp;title=Cytoprotective+effects+of+Vitamin+E+homologues+against+glutamate-induced+cell+death+in+immature+primary+cortical+neuron+cultures:+tocopherols+and+tocotrienols+exert+similar+effects+by+antioxidant+function&amp;volume=49&amp;publication_year=2010&amp;pages=1542-1549&amp;pmid=20736061&amp;doi=10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.08.016&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0052" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">52.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Lee CY, Wan F.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E supplementation improves cell-mediated immunity and oxidative stress of Asian men and women</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Nutr</em></span>. 2000;<span class="ref-vol">130</span>(<span class="ref-iss">12</span>):2932&#8211;2937. doi:10.1093/jn/130.12.2932 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11110849" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fjn%2F130.12.2932" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Nutr&amp;title=Vitamin+E+supplementation+improves+cell-mediated+immunity+and+oxidative+stress+of+Asian+men+and+women&amp;volume=130&amp;issue=12&amp;publication_year=2000&amp;pages=2932-2937&amp;pmid=11110849&amp;doi=10.1093/jn/130.12.2932&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0053" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">53.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">De la Fuente M, Hernanz A, Guayerbas N. Manuel Victor V, Amalich F.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E ingestion improves several immune functions in elderly men and women</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Free Radic Res</em></span>. 2008;<span class="ref-vol">42</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):272&#8211;280. doi:10.1080/10715760801898838 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18344122" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1080%2F10715760801898838" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Free+Radic+Res&amp;title=Vitamin+E+ingestion+improves+several+immune+functions+in+elderly+men+and+women&amp;volume=42&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2008&amp;pages=272-280&amp;pmid=18344122&amp;doi=10.1080/10715760801898838&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0054" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">54.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Rota C, Rimbach G, Minihane AM, Stoecklin E, Barella L.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Dietary vitamin E modulates differential gene expression&#8206; in the rat hippocampus: potential implications for its neuroprotective properties</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Nutr Neurosci</em></span>. 2005;<span class="ref-vol">8</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):21&#8211;29. doi:10.1080/10284150400027123 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15909764" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1080%2F10284150400027123" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Nutr+Neurosci&amp;title=Dietary+vitamin+E+modulates+differential+gene+expression&#8206;+in+the+rat+hippocampus:+potential+implications+for+its+neuroprotective+properties&amp;volume=8&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2005&amp;pages=21-29&amp;pmid=15909764&amp;doi=10.1080/10284150400027123&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0055" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">55.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Giraldo E, Lloret A, Fuchsberger T, Vi&#241;a J.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Aβ and tau toxicities in Alzheimer’s are linked via oxidative stress-induced p38 activation: protective role of vitamin E</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Redox Biol</em></span>. 2014;<span class="ref-vol">2</span>:873&#8211;877. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2014.03.002&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4099506/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25061569" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.redox.2014.03.002" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Redox+Biol&amp;title=A%CE%B2+and+tau+toxicities+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+are+linked+via+oxidative+stress-induced+p38+activation:+protective+role+of+vitamin+E&amp;volume=2&amp;publication_year=2014&amp;pages=873-877&amp;pmid=25061569&amp;doi=10.1016/j.redox.2014.03.002&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0056" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">56.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Jiang Q, Yin X, Lill MA, Danielson ML, Freiser H, Huang J.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Long-chain carboxychromanols, metabolites of vitamin E, are potent inhibitors of cyclooxygenases</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Proc Natl Acad Sci USA</em></span>. 2008;<span class="ref-vol">105</span>(<span class="ref-iss">51</span>):20464&#8211;20469. doi:10.1073/pnas.0810962106&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2629323/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19074288" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1073%2Fpnas.0810962106" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Proc+Natl+Acad+Sci+USA&amp;title=Long-chain+carboxychromanols,+metabolites+of+vitamin+E,+are+potent+inhibitors+of+cyclooxygenases&amp;volume=105&amp;issue=51&amp;publication_year=2008&amp;pages=20464-20469&amp;pmid=19074288&amp;doi=10.1073/pnas.0810962106&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0057" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">57.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Copp RP, Wisniewski T, Hentati F, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Localization of alpha-tocopherol transfer protein in the brains of patients with ataxia with vitamin E deficiency and other oxidative stress related neurodegenerative disorders</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Brain Res</em></span>. 1999;<span class="ref-vol">822</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1&#8211;2</span>):80&#8211;87. doi:10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01090-2 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10082886" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fs0006-8993(99)01090-2" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Brain+Res&amp;title=Localization+of+alpha-tocopherol+transfer+protein+in+the+brains+of+patients+with+ataxia+with+vitamin+E+deficiency+and+other+oxidative+stress+related+neurodegenerative+disorders&amp;volume=822&amp;issue=1%E2%80%932&amp;publication_year=1999&amp;pages=80-87&amp;pmid=10082886&amp;doi=10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01090-2&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0058" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">58.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Elkamil A, Johansen KK, Aasly J.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Ataxia with vitamin E deficiency in Norway</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Mov Disord</em></span>. 2015;<span class="ref-vol">8</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):33. doi:10.14802/jmd.14030&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4298717/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25614784" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.14802%2Fjmd.14030" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Mov+Disord&amp;title=Ataxia+with+vitamin+E+deficiency+in+Norway&amp;volume=8&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2015&amp;pages=33&amp;doi=10.14802/jmd.14030&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0059" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">59.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Wang H, O’Reilly EJ, Weisskopf MG, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E intake and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a pooled analysis of data from 5 prospective cohort studies</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Am J Epidemiol</em></span>. 2011;<span class="ref-vol">173</span>(<span class="ref-iss">6</span>):595&#8211;602. doi:10.1093/aje/kwq416&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3105261/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21335424" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Faje%2Fkwq416" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Am+J+Epidemiol&amp;title=Vitamin+E+intake+and+risk+of+amyotrophic+lateral+sclerosis:+a+pooled+analysis+of+data+from+5+prospective+cohort+studies&amp;volume=173&amp;issue=6&amp;publication_year=2011&amp;pages=595-602&amp;pmid=21335424&amp;doi=10.1093/aje/kwq416&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0060" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">60.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Etminan M, Gill SS, Samii A.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Intake of vitamin E, vitamin C, and carotenoids and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Lancet Neurol</em></span>. 2005;<span class="ref-vol">4</span>(<span class="ref-iss">6</span>):362&#8211;365. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(05)70097-1 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15907740" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2FS1474-4422(05)70097-1" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Lancet+Neurol&amp;title=Intake+of+vitamin+E,+vitamin+C,+and+carotenoids+and+the+risk+of+Parkinson%E2%80%99s+disease:+a+meta-analysis&amp;volume=4&amp;issue=6&amp;publication_year=2005&amp;pages=362-365&amp;pmid=15907740&amp;doi=10.1016/S1474-4422(05)70097-1&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0061" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">61.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Chin KY, Tay S.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">A review on the relationship between tocotrienol and Alzheimer Disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Nutrients</em></span>. 2018;<span class="ref-vol">10</span>:(7)881. doi:10.3390/nu10070881&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6073491/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29987193" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.3390%2Fnu10070881" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Nutrients&amp;title=A+review+on+the+relationship+between+tocotrienol+and+Alzheimer+Disease&amp;volume=10&amp;publication_year=2018&amp;doi=10.3390/nu10070881&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0062" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">62.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Krycer JR, Phan L, Brown AJ.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">A key regulator of cholesterol homoeostasis, SREBP-2, can be targeted in prostate cancer cells with natural products</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Biochem J</em></span>. 2012;<span class="ref-vol">446</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):191&#8211;201. doi:10.1042/BJ20120545 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22657538" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1042%2FBJ20120545" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Biochem+J&amp;title=A+key+regulator+of+cholesterol+homoeostasis,+SREBP-2,+can+be+targeted+in+prostate+cancer+cells+with+natural+products&amp;volume=446&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;pages=191-201&amp;pmid=22657538&amp;doi=10.1042/BJ20120545&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0063" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">63.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mo H, Yeganehjoo H, Shah A, Mo WK, Soelaiman IN, Shen CL.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Meval&#8206;onate-suppressive dietary isoprenoids for bone health</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Nutr Biochem</em></span>. 2012;<span class="ref-vol">23</span>(<span class="ref-iss">12</span>):1543&#8211;1551. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.07.007 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22981371" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.jnutbio.2012.07.007" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Nutr+Biochem&amp;title=Meval&#8206;onate-suppressive+dietary+isoprenoids+for+bone+health&amp;volume=23&amp;issue=12&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;pages=1543-1551&amp;pmid=22981371&amp;doi=10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.07.007&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0064" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">64.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Song B-L, DeBose-Boyd RA.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Insig-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase stimulated by delta- and gamma-tocotrienols</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Biol Chem</em></span>. 2006;<span class="ref-vol">281</span>(<span class="ref-iss">35</span>):25054&#8211;25061. doi:10.1074/jbc.M605575200 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16831864" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1074%2Fjbc.M605575200" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Biol+Chem&amp;title=Insig-dependent+ubiquitination+and+degradation+of+3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl+coenzyme+a+reductase+stimulated+by+delta-+and+gamma-tocotrienols&amp;volume=281&amp;issue=35&amp;publication_year=2006&amp;pages=25054-25061&amp;pmid=16831864&amp;doi=10.1074/jbc.M605575200&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0065" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">65.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Khor HT, Ng TT.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Effects of administration of alpha-tocopherol and tocotrienols on serum lipids and liver HMGCoA reductase activity</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Int J Food Sci Nutr</em></span>. 2000;<span class="ref-vol">51Suppl</span>:S3&#8211;S11. doi:10.1080/096374800750049521 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11271854" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1080%2F096374800750049521" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Int+J+Food+Sci+Nutr&amp;title=Effects+of+administration+of+alpha-tocopherol+and+tocotrienols+on+serum+lipids+and+liver+HMGCoA+reductase+activity&amp;volume=51Suppl&amp;publication_year=2000&amp;pages=S3-S11&amp;doi=10.1080/096374800750049521&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0066" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">66.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Zaman Z, Roche S, Fielden P, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Plasma concentrations of vitamins and E and carotenoids in Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Age Ageing</em></span>. 1992;<span class="ref-vol">104</span>(<span class="ref-iss">6&#8211;7</span>):703&#8211;710.&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Age+Ageing&amp;title=Plasma+concentrations+of+vitamins+and+E+and+carotenoids+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=104&amp;issue=6%E2%80%937&amp;publication_year=1992&amp;pages=703-710&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0067" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">67.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Jim&#233;nez-Jim&#233;nez FJ, de Bustos F, Molina JA, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Cerebrospinal fluid levels of alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) in Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Neural Transm</em></span>. 1997;<span class="ref-vol">21</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):91&#8211;94.&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Neural+Transm&amp;title=Cerebrospinal+fluid+levels+of+alpha-tocopherol+(vitamin+E)+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=21&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=1997&amp;pages=91-94&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0068" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">68.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Sinclair AJ, Bayer AJ, Johnston J, Warner C, Maxwell SR.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Alterd plasma antioxidant status in subjects with Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Int J Geriatr Psychiatry</em></span>. 1998;<span class="ref-vol">13</span>(<span class="ref-iss">12</span>):840&#8211;845. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9884908" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Int+J+Geriatr+Psychiatry&amp;title=Alterd+plasma+antioxidant+status+in+subjects+with+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+and+vascular+dementia&amp;volume=13&amp;issue=12&amp;publication_year=1998&amp;pages=840-845&amp;pmid=9884908&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0069" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">69.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Foy CJ, Passmore AP, Vahidassr MD, Young IS, Lawson JT.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Plasma chain-breaking antioxidants in Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia and Parkinson’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Q J Med</em></span>. 1999;<span class="ref-vol">92</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):39&#8211;45. doi:10.1093/qjmed/92.1.39 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10209671" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fqjmed%2F92.1.39" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Q+J+Med&amp;title=Plasma+chain-breaking+antioxidants+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease,+vascular+dementia+and+Parkinson%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=92&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=1999&amp;pages=39-45&amp;doi=10.1093/qjmed/92.1.39&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0070" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">70.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Bourdel-Marchasson I, Delmas-Beauvieux MC, Peuchant E, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Antioxidant defences and oxidative stress markers in erythrocytes and plasma from normally nourished elderly Alzheimer patients</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Age Ageing</em></span>. 2001;<span class="ref-vol">30</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):235&#8211;241. doi:10.1093/ageing/30.3.235 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11443025" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fageing%2F30.3.235" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Age+Ageing&amp;title=Antioxidant+defences+and+oxidative+stress+markers+in+erythrocytes+and+plasma+from+normally+nourished+elderly+Alzheimer+patients&amp;volume=30&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2001&amp;pages=235-241&amp;pmid=11443025&amp;doi=10.1093/ageing/30.3.235&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0071" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">71.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Polidori MC, Mecocci P.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Plasma susceptibility to free radical-induced antioxidant consumption and lipid peroxidation is increased in very old subjects with Alzheimer disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Alzheimers Dis</em></span>. 2002;<span class="ref-vol">4</span>(<span class="ref-iss">6</span>):517&#8211;522. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12629261" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Alzheimers+Dis&amp;title=Plasma+susceptibility+to+free+radical-induced+antioxidant+consumption+and+lipid+peroxidation+is+increased+in+very+old+subjects+with+Alzheimer+disease&amp;volume=4&amp;issue=6&amp;publication_year=2002&amp;pages=517-522&amp;pmid=12629261&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0072" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">72.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mecocci P, Polidori M, Cherubini A, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Lymphocyte oxidative DNA damage and plasma antioxidants in Alzheimer disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Arch Neurol</em></span>. 2002;<span class="ref-vol">59</span>(<span class="ref-iss">5</span>):794&#8211;798. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12020262" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Arch+Neurol&amp;title=Lymphocyte+oxidative+DNA+damage+and+plasma+antioxidants+in+Alzheimer+disease&amp;volume=59&amp;issue=5&amp;publication_year=2002&amp;pages=794-798&amp;pmid=12020262&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0073" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">73.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Rinaldi P, Poliori MC, Metastasio A, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Plasma antioxidants are similarly depleted in mild cognitive impairment and in Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Neurobiol Aging</em></span>. 2003;<span class="ref-vol">24</span>(<span class="ref-iss">7</span>):915&#8211;919. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12928050" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Neurobiol+Aging&amp;title=Plasma+antioxidants+are+similarly+depleted+in+mild+cognitive+impairment+and+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=24&amp;issue=7&amp;publication_year=2003&amp;pages=915-919&amp;pmid=12928050&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0074" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">74.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Baldeiras I, Santana I, Proenca MT, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Peripheral oxidative damage in mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Alzheimers Dis</em></span>. 2008;<span class="ref-vol">15</span>:117&#8211;128. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18780972" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Alzheimers+Dis&amp;title=Peripheral+oxidative+damage+in+mild+cognitive+impairment+and+mild+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=15&amp;publication_year=2008&amp;pages=117-128&amp;pmid=18780972&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0075" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">75.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mangialasche F, Xu W, Kivipelto M, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Tocopherols and tocotrienols plasma levels are associated with cognitive impairment</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Nerurobiol Aging</em></span>. 2012;<span class="ref-vol">33</span>(<span class="ref-iss">10</span>):2282&#8211;2290. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.11.019 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22192241" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.neurobiolaging.2011.11.019" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Nerurobiol+Aging&amp;title=Tocopherols+and+tocotrienols+plasma+levels+are+associated+with+cognitive+impairment&amp;volume=33&amp;issue=10&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;pages=2282-2290&amp;doi=10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.11.019&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0076" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">76.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Giavarotti L, Simon KA, Azzalis LA, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Mild systemic oxidative stress in the subclinical stage of Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Oxid Med Cell Longev</em></span>. 2013;<span class="ref-vol">2013</span>:609019. doi:10.1155/2013/609019&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3880752/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24454987" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1155%2F2013%2F609019" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Oxid+Med+Cell+Longev&amp;title=Mild+systemic+oxidative+stress+in+the+subclinical+stage+of+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=2013&amp;publication_year=2013&amp;pages=609019&amp;pmid=24454987&amp;doi=10.1155/2013/609019&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0077" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">77.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mullan K, Williams MA, Cardwell CR, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Serum concentrations of vitamin E and carotenoids are altered in Alzheimer’s disease: a case-control study</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Alzheimers Dement Trans Clin Interv</em></span>. 2017;<span class="ref-vol">3</span>:432&#8211;439.&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5651431/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29067349" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Alzheimers+Dement+Trans+Clin+Interv&amp;title=Serum+concentrations+of+vitamin+E+and+carotenoids+are+altered+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease:+a+case-control+study&amp;volume=3&amp;publication_year=2017&amp;pages=432-439&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0078" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">78.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Schippling S, Kontush A, Arlt S, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Increased lipoprotein oxidation in Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Free Radic Biol Med</em></span>. 2000;<span class="ref-vol">28</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):351&#8211;360. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10699746" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Free+Radic+Biol+Med&amp;title=Increased+lipoprotein+oxidation+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=28&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2000&amp;pages=351-360&amp;pmid=10699746&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0079" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">79.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Ryglewicz D, Rodo M, Kunicki PK, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Plasma antioxidant activity and vascular dementia</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Neurol Sci</em></span>. 2002;<span class="ref-vol">203</span>:195&#8211;197. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12417383" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Neurol+Sci&amp;title=Plasma+antioxidant+activity+and+vascular+dementia&amp;volume=203&amp;publication_year=2002&amp;pages=195-197&amp;pmid=12417383&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0080" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">80.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Charlton KE, Rabinowitz TL, Geffen LN, Dhansay MA.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Lowered plasma vitamin C but not vitamin E concentration in dementia patients</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Nutr Health Aging</em></span>. 2004;<span class="ref-vol">8</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):99&#8211;108. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14978605" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Nutr+Health+Aging&amp;title=Lowered+plasma+vitamin+C+but+not+vitamin+E+concentration+in+dementia+patients&amp;volume=8&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2004&amp;pages=99-108&amp;pmid=14978605&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0081" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">81.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mas E, Dupuy AM, Artero S, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Functional vitamin E deficiency in ApoE4 patients with Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord</em></span>. 2006;<span class="ref-vol">21</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):198&#8211;204. doi:10.1159/000090868 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16407653" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1159%2F000090868" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Dement+Geriatr+Cogn+Disord&amp;title=Functional+vitamin+E+deficiency+in+ApoE4+patients+with+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=21&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2006&amp;pages=198-204&amp;pmid=16407653&amp;doi=10.1159/000090868&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0082" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">82.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Von Arnim CA, Herbolsheimer F, Nikolaus T, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Dietary antioxidants and dementia in a population-based case-control study among older people in South Germany</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Alzheimers Dis</em></span>. 2012;<span class="ref-vol">31</span>(<span class="ref-iss">4</span>):717&#8211;724. doi:10.3233/JAD-2012-120634 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22710913" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.3233%2FJAD-2012-120634" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Alzheimers+Dis&amp;title=Dietary+antioxidants+and+dementia+in+a+population-based+case-control+study+among+older+people+in+South+Germany&amp;volume=31&amp;issue=4&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;pages=717-724&amp;pmid=22710913&amp;doi=10.3233/JAD-2012-120634&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0083" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">83.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Jeandel C, Nicolas MB, Dubois F, Nabet-Belleville F.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Penin F and Cuny G. Lipid peroxidation and free radical scavengers in Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Gerontology</em></span>. 1989;<span class="ref-vol">35</span>(<span class="ref-iss">5&#8211;6</span>):275&#8211;282. doi:10.1159/000213037 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2630382" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1159%2F000213037" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Gerontology&amp;title=Penin+F+and+Cuny+G.+Lipid+peroxidation+and+free+radical+scavengers+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=35&amp;issue=5%E2%80%936&amp;publication_year=1989&amp;pages=275-282&amp;pmid=2630382&amp;doi=10.1159/000213037&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0084" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">84.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Lopes Da Silva S, Vellas B, Elemans S, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Plasma nutrient status of patients with Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Alzheimers Dement</em></span>. 2014;<span class="ref-vol">10</span>(<span class="ref-iss">4</span>):485&#8211;502. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2013.05.1771 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24144963" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.jalz.2013.05.1771" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Alzheimers+Dement&amp;title=Plasma+nutrient+status+of+patients+with+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease:+systematic+review+and+meta-analysis&amp;volume=10&amp;issue=4&amp;publication_year=2014&amp;pages=485-502&amp;pmid=24144963&amp;doi=10.1016/j.jalz.2013.05.1771&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0085" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">85.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mullan K, Cardwell CR, McGuinness B, Woodside JV, McKay GJ.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Plasma antioxidant status in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and cognitively intact elderly: a meta-analysis of case-control studies</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Alzheimers Dis</em></span>. 2018;<span class="ref-vol">62</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):305&#8211;317. doi:10.3233/JAD-170758 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29439339" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.3233%2FJAD-170758" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Alzheimers+Dis&amp;title=Plasma+antioxidant+status+in+patients+with+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+and+cognitively+intact+elderly:+a+meta-analysis+of+case-control+studies&amp;volume=62&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2018&amp;pages=305-317&amp;pmid=29439339&amp;doi=10.3233/JAD-170758&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0086" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">86.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Dong Y, Chen X, Liu Y, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Do low-serum vitamin E levels increase the risk of Alzheimer disease in older people? Evidence from a meta-analysis of case-control studies</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Int J Geriatr Psychiatry</em></span>. 2018;<span class="ref-vol">33</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):e257&#8211;e263. doi:10.1002/gps.4780 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28833475" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fgps.4780" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Int+J+Geriatr+Psychiatry&amp;title=Do+low-serum+vitamin+E+levels+increase+the+risk+of+Alzheimer+disease+in+older+people?+Evidence+from+a+meta-analysis+of+case-control+studies&amp;volume=33&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2018&amp;pages=e257-e263&amp;pmid=28833475&amp;doi=10.1002/gps.4780&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0087" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">87.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">De Wilde MC, Vellas B, Girault E, Yavuz AC, Sijben JW.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Lower brain and blood nutrient status in Alzheimer’s disease: results from meta-analyses</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Alzheimers Dement</em></span>. 2017;<span class="ref-vol">3</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):416&#8211;431.&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5651428/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29067348" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Alzheimers+Dement&amp;title=Lower+brain+and+blood+nutrient+status+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease:+results+from+meta-analyses&amp;volume=3&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=2017&amp;pages=416-431&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0088" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">88.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Liu G, Zhao Y, Jin S, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Circulating vitamin E levels and Alzheimer’s disease: a Mendelian randomization study</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Neurobiol Aging</em></span>. 2018;<span class="ref-vol">72</span>:189&#8211;e1. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30174138" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Neurobiol+Aging&amp;title=Circulating+vitamin+E+levels+and+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease:+a+Mendelian+randomization+study&amp;volume=72&amp;publication_year=2018&amp;pages=189-e1&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0089" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">89.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mangialasche F, Kivipelto M, Mecocci P, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">High plasma levels of vitamin E forms and reduced Alzheimer’s disease risk in advanced age</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Alzheimers Dis</em></span>. 2010;<span class="ref-vol">20</span>(<span class="ref-iss">4</span>):1029&#8211;1037. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20413888" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Alzheimers+Dis&amp;title=High+plasma+levels+of+vitamin+E+forms+and+reduced+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+risk+in+advanced+age&amp;volume=20&amp;issue=4&amp;publication_year=2010&amp;pages=1029-1037&amp;pmid=20413888&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0090" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">90.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mangialasche F, Westman E, Kivipelto M, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Classification and prediction of clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease based on MRI and plasma measures of α&#8208;/γ&#8208;tocotrienols and γ&#8208;tocopherol</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Intern Med</em></span>. 2013;<span class="ref-vol">273</span>(<span class="ref-iss">6</span>):602&#8211;621. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23343471" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Intern+Med&amp;title=Classification+and+prediction+of+clinical+diagnosis+of+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+based+on+MRI+and+plasma+measures+of+%CE%B1%E2%80%90/%CE%B3%E2%80%90tocotrienols+and+%CE%B3%E2%80%90tocopherol&amp;volume=273&amp;issue=6&amp;publication_year=2013&amp;pages=602-621&amp;pmid=23343471&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0091" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">91.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mangialasche F, Solomon A, K&#224;rehold I, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Serum levels of vitamin E forms and risk of cognitive impairment in a Finnish cohort of older adults</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Exp Gerontol</em></span>. 2013;<span class="ref-vol">48</span>(<span class="ref-iss">12</span>):1428&#8211;1435. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24113154" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Exp+Gerontol&amp;title=Serum+levels+of+vitamin+E+forms+and+risk+of+cognitive+impairment+in+a+Finnish+cohort+of+older+adults&amp;volume=48&amp;issue=12&amp;publication_year=2013&amp;pages=1428-1435&amp;pmid=24113154&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0092" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">92.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Morris MC, Beckett LA, Scherr PA, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E and vitamin E supplement use and the risk of incident Alzheimer disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord</em></span>. 1998;<span class="ref-vol">12</span>:121&#8211;126. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9772012" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Alzheimer+Dis+Assoc+Disord&amp;title=Vitamin+E+and+vitamin+E+supplement+use+and+the+risk+of+incident+Alzheimer+disease&amp;volume=12&amp;publication_year=1998&amp;pages=121-126&amp;pmid=9772012&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0093" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">93.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Zandi PP, Anthony JC, Khachaturian AS, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Reduced risk of Alzheimer disease in users of antioxidant vitamin supplements: the Cache County Study</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Arch Neurol</em></span>. 2004;<span class="ref-vol">61</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):82&#8211;88. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14732624" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Arch+Neurol&amp;title=Reduced+risk+of+Alzheimer+disease+in+users+of+antioxidant+vitamin+supplements:+the+Cache+County+Study&amp;volume=61&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2004&amp;pages=82-88&amp;pmid=14732624&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0094" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">94.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Basambombo LL, Carmichael PH, C&#244;t&#233; S, Laurin D.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Use of vitamin E and C supplements for the prevention of cognitive decline</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Ann Pharmacother</em></span>. 2017;<span class="ref-vol">51</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):118&#8211;124. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27708183" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Ann+Pharmacother&amp;title=Use+of+vitamin+E+and+C+supplements+for+the+prevention+of+cognitive+decline&amp;volume=51&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2017&amp;pages=118-124&amp;pmid=27708183&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0095" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">95.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Morris MC, Evans DA, Bienias JL, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Dietary intake of antioxidant nutrients and the risk of incident Alzheimer disease in a biracial community study</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>JAMA</em></span>. 2002;<span class="ref-vol">287</span>(<span class="ref-iss">24</span>):3230&#8211;3237. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12076219" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=JAMA&amp;title=Dietary+intake+of+antioxidant+nutrients+and+the+risk+of+incident+Alzheimer+disease+in+a+biracial+community+study&amp;volume=287&amp;issue=24&amp;publication_year=2002&amp;pages=3230-3237&amp;pmid=12076219&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0096" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">96.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Engelhart MJ, Geerlings MI, Ruitenberg A, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Dietary intake of antioxidants and risk of Alzheimer disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>JAMA</em></span>. 2002;<span class="ref-vol">287</span>(<span class="ref-iss">24</span>):3223&#8211;3229. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12076218" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=JAMA&amp;title=Dietary+intake+of+antioxidants+and+risk+of+Alzheimer+disease&amp;volume=287&amp;issue=24&amp;publication_year=2002&amp;pages=3223-3229&amp;pmid=12076218&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0097" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">97.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Morris MC, Evans DA, Tangney CC, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Relation of the tocopherol forms to incident Alzheimer disease and to cognitive change</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Am J Clin Nutr</em></span>. 2005;<span class="ref-vol">81</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):508&#8211;514. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15699242" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Am+J+Clin+Nutr&amp;title=Relation+of+the+tocopherol+forms+to+incident+Alzheimer+disease+and+to+cognitive+change&amp;volume=81&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2005&amp;pages=508-514&amp;pmid=15699242&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0098" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">98.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Devore EE, Grodstein F, van Rooij FJ, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Dietary antioxidants and long-term risk of dementia</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Arch Neurol</em></span>. 2010;<span class="ref-vol">67</span>(<span class="ref-iss">7</span>):819&#8211;825.&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2923546/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20625087" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Arch+Neurol&amp;title=Dietary+antioxidants+and+long-term+risk+of+dementia&amp;volume=67&amp;issue=7&amp;publication_year=2010&amp;pages=819-825&amp;pmid=20625087&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0099" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">99.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Masaki KH, Losonczy KG, Ismirlian G, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Association of vitamin E and C supplement use with cognitive function and dementia in elderly men</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Neurology</em></span>. 2000;<span class="ref-vol">54</span>(<span class="ref-iss">6</span>):1265&#8211;1272. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10746596" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Neurology&amp;title=Association+of+vitamin+E+and+C+supplement+use+with+cognitive+function+and+dementia+in+elderly+men&amp;volume=54&amp;issue=6&amp;publication_year=2000&amp;pages=1265-1272&amp;pmid=10746596&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0100" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">100.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Luchsinger JA, Tang MX, Shea S, Maveux R.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Antioxidant vitamin intake and risk of Alzheimer disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Arch Neurol</em></span>. 2003;<span class="ref-vol">60</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):203&#8211;208. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12580704" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Arch+Neurol&amp;title=Antioxidant+vitamin+intake+and+risk+of+Alzheimer+disease&amp;volume=60&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2003&amp;pages=203-208&amp;pmid=12580704&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0101" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">101.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Gray SL, Anderson ML, Crane PK, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Antioxidant vitamin supplement use and risk of dementia or Alzheimer’s disease in older adults</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Am Geriatr Soc</em></span>. 2008;<span class="ref-vol">56</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):291&#8211;295. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01531.x [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18047492" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1111%2Fj.1532-5415.2007.01531.x" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Am+Geriatr+Soc&amp;title=Antioxidant+vitamin+supplement+use+and+risk+of+dementia+or+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+in+older+adults&amp;volume=56&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2008&amp;pages=291-295&amp;pmid=18047492&amp;doi=10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01531.x&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0102" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">102.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Sano M, Ernesto C, Thomas RG, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">A controlled trial of selegiline, alpha-tocopherol, or both as treatment for Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>New Engl J Med</em></span>. 1997;<span class="ref-vol">336</span>(<span class="ref-iss">17</span>):1216&#8211;1222. doi:10.1056/NEJM199704243361704 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9110909" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1056%2FNEJM199704243361704" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=New+Engl+J+Med&amp;title=A+controlled+trial+of+selegiline,+alpha-tocopherol,+or+both+as+treatment+for+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=336&amp;issue=17&amp;publication_year=1997&amp;pages=1216-1222&amp;pmid=9110909&amp;doi=10.1056/NEJM199704243361704&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0103" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">103.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Petersen RC, Thomas RG, Grundman M, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E and donepezil for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>New Engl J Med</em></span>. 2005;<span class="ref-vol">352</span>(<span class="ref-iss">23</span>):2379&#8211;2388. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa050151 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15829527" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1056%2FNEJMoa050151" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=New+Engl+J+Med&amp;title=Vitamin+E+and+donepezil+for+the+treatment+of+mild+cognitive+impairment&amp;volume=352&amp;issue=23&amp;publication_year=2005&amp;pages=2379-2388&amp;pmid=15829527&amp;doi=10.1056/NEJMoa050151&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0104" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">104.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Lloret A, Bad&#237;a MC, Mora NJ, Pallard&#243; FV, Alonso MD, Vi&#241;a J.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E paradox in Alzheimer’s disease: it does not prevent loss of cognition and may even be detrimental</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Alzheimers Dis</em></span>. 2009;<span class="ref-vol">17</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):143&#8211;149. doi:10.3233/JAD-2009-1033 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19494439" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.3233%2FJAD-2009-1033" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Alzheimers+Dis&amp;title=Vitamin+E+paradox+in+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease:+it+does+not+prevent+loss+of+cognition+and+may+even+be+detrimental&amp;volume=17&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2009&amp;pages=143-149&amp;pmid=19494439&amp;doi=10.3233/JAD-2009-1033&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0105" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">105.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Dysken MW, Sano M, Asthana S, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Effect of vitamin E and memantine on functional decline in Alzheimer disease: the TEAM-AD VA cooperative randomized trial</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>JAMA</em></span>. 2014;<span class="ref-vol">311</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):33&#8211;44. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.282834&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4109898/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24381967" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1001%2Fjama.2013.282834" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=JAMA&amp;title=Effect+of+vitamin+E+and+memantine+on+functional+decline+in+Alzheimer+disease:+the+TEAM-AD+VA+cooperative+randomized+trial&amp;volume=311&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2014&amp;pages=33-44&amp;pmid=24381967&amp;doi=10.1001/jama.2013.282834&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0106" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">106.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Kryscio RJ, Abner EL, Caban-Holt A, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Association of antioxidant supplement use and dementia in the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease by vitamin E and selenium trial (PREADViSE)</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>JAMA Neurol</em></span>. 2017;<span class="ref-vol">74</span>(<span class="ref-iss">5</span>):567&#8211;573. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.5778&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5506489/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28319243" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1001%2Fjamaneurol.2016.5778" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=JAMA+Neurol&amp;title=Association+of+antioxidant+supplement+use+and+dementia+in+the+prevention+of+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+by+vitamin+E+and+selenium+trial+(PREADViSE)&amp;volume=74&amp;issue=5&amp;publication_year=2017&amp;pages=567-573&amp;pmid=28319243&amp;doi=10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.5778&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0107" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">107.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Miller ER III, Pastor-Barriuso R, Dalal D, Riemersma RA, Appel LJ, Guallar E.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Meta-analysis: high-dosage vitamin E supplementation may increase all-cause mortality</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Ann Intern Med</em></span>. 2005;<span class="ref-vol">142</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):37&#8211;46. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-142-1-200501040-00110 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15537682" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.7326%2F0003-4819-142-1-200501040-00110" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Ann+Intern+Med&amp;title=Meta-analysis:+high-dosage+vitamin+E+supplementation+may+increase+all-cause+mortality&amp;volume=142&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2005&amp;pages=37-46&amp;pmid=15537682&amp;doi=10.7326/0003-4819-142-1-200501040-00110&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0108" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">108.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Naeini AA, Elmadfa I, Djazayery A, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The effect of antioxidant vitamins E and C on cognitive performance of the elderly with mild cognitive impairment in Isfahan, Iran: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Eur J Nutr</em></span>. 2014;<span class="ref-vol">53</span>(<span class="ref-iss">5</span>):1255&#8211;1262. doi:10.1007/s00394-013-0628-1 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24326981" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2Fs00394-013-0628-1" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Eur+J+Nutr&amp;title=The+effect+of+antioxidant+vitamins+E+and+C+on+cognitive+performance+of+the+elderly+with+mild+cognitive+impairment+in+Isfahan,+Iran:+a+double-blind,+randomized,+placebo-controlled+trial&amp;volume=53&amp;issue=5&amp;publication_year=2014&amp;pages=1255-1262&amp;pmid=24326981&amp;doi=10.1007/s00394-013-0628-1&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0109" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">109.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Galasko DR, Peskind E, Clark CM, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">For Alzheimer disease: a randomized clinical trial with cerebrospinal fluid biomarker measures</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Arch Neurol</em></span>. 2012;<span class="ref-vol">69</span>(<span class="ref-iss">7</span>):836&#8211;841. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2012.85&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3661272/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22431837" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1001%2Farchneurol.2012.85" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Arch+Neurol&amp;title=For+Alzheimer+disease:+a+randomized+clinical+trial+with+cerebrospinal+fluid+biomarker+measures&amp;volume=69&amp;issue=7&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;pages=836-841&amp;pmid=22431837&amp;doi=10.1001/archneurol.2012.85&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0110" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">110.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Harman D.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Aging: a theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Gerontol</em></span>. 1956;<span class="ref-vol">11</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):298&#8211;300. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/13332224" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Gerontol&amp;title=Aging:+a+theory+based+on+free+radical+and+radiation+chemistry&amp;volume=11&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=1956&amp;pages=298-300&amp;pmid=13332224&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0111" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">111.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Ghezzi P, Jaquet V, Marcucci F, Schmidt HH.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The oxidative stress theory of disease: levels of evidence and epistemological aspects</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Br J Pharmacol</em></span>. 2017;<span class="ref-vol">174</span>(<span class="ref-iss">12</span>):1784&#8211;1796. doi:10.1111/bph.13544&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5446567/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27425643" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1111%2Fbph.13544" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Br+J+Pharmacol&amp;title=The+oxidative+stress+theory+of+disease:+levels+of+evidence+and+epistemological+aspects&amp;volume=174&amp;issue=12&amp;publication_year=2017&amp;pages=1784-1796&amp;pmid=27425643&amp;doi=10.1111/bph.13544&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0112" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">112.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud LL, Simonetti RG, Gluud C.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Antioxidant supplements for prevention of mortality in healthy participants and patients with various diseases</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Cochrane Database Syst Rev</em></span>. 2012:(3):CD007176. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007176.pub2 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22419320" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2F14651858.CD007176.pub2" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Cochrane+Database+Syst+Rev&amp;title=Antioxidant+supplements+for+prevention+of+mortality+in+healthy+participants+and+patients+with+various+diseases&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;doi=10.1002/14651858.CD007176.pub2&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0113" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">113.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Winterbourn CC.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The challenges of using fluorescent probes to detect and quantify specific reactive oxygen species in living cells</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Biochim Biophys Acta</em></span>. 2014;<span class="ref-vol">1840</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):730&#8211;738. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.05.004 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23665586" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.bbagen.2013.05.004" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Biochim+Biophys+Acta&amp;title=The+challenges+of+using+fluorescent+probes+to+detect+and+quantify+specific+reactive+oxygen+species+in+living+cells&amp;volume=1840&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=2014&amp;pages=730-738&amp;pmid=23665586&amp;doi=10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.05.004&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0114" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">114.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Zielonka J, Hardy M, Michalski R, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Recent developments in the probes and assays for measurement of the activity of NADPH oxidases</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Cell Biochem Biophys</em></span>. 2017;<span class="ref-vol">75</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3&#8211;4</span>):335&#8211;349. doi:10.1007/s12013-017-0813-6&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5693611/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28660426" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2Fs12013-017-0813-6" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Cell+Biochem+Biophys&amp;title=Recent+developments+in+the+probes+and+assays+for+measurement+of+the+activity+of+NADPH+oxidases&amp;volume=75&amp;issue=3%E2%80%934&amp;publication_year=2017&amp;pages=335-349&amp;pmid=28660426&amp;doi=10.1007/s12013-017-0813-6&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0115" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">115.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Frijhoff J, Winyard PG, Zarkovic N, Davies SS, Stocker R, Cheng D.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Clinical relevance of biomarkers of oxidative stress</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Antioxid Redox Signal</em></span>. 2015;<span class="ref-vol">23</span>(<span class="ref-iss">14</span>):1144&#8211;1170. doi:10.1089/ars.2015.6317&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4657513/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26415143" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1089%2Fars.2015.6317" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Antioxid+Redox+Signal&amp;title=Clinical+relevance+of+biomarkers+of+oxidative+stress&amp;volume=23&amp;issue=14&amp;publication_year=2015&amp;pages=1144-1170&amp;pmid=26415143&amp;doi=10.1089/ars.2015.6317&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0116" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">116.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mariani E, Mangialasche F, Feliziani FT, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Effects of zinc supplementation on antioxidant enzyme activities in healthy old subjects</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Exp Gerontol</em></span>. 2008;<span class="ref-vol">43</span>(<span class="ref-iss">5</span>):445&#8211;451. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2007.10.012 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18078731" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.exger.2007.10.012" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Exp+Gerontol&amp;title=Effects+of+zinc+supplementation+on+antioxidant+enzyme+activities+in+healthy+old+subjects&amp;volume=43&amp;issue=5&amp;publication_year=2008&amp;pages=445-451&amp;pmid=18078731&amp;doi=10.1016/j.exger.2007.10.012&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0117" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">117.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Farina N, Llewellyn D, Isaac MG, Tabet N.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment</span>.&nbsp;&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6464807/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28128435" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar?q=Farina++N+,++Llewellyn++D+,++Isaac++MG+,++Tabet++N+.++Vitamin+E+for+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+dementia+and+mild+cognitive+impairment+.++" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0118" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">118.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Corbett A, Ballard C.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The value of vitamin E as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease remains unproven despite functional improvement, due to a lack of established effect on cognition or other outcomes from RCTs</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Evid Based Med</em></span>. 2014;<span class="ref-vol">19</span>(<span class="ref-iss">4</span>):140. doi:10.1136/eb-2014-101741 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24639394" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1136%2Feb-2014-101741" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Evid+Based+Med&amp;title=The+value+of+vitamin+E+as+a+treatment+for+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease+remains+unproven+despite+functional+improvement,+due+to+a+lack+of+established+effect+on+cognition+or+other+outcomes+from+RCTs&amp;volume=19&amp;issue=4&amp;publication_year=2014&amp;pages=140&amp;pmid=24639394&amp;doi=10.1136/eb-2014-101741&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0119" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">119.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Ancelin ML, Christen Y, Ritchie K.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Is antioxidant therapy a viable alternative for mild cognitive impairment? Examination of the evidence</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Dement Geratr Cogn Dis</em></span>. 2007;<span class="ref-vol">24</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):1&#8211;9. doi:10.1159/000102567 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17495472" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1159%2F000102567" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Dement+Geratr+Cogn+Dis&amp;title=Is+antioxidant+therapy+a+viable+alternative+for+mild+cognitive+impairment?+Examination+of+the+evidence&amp;volume=24&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2007&amp;pages=1-9&amp;doi=10.1159/000102567&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0120" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">120.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Niki E.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Role of vitamin E as a lipid-soluble peroxyl radical scavenger: in vitro and in vivo evidence</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Free Radic Biol Med</em></span>. 2014;<span class="ref-vol">66</span>:3&#8211;12. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.03.022 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23557727" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.freeradbiomed.2013.03.022" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Free+Radic+Biol+Med&amp;title=Role+of+vitamin+E+as+a+lipid-soluble+peroxyl+radical+scavenger:+in+vitro+and+in+vivo+evidence&amp;volume=66&amp;publication_year=2014&amp;pages=3-12&amp;pmid=23557727&amp;doi=10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.03.022&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0121" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">121.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Constantinescu A, Han D, Packer L.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E recycling in human erythrocyte membranes</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Biol Chem</em></span>. 1993;<span class="ref-vol">268</span>(<span class="ref-iss">15</span>):10906&#8211;10913. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8388377" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Biol+Chem&amp;title=Vitamin+E+recycling+in+human+erythrocyte+membranes&amp;volume=268&amp;issue=15&amp;publication_year=1993&amp;pages=10906-10913&amp;pmid=8388377&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0122" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">122.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Bowry VW, Ingold KU, Stocker R.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E in human low-density lipoprotein: when and how this antioxidant becomes a pro- oxidant</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Biochem J</em></span>. 1992;<span class="ref-vol">288</span>(<span class="ref-iss">2</span>):341&#8211;344. doi:10.1042/bj2880341&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1132016/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1463440" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1042%2Fbj2880341" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Biochem+J&amp;title=Vitamin+E+in+human+low-density+lipoprotein:+when+and+how+this+antioxidant+becomes+a+pro-+oxidant&amp;volume=288&amp;issue=2&amp;publication_year=1992&amp;pages=341-344&amp;pmid=1463440&amp;doi=10.1042/bj2880341&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0123" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">123.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Rietjens IM, Boersma MG, de Haan L, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The pro-oxidant chemistry of the natural antioxidants vitamin C, vitamin E, carotenoids and flavonoids</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Environ Toxicol Pharmacol</em></span>. 2002;<span class="ref-vol">11</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3&#8211;4</span>):321&#8211;333. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21782615" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Environ+Toxicol+Pharmacol&amp;title=The+pro-oxidant+chemistry+of+the+natural+antioxidants+vitamin+C,+vitamin+E,+carotenoids+and+flavonoids&amp;volume=11&amp;issue=3%E2%80%934&amp;publication_year=2002&amp;pages=321-333&amp;pmid=21782615&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0124" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">124.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Pearson P, Lewis SA, Britton J, Young IS, Fogarty A.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The pro-oxidant activity of high-dose vitamin E supplements in vivo</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>BioDrugs</em></span>. 2006;<span class="ref-vol">20</span>(<span class="ref-iss">5</span>):271&#8211;273. doi:10.2165/00063030-200620050-00002 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17025373" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.2165%2F00063030-200620050-00002" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=BioDrugs&amp;title=The+pro-oxidant+activity+of+high-dose+vitamin+E+supplements+in+vivo&amp;volume=20&amp;issue=5&amp;publication_year=2006&amp;pages=271-273&amp;pmid=17025373&amp;doi=10.2165/00063030-200620050-00002&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0125" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">125.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Mecocci P, Polidori MC.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Antioxidant clinical trials in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Basis Dis</em></span>. 2012;<span class="ref-vol">1822</span>(<span class="ref-iss">5</span>):631&#8211;638. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.10.006 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22019723" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.bbadis.2011.10.006" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Biochim+Biophys+Acta+-+Mol+Basis+Dis&amp;title=Antioxidant+clinical+trials+in+mild+cognitive+impairment+and+Alzheimer%E2%80%99s+disease&amp;volume=1822&amp;issue=5&amp;publication_year=2012&amp;pages=631-638&amp;doi=10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.10.006&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0126" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">126.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Bjørneboe A, Bjørneboe GE, Drevon CA.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Absorption, transport and distribution of vitamin E</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Nutr</em></span>. 1990;<span class="ref-vol">120</span>(<span class="ref-iss">3</span>):233&#8211;242. doi:10.1093/jn/120.3.233 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2181082" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fjn%2F120.3.233" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Nutr&amp;title=Absorption,+transport+and+distribution+of+vitamin+E&amp;volume=120&amp;issue=3&amp;publication_year=1990&amp;pages=233-242&amp;pmid=2181082&amp;doi=10.1093/jn/120.3.233&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0127" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">127.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Richelle M, Enslen M, Hager C, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Both free and esterified plant sterols reduce cholesterol absorption and the bioavailability of β-carotene and α-tocopherol in normocholesterolemic humans</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Am J Clin Nutr</em></span>. 2004;<span class="ref-vol">80</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):171&#8211;177. doi:10.1093/ajcn/80.1.171 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15213045" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fajcn%2F80.1.171" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Am+J+Clin+Nutr&amp;title=Both+free+and+esterified+plant+sterols+reduce+cholesterol+absorption+and+the+bioavailability+of+%CE%B2-carotene+and+%CE%B1-tocopherol+in+normocholesterolemic+humans&amp;volume=80&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2004&amp;pages=171-177&amp;pmid=15213045&amp;doi=10.1093/ajcn/80.1.171&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0128" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">128.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Goti D, Hammer A, Galla HJ, Malle E, Sattler W.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Uptake of lipoprotein&#8208;associated α&#8208;tocopherol by primary porcine brain capillary endothelial cells</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Neurochem</em></span>. 2000;<span class="ref-vol">74</span>(<span class="ref-iss">4</span>):1374&#8211;1383. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0741374.x [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10737592" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1046%2Fj.1471-4159.2000.0741374.x" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Neurochem&amp;title=Uptake+of+lipoprotein%E2%80%90associated+%CE%B1%E2%80%90tocopherol+by+primary+porcine+brain+capillary+endothelial+cells&amp;volume=74&amp;issue=4&amp;publication_year=2000&amp;pages=1374-1383&amp;pmid=10737592&amp;doi=10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0741374.x&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0129" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">129.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Leonard SW, Paterson E, Atkinson JK, Ramakrishnan R, Cross CE, Traber MG.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Studies in humans using deuterium-labeled α-and γ-tocopherols demonstrate faster plasma γ-tocopherol disappearance and greater γ-metabolite production</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Free Radic Biol Med</em></span>. 2005;<span class="ref-vol">38</span>(<span class="ref-iss">7</span>):857&#8211;866. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.12.001 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15749381" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.freeradbiomed.2004.12.001" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Free+Radic+Biol+Med&amp;title=Studies+in+humans+using+deuterium-labeled+%CE%B1-and+%CE%B3-tocopherols+demonstrate+faster+plasma+%CE%B3-tocopherol+disappearance+and+greater+%CE%B3-metabolite+production&amp;volume=38&amp;issue=7&amp;publication_year=2005&amp;pages=857-866&amp;pmid=15749381&amp;doi=10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.12.001&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0130" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">130.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Campbell D, Bunker VW, Thomas AJ, Clayton BE.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Selenium and vitamin E status of healthy and institutionalized elderly subjects: analysis of plasma, erythrocytes and platelets</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Br J Nutr</em></span>. 1989;<span class="ref-vol">62</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):221&#8211;227. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2789985" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Br+J+Nutr&amp;title=Selenium+and+vitamin+E+status+of+healthy+and+institutionalized+elderly+subjects:+analysis+of+plasma,+erythrocytes+and+platelets&amp;volume=62&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=1989&amp;pages=221-227&amp;pmid=2789985&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0131" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">131.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Shah AA, Khand F, Khand TU.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Effect of smoking on serum xanthine oxidase, malondialdehyde, ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol levels in healthy male subjects</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Pak J Med Sci</em></span>. 2015;<span class="ref-vol">31</span>(<span class="ref-iss">1</span>):146.&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4386175/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25878632" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Pak+J+Med+Sci&amp;title=Effect+of+smoking+on+serum+xanthine+oxidase,+malondialdehyde,+ascorbic+acid+and+%CE%B1-tocopherol+levels+in+healthy+male+subjects&amp;volume=31&amp;issue=1&amp;publication_year=2015&amp;pages=146&amp;pmid=25878632&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0132" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">132.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Gunanti IR, Marks GC, Al-Mamun A, Long KZ.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Low serum concentrations of carotenoids and vitamin E are associated with high adiposity in Mexican-American children</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Nutr</em></span>. 2014;<span class="ref-vol">144</span>(<span class="ref-iss">4</span>):489&#8211;495. doi:10.3945/jn.113.183137 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24500938" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.3945%2Fjn.113.183137" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Nutr&amp;title=Low+serum+concentrations+of+carotenoids+and+vitamin+E+are+associated+with+high+adiposity+in+Mexican-American+children&amp;volume=144&amp;issue=4&amp;publication_year=2014&amp;pages=489-495&amp;pmid=24500938&amp;doi=10.3945/jn.113.183137&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0133" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">133.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Borel P, Desmarchelier C, Nowicki M, Bott R, Tourniaire F.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Can genetic variability in α-tocopherol bioavailability explain the heterogeneous response to α-tocopherol supplements?</span>&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Antioxid Redox Signal</em></span>. 2015;<span class="ref-vol">22</span>:669&#8211;678. doi:10.1089/ars.2014.6144 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25289663" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1089%2Fars.2014.6144" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Antioxid+Redox+Signal&amp;title=Can+genetic+variability+in+%CE%B1-tocopherol+bioavailability+explain+the+heterogeneous+response+to+%CE%B1-tocopherol+supplements?&amp;volume=22&amp;publication_year=2015&amp;pages=669-678&amp;pmid=25289663&amp;doi=10.1089/ars.2014.6144&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0134" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">134.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Major JM, Yu K, Wheeler W, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Genome-wide association study identifies common variants associated with circulating vitamin E levels</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Hum Mol Genet</em></span>. 2011;<span class="ref-vol">20</span>(<span class="ref-iss">19</span>):3876&#8211;3883. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr296&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3168288/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21729881" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fhmg%2Fddr296" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Hum+Mol+Genet&amp;title=Genome-wide+association+study+identifies+common+variants+associated+with+circulating+vitamin+E+levels&amp;volume=20&amp;issue=19&amp;publication_year=2011&amp;pages=3876-3883&amp;pmid=21729881&amp;doi=10.1093/hmg/ddr296&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0135" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">135.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Galm&#233;s S, Serra F, Palou A.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E metabolic effects and genetic variants: a challenge for precision nutrition in obesity and associated disturbances</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Nutrients</em></span>. 2018;<span class="ref-vol">10</span>(<span class="ref-iss">12</span>):1919. doi:10.3390/nu10121919&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6316334/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30518135" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.3390%2Fnu10121919" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Nutrients&amp;title=Vitamin+E+metabolic+effects+and+genetic+variants:+a+challenge+for+precision+nutrition+in+obesity+and+associated+disturbances&amp;volume=10&amp;issue=12&amp;publication_year=2018&amp;pages=1919&amp;doi=10.3390/nu10121919&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0136" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">136.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Galli F, Azzi A, Birringer M, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E: emerging aspects and new directions</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Free Radic Biol Med</em></span>. 2017;<span class="ref-vol">102</span>:16&#8211;36. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.09.017 [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27816611" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.freeradbiomed.2016.09.017" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Free+Radic+Biol+Med&amp;title=Vitamin+E:+emerging+aspects+and+new+directions&amp;volume=102&amp;publication_year=2017&amp;pages=16-36&amp;pmid=27816611&amp;doi=10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.09.017&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0137" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">137.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Steiner M.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E, a modifier of platelet function: rationale and use in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Nutr Rev</em></span>. 1999;<span class="ref-vol">57</span>(<span class="ref-iss">10</span>):306&#8211;309. doi:10.1111/j.1753-4887.1999.tb06903.x [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10575906" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1111%2Fj.1753-4887.1999.tb06903.x" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Nutr+Rev&amp;title=Vitamin+E,+a+modifier+of+platelet+function:+rationale+and+use+in+cardiovascular+and+cerebrovascular+disease&amp;volume=57&amp;issue=10&amp;publication_year=1999&amp;pages=306-309&amp;pmid=10575906&amp;doi=10.1111/j.1753-4887.1999.tb06903.x&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0138" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">138.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Sch&#252;rks M, Glynn RJ, Rist PM, Tzourio C, Kurth T.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Effects of vitamin E on stroke subtypes: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>BMJ</em></span>. 2010;<span class="ref-vol">341</span>:c5702. doi:10.1136/bmj.c5702&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2974412/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21051774" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1136%2Fbmj.c5702" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=BMJ&amp;title=Effects+of+vitamin+E+on+stroke+subtypes:+meta-analysis+of+randomised+controlled+trials&amp;volume=341&amp;publication_year=2010&amp;pages=c5702&amp;pmid=21051774&amp;doi=10.1136/bmj.c5702&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0139" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">139.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Klein EA, Thompson IM, Tangen CM, et al.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Vitamin E and the risk of prostate cancer: the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT)</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>JAMA</em></span>. 2011;<span class="ref-vol">306</span>:1549&#8211;1556. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.1437&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a class="int-reflink" href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4169010/" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PMC free article</a>]</span>&nbsp;[<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21990298" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>] [<a href="https://dx.doi.org/10.1001%2Fjama.2011.1437" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CCrosslink%7CDOI" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">CrossRef</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=JAMA&amp;title=Vitamin+E+and+the+risk+of+prostate+cancer:+the+Selenium+and+Vitamin+E+Cancer+Prevention+Trial+(SELECT)&amp;volume=306&amp;publication_year=2011&amp;pages=1549-1556&amp;pmid=21990298&amp;doi=10.1001/jama.2011.1437&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0140" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">140.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Gerss J, Kopcke W.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">The questionable association of vitamin E supplementation and mortality &#8211; inconsistent results of different meta-analytic approaches</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>Cell Mol Biol</em></span>. 2009;<span class="ref-vol">55</span>:OL1111&#8211;Q1120. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19267994" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Cell+Mol+Biol&amp;title=The+questionable+association+of+vitamin+E+supplementation+and+mortality+%E2%80%93+inconsistent+results+of+different+meta-analytic+approaches&amp;volume=55&amp;publication_year=2009&amp;pages=OL1111-Q1120&amp;pmid=19267994&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div><div class="ref-cit-blk half_rhythm" id="CIT0141" style="margin: 0.6923em 0px;">141.&nbsp;<span class="mixed-citation">Jiang S, Pan Z, Li H, Li F, Song Y, Qiu Y.&nbsp;<span class="ref-title">Meta-analysis: low-dose intake of vitamin E combined with other vitamins or minerals may decrease all-cause mortality</span>.&nbsp;<span class="ref-journal"><em>J Nutr Sci Vitaminol</em></span>. 2014;<span class="ref-vol">60</span>:194&#8211;205. [<a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25078376" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=pubmed&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Entrez%7CPubMed%7CRecord" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">PubMed</a>]&nbsp;<span class="nowrap" style="white-space: nowrap;">[<a href="https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=J+Nutr+Sci+Vitaminol&amp;title=Meta-analysis:+low-dose+intake+of+vitamin+E+combined+with+other+vitamins+or+minerals+may+decrease+all-cause+mortality&amp;volume=60&amp;publication_year=2014&amp;pages=194-205&amp;pmid=25078376&amp;" target="pmc_ext" ref="reftype=other&amp;article-id=6645610&amp;issue-id=326156&amp;journal-id=502&amp;FROM=Article%7CCitationRef&amp;TO=Content%20Provider%7CLink%7CGoogle%20Scholar" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" style="color: rgb(100, 42, 143);">Google Scholar</a>]</span></span></div></div></div><p><br></p>
<!-- -->
카페 게시글
orthomolecular medicine
Re:Vitamin E and Alzheimer’s disease: what do we know so far?
문형철
추천 0
조회 788
20.01.06 18:32
댓글 0
다음검색